4739
Evaluating Ki-67 status in breast cancer with DCE-MRI features
Jing Zhou1,2, Hongna Tan1,2, and Meiyun Wang1,2
1Department of Radiology, Henan Provincial People’s Hospital & Zhengzhou University People’s Hospital, Zhengzhou City, China, 2Imaging Diagnosis of Neurological Diseases and Research Laboratory of Henan Province, Zhengzhou City, China
1Department of Radiology, Henan Provincial People’s Hospital & Zhengzhou University People’s Hospital, Zhengzhou City, China, 2Imaging Diagnosis of Neurological Diseases and Research Laboratory of Henan Province, Zhengzhou City, China
Synopsis
Breast cancer is one most common cancer in female worldwide. Ki-67 index is an significant biomarker whose expression status is closely related with response to chemotherapy and the disease prognosis in patients with breast cancer. This study retrospectively investigated the relationship between DCE-MRI features and Ki-67 status in breast carcinoma. The results indicated the type of washout TIC and heterogeneous type of reinforcement is more common in high Ki-67 status in patients with breast cancer. The DCE-MRI imaging features can non-invasively assess Ki-67 status in breast carcinoma before surgery.
Background and Purpose
Breast carcinoma is now one of the most frequent cancer in Chinese and become more prevalent among female[1]. Several bio-markers are routinely used to guide its treatment and prognosis[2]. Among them, the Ki-67 index plays a significant role in determining the treatment strategy. The aim is to investigate the relationship between DCE-MRI features and Ki-67 index in breast cancer.Methods
A total of 95 patients with breast cancer diagnosed with invasive breast carcinoma of non-special type(IDC-NST) confirmed at histopathology postoperatively in our institution were retrospectively enrolled in this research from May 2018 to July 2019. Imaging data were collected on a 3T MAGNETOM 750 discovery MR scanner (GE, Boston, Massachusetts, USA). All patients performed preoperatively MRI dynamic contrast enhanced scan. The detailed parameters are as follows:T1WI FoV read: 34cm, TR:792ms, TE:10ms, Slices:24, Slice thickness:5mm; Fat-suppressed T2WI FoV read: 34cm, TR:3274ms, TE:68ms, Slices:24, Slice thickness:5mm; Three-dimensional breast volume scan sequence (LAVA) FoV read: 36cm, TR:4ms, TE:2.2ms, Slices:136, Slice thickness:1.1mm. the imaging were viewed according to the 4th edition of Breast imaging reporting and data system (BI-RADS) published by American College of Radiology(ACR). Based on Ki-67 proliferation index, the patients divided into two groups: Low-Ki-67 group (Ki-67≤14%) and high-Ki-67 group (Ki-67>14%). the relationship between DCE-MRI features and Ki-67 status was analyzed by using statistical software (SPSS, version 22.0; SPSS, Chicago, Ill), with P<0.05 considered to indicate a significant difference.Results
The DCE-MRI features between low Ki-67 group and high Ki-67 group of the patients with breast carcinoma are summarized in Table 1. The TIC appeared as washout in breast cancer was more frequently detected in high-Ki-67 group 62.5% (40/64), and the plateau were relatively low at 37.5% (24/64), and the difference was statistically significant, P value <0.05. Heterogeneous type of reinforcement in breast cancer was 76.6% (49/64) in high-Ki-67 group, Homogeneous type of reinforcement and rim type of reinforcement were relatively low at 6.3% (4/64) and 17.2% (11/64) respectively, and the difference was statistically significant, P value <0.05. Irregular mass were more frequently detected in high-Ki-67 group, accounting for 75% (42/64), and the Round-lobulated mass 25% (22/64), but the difference was not statistically significant, P value>0.05(Figure A-F).Discussion
Breast carcinoma with high Ki-67 proliferation index responds better to chemotherapy but is a parameter associated with an unfavorable prognosis[3]. Early acquisition of Ki-67 status is important for the treatment and prognosis assessment in patients with breast carcinoma. At present, preoperative evaluation of Ki-67 is frequently based on immunohistochemistry (IHC), which requires tissue samples typically obtained by needle biopsy or surgery. However this method is invasive and difficult to implement because of limitations in equipment, technology, and cost in primary hospital. MRI shows higher resolution for soft tissue and some of imaging features is related to histopathological grade[4].In our study, we found a relationship between DCE-MRI features and Ki-67 status in patients with breast cancer. Heterogeneous type of reinforcement and TIC appeared as washout are more likely to present in high Ki-67group. The results of the our study suggested that the DCE-MRI enhancement patterns of tumors and TIC curves were associated with Ki-67 level in patient with breast cancer.Conclusion
The Ki-67 status can be evaluated by DCE-MRI imaging features, which can provide some help for clinical guidance of treatment and evaluation of prognosis.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81601466; 81720108021; 81271565; 81401378), Henan Provincial Department of Science and Technology Research Project (No.201602221).References
[1] DeSantis C E, Ma J, Gaudet M M, et al. Breast cancer statistics, 2019[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2019, 10.3322/caac.21583: [2] Uematsu T, Kasami M, Yuen S. Triple-negative breast cancer: correlation between MR imaging and pathologic findings[J]. Radiology, 2009, 250(3): 638-647. [3] Cuzick J, Dowsett M, Pineda S, et al. Prognostic value of a combined estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, Ki-67, and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 immunohistochemical score and comparison with the Genomic Health recurrence score in early breast cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2011, 29(32): 4273-4278. [4] Huang J, Yu J, Peng Y. Association between dynamic contrast enhanced MRI imaging features and WHO histopathological grade in patients with invasive ductal breast cancer[J]. Oncol Lett, 2016, 11(5): 3522-3526.Figures
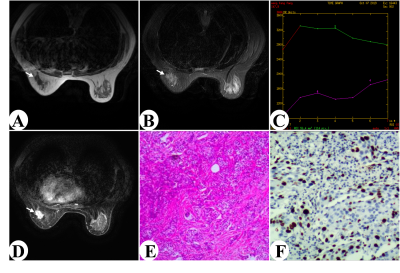
Figure A-F
Female Patient, 43 years old, left breast invasive carcinoma of non-special
type(IDC-NST), histopathology grade II, Figure A.: Axis T1WI lesions are hypointensity; B: Fat-suppressed
T2WI lesions show Low/intermediate signal and irregular
shape; C:Axial dynamic enhancement
showed type of homogeneous reinforcement;
D:TIC curve type was Ⅲ(washout); E:
HE staining (×200); F:
Immunohistochemical staining (SP×200) Ki-67 showing labelling of
roughly 40% of nuclei was defined as high Ki-67 level.
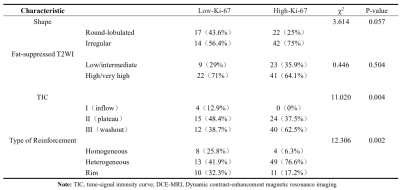
Table 1
Relationship between DCE-MRI imaging features and Ki-67 status