4688
Correlation analysis between amide proton transfer weighted and blood flow status in infarct core of patients with subacute ischemic stroke1the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, Dalian, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Amide proton transfer weighted (APTw) MR imaging enables detections of metabolite and pH value changes, while the arterial spin label (ASL) imaging can assess hemodynamic changes in brain tissue after cerebral infarction. This study aimed to evaluate correlation between APT-related metabolic changes and blood flow status in the infarct core of patients with subacute ischemic stroke by APTw and ASL MR techniques. Significant correlations of APT to apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and cerebral blood flow (CBF) values in the infarct region were observed.
Introduction
Stroke as a serious cerebrovascular disease is the main cause of long-term disability and death, and seriously affects the quality of people's life[1]. The conventional MRI diagnostic techniques for cerebral infarction, such as perfusion-weighted imaging (PWI) and diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), are insufficient to observe changes in pH of the brain tissue. Although MR spectroscopy (MRS) has been explored to assess the pH of brain tissue during stroke[2]. However, its practical applicability is limited due to the low spatial and temporal resolutions. As a new type of MR technique, the amide proton transfer weighted (APTw) MRI enables detection of brain metabolite changes with much higher sensitivity than MRS. Characterizations of hyperacute and acute cerebral ischemic strokes using APTw MRI have been previously studied, but little attention has been paid to the subacute ischemic stroke [3]. In addition, there is currently no study to combine the APTw MRI with the blood flow measurements for stoke analyses. Purpose of this study was to evaluate the correlation between APT-related metabolic changes and blood flow status in the infarct core of patients with subacute ischemic stroke in the unilateral middle cerebral artery blood supply area by APTw and ASL MR techniques.Materials and Methods
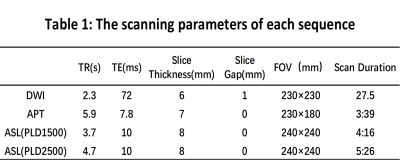
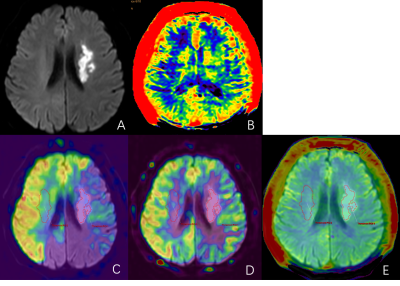
This study was approved by the ethics committee of the hospital. A total of 40 patients (23 males, age 44-87 years) with clinically suspected ischemic stroke was prospectively collected and underwent routine sequences and APTw imaging on a 3.0 T MR scanner (Ingenia CX, Philips Healthcare, Best, the Netherlands). Excluding the scanning artifacts and interrupted scans due to poor patient cooperation, a total of 16 patients (9 males, age 44-86 years) with subacute ischemic stroke in the unilateral middle cerebral artery blood were collected. After scanning, image was automatically transmitted to the vender-provided workstation (IntelliSpace Portal), where the data post-processing was independently carried out by two observers. The DWI images were fused with ADC, APTw and arterial spin label (ASL) images. 3D ROI was delineated on the infarct area of DWI image, and used to obtain ADC, APTw (including APTwmax, APTwmin, APTwmean), and CBF (PLD1.5 and PLD2.5 on ASL image) values. The rCBF value was calculated by dividing CBF value of the affected side by that of the contralateral side. Calculate the difference between the maximum and minimum values (APTwmax-APTwmin), defined as APTwmax-min, which is used to reflect the APTw signal heterogeneity. The interclass correlation coefficient (ICC) was used to evaluate measurement consistency between the two observers. The paired sample t test was used to analyze differences of bilateral APTw values. The Pearson correlation test was used to analyze correlations of APTw to ADC and CBF values.Results
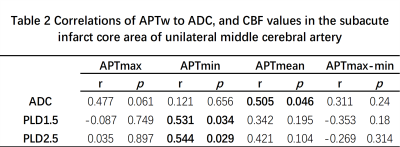
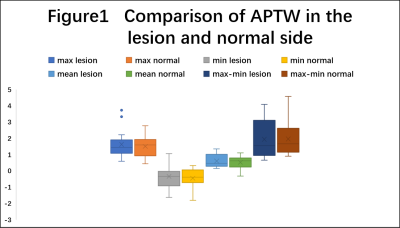
Measurements by the two observers are in good agreement (ICC > 0.75). There was no difference in APTW values between the subacute infarction core and the contralateral normal sides (Figure 1). ADC values were observed to be positively correlated to APTwmean values in the infarct area (p = 0.046, r = 0.505). Significant correlations of APTwmin values to CBF values of both PLD1.5 and PLD2.5 (p=0.034, r=0.531; p=0.029, r=0.544) were also observed. (Table 2)Discussion and conclusions
Results of this study showed that APTwmin values was positively correlated with blood flow status of PLD1.5 and PLD2.5 in the subacute infarct core region of the unilateral middle cerebral artery supply area. The acidosis of the infarct core tissue is severe. In the subacute infarction, with blood perfusion further reduced, APTwmin reduced, which may indicate that there is a certain period of persistent acidosis in the tissue after ischemic stroke. However, no difference was observed between APTw values measured from the subacute infarction core and the contralateral normal sides, which may be due to the decreased sensitivity of APT to pH changes in the subacute phase or due to the progressive conversion of acidosis in the ischemic area to alkali poisoning.Besides, the limited number of subjects may also affect research results.Acknowledgements
References
[1] Johnston SC, Mendis S, Mathers CD. Global variation in stroke burden and mortality: estimates from monitoring, surveillance, and modelling. Lancet Neurology, 2009;8(4):345-354.
[2] Gillard J H, Barker P B, Zijl P C V, et al. Proton MR spectroscopy in acute middle cerebral artery stroke.[J]. Ajnr American Journal of Neuroradiology, 1996, 17(5):873.
[3] Song G, Li C, Luo X, et al. Evolution of cerebral ischemia assessed by amide proton transfer-weighted MRI. Frontiers in neurology, 2017;8:67.
Figures