4756
The feasibility of StarVibe in MR imaging and CT volume imaging in measuring the length of esophageal cancer after neo-adjuvant therapy on 3-T1National Cancer Center/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing, China, 2MR Scientific Marketing, Diagnostic Imaging, Siemens Healthcare Ltd, Beijing, China
Synopsis
This study evaluated the length of esophageal cancer lesions after neoadjuvant treatment with MR and thin-layer CT scanning using the length of gross specimens as the gold standard. MR sequence included T2WI and contrast-enhanced StarVibe (DCE StarVibe). In this study, two readers measured the length of esophageal cancer lesions on T2WI, DCE StarVibe and CT images. It was found that contrast-enhanced Starvibe and thin-slice CT can be used to measure the lenth of esophageal cancer after neoadjuvant treatment.
Purpose
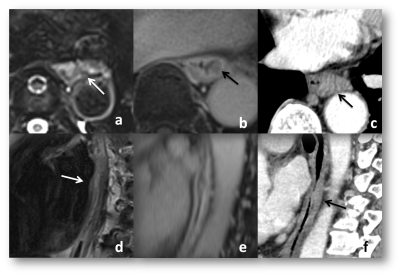
This study investigated the feasibility of StarVibe in MR imaging and CT volume imaging in measuring the length of esophageal cancer after neo-adjuvant therapy on 3-T, with gross tumor specimen as golden standard.Methods
16 patients (13 males and 2 females; mean age: 57±6.9y) with esophageal cancer were enrolled and underwent MRI scan at a 3T scanner (MAGNETOM Prisma, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) with an 18 channels phased-array body matrix coil. All patients underwent neo-adjuvant treatment and were confirmed by endoscopy, and 5 patients of them were treated with neoadjuvant immunotherapy alone while 11 ones underwent neoadjuvant immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy. One patient could not do esophagectomy due to closely relationship between cancer and bronchial membrane intraoperation. The MR protocol included fat-suppression T2-weighted imaging (FS-T2WI) and contrast-enhanced StarVIBE scanning with following parameters: FS-T2WI: TR/TE = 2340.0/92 ms, FOV = 400-300 mm2, slice hickness = 4.0 mm, voxel size = 1.2×1.3×5.0 mm3 and 46 slices. contrast-enhanced StarVIBE: TR/TE = 3.15/1.49 ms, FOV=180-180 mm2 , voxel size = 1.1 × 1.1 × 2.5 mm3 , 48 slices per stab, slice oversampling = 16.7%. Two experienced readers independently measured the lesion length of the esophagus cancer. We than compared the length of the two readers data with gross pathological specimen. Also consistency test was used to evaluate between the two readers. All statistics are analyzed using SPSS 23.0.Results
The length of gross specimen was (3.7±3.3cm; range 0.8-9.0cm), and the length measured by reader 1 were (4.2±1.6) cm, (3.5±3.2) cm and (3.1±2.1)cm on T2WI images, DCE StarVibe images and on CT images. Length measured by reader 2 were (3.9±2.7) cm, (3.7±3.4) cm and (3.2±2.8) cm on T2WI, DCE StarVibe and CT. There is significant difference between measured length on T2WI (p=0.049) and no significant differences on both DCE StarVibe and CT with gross specimen (p=0.427 and p=0.160). There is no significant difference in the measurement of the length between two readers (p=0.563).Discussion
The lesion length is an important index for patient of esophagus cancer. Several studies showed that tumor length is a prognostic factor for esophageal cancer1. In addition, due to the great significance of radiotherapy in the treatment of esophageal cancer, the accurate delineation of esophageal cancer depends on the accurate measure of the length. However there are few studies on MR evaluation of esophageal cancer and mainly focused on TNM staging evaluation2. None study on length assessment by MR imagings. Our study suggests that T2WI is not able to measure the length of esophageal cancer after neoadjuvant treatment statistically. It may be because of the inflammation and edema which cause of the treatment, and some fluid in lumen which showed high signal on T2WI also interfere the judgement of mucosal. DCE StarVibe is a new enhanced scanning sequence in recent years, which is a free breathing protocol with diaphragm navigation. Compared to the conventional breath holding sequence, it can show the lesions more clearly with few respiratory artifacts. In our study it show the ability on mearsure the length and clearly showed details in the lesion.There is no statistical difference between thin-layer CT scan measurement and gross pathology specimen in judging the length of esophageal cancer, which shows that it has considerable value in clinical application. But it is weaker in detail display than MR images.Conclusion
DCE StarVibe sequence can be used to judge the length of esophageal cancer after neoadjuvant therapy, and it will have a broad application prospect in the future. Also CT scanning is uesful to assess the lenth of esophageal cancer.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1.Gaur P1, Sepesi B, Hofstetter WL, et al.Endoscopic esophageal tumor length: a prognostic factor for patients with esophageal cancer.Cancer. 2011 Jan 1;117(1):63-9.
2.Luo LN, He LJ, Gao XY, Huang XX, et al.Evaluation of preoperative staging for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Aug 7;22(29):6683-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i29.6683. Review.
Figures