4735
Quantitative Diagnosis of Microvascular Invasion of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in IVIM diffusion-weighted MR imaging1Zhujiang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China
Synopsis
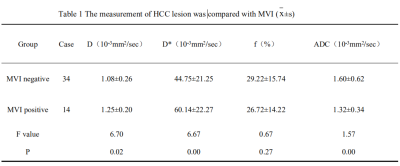
This study selected 48 HCC patients admitted to our hospital from January 2018 to June 2019, and divided them into 34 HCC patients in the MVI negative group and 14 HCC patients in the MVI positive group according to the postoperative pathological results. And then the round area of ROI was used to measure the lesion on the IVIM image. Finally, the diagnostic value of D, D*, f and ADC to MVI was analyzed by statistical software. The results showed that IVIM-DWI was helpful in evaluating the MVI of HCC, and D value had the best diagnostic efficacy.
Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common malignant tumors. Although the treatment of HCCs is evolving, hepatic resection or liver transplantation remains the possible treatment to cure HCCs for eligible patients. Unfortunately, the postoperative recurrence rate of HCC remains high . In particular, microvascular invasion (MVI) is a major risk factor for overall survival and recurrence rates of HCC after liver resection or liver transplant . However, identification of the MVI requires a definitively histological evaluation of surgical specimens obtained after resection and transplantation, which limits its usefulness onpreoperative clinical-decision making. At present, clinical study of using IVIM-DWI to evaluate hepatocellular carcinoma MVI is rare. Therefore,the purpose of this study is provided reference for selecting proper examination means in evluating and investigating hepatocellular carcinoma by comprehensively evaluating value of IVIM-DWI parameters in preoperation prediction of single occurrence of MVI, summarizing better clinical diagnosis parameter for prediction of MVI occurrence in HCC and elevating MVI level used in preoperative prediction of HCC.Methods
Forty-eight with HCC who were admitted to our hospital from January 2018 to June 2019 were enrolled. According to the postoperative pathological results, they were divided into MVI positive and MVI negative group HCC. And there were 14 cases in the positive group and 34 cases in the negative group. All cases underwent MRI upper abdominal contrast enhancement scan of Gd-EOB-DTPA and multi-b IVIM diffusion-weighted imaging scan. Scanning parameters were as follows: TR=2691ms;TE=51ms;FOV=300mm×381mm;Matrix=120×146 ;slicethickness=0.6mm;scanningtime=486s;b values=0,25,50,100,200,400,800,1000. Finally, DWI and ImageJ Tools was used. Software analysis of D, D*, f and ADC values, and mapping of ROC curves to evaluate the diagnostic value of IVIM-DWI diagnosis for MVI.Results and Discussion
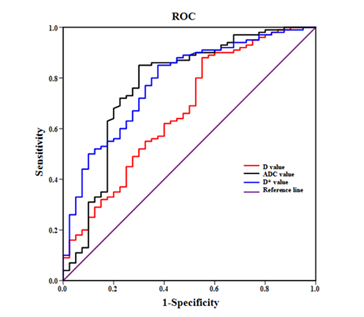
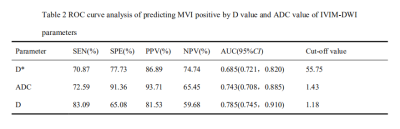
The comparison of IVIM-DWI parameters between HCC in the two groups showed that MVI positive group had lower D and ADC values than MVI negative group, and the difference was statistically significant between the two groups (P < 0.05); the D* value of the MVI positive group was higher than that of the MVI negative group (P<0.05); the f value was not significantly different between the two groups (P>0.05), the cause may be related to the location of lesion and the supplying artery. Compared with D* and ADC values, the AUC value of D value is 0.785, which was the largest, and its sensitivity of MVI diagnosis was 83.09%(Fig1).Conclusion
IVIM-DWI helps to assess the MVI of HCC, where the D value predicts the best diagnostic power of MVI.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1、Li, H., et al. (2018). Eur J Radiol 105: 65-71.
2、Zhao, W., et al. (2018). PLoS One 13(5): e0197488.
3、Wu D,Tan M,Zhou M,et a1. ,Invest Radiol,2015, 50(4):188-194.
4、Kamura S,Sumie S,Tonan T,et a1. ,Dig Liver Dis,2016,48(8):945-952.
5、Zhao J,Li X,Zhang K,et a1.,Eur J Radiol,2017,88:32-40.
6、Yuan M,Zhong Y,Zhang Y D,et a1.,Acta Radiol,2017,58(12):1448-1456.
7、Lee Y J,Kim S H,Kang B J,et a1.,Magn Reson Imaging,2017,45(5):1394-1406.
8、Shan Q,Chen J,Zhang T,et a1.,Abdom Radiol fNV),2017,42(8):2079.2088.