4601
Abnormal Left Atrial Performance in Children with Repair Tetralogy of Fallot using CMR Feature Tracking
Liwei Hu1, Xiaodan Zhao2, Rongzhen Ouyang1, Shuang Leng2, WeiHui Xie1, Yafeng Peng1, Xiaofen Yao1, Yong Zhang3, Ru San Tan2,4, Liang Zhong2,4, and Yumin Zhong1
1Radiology, Shanghai Children's Medical Center, Shanghai, China, 2National Heart Centre Singapore, Singapore, Singapore, 3GE Healthcare, Shanghai, China, 4Duke-NUS Medical School, National University of Singapore, Singapore, Singapore
1Radiology, Shanghai Children's Medical Center, Shanghai, China, 2National Heart Centre Singapore, Singapore, Singapore, 3GE Healthcare, Shanghai, China, 4Duke-NUS Medical School, National University of Singapore, Singapore, Singapore
Synopsis
Right ventricular (RV) and atrial (RA) dilation has been clinically observed in patients after initial repair of tetralogy of Fallot (rTOF) and is associated with adverse long-term outcomes. Due to RA and left atrial (LA) interaction, we aimed to determine the effect of RA dilation on LA performance from feature tracking cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) in pediatric rTOF patients. Results revealed that LA strains and strain rates were impaired in rTOF than age- and gender-matched healthy volunteers. RA volumes are negatively associated with LA strains. These findings may suggest LA diastolic dysfunction from chronic RV and RA dilations in rTOF, even at early stage after initial repair.
Introduction
Right ventricular (RV) and atrial (RA) dilation have been observed in conjunction pulmonary regurgitation developing after repaired Tetralogy of Fallot (rTOF). Left ventricular (LV) and (LA) function may be perturbed due to RV-LV and RA-LA interactions. Quantitation LA phasic reservoir, conduit and contractile function has recently become feasible with cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) feature tracking (Leng et al 2018). We aimed to study the relationship between LA performance and RA Volumes in pediatric rTOF patients versus age- and gender-matched healthy volunteers.Methods
Pediatric rTOF patients (11±4 years) and age- and sex-matched healthy controls (11±2 years) were prospectively recruited between June 2017 - August 2019. Standard steady state free precession cine CMR were acquired on 3T (Discovery MR 750, GE, USA) and 1.5 Tesla scanners (Achieva, Philips Healthcare, Netherlands). Ventricular and atrial volumes and ejection fractions were measured using CVI42 software (Circle Cardiovascular Imaging, Calgary. Using CMR feature tracking software (CVI42), LA reservoir (Ɛs), conduit (Ɛe) and booster strains (Ɛa) were determined at LV end-systole, LV diastasis and pre-LA systole respectively. First derivatives of the respective strains yielded corresponding peak strain rates. Statistical analysis was performed using t test Mann-Whitney test for parametric and non-parametric variables, respectively. Intra-observer and inter-observer variability of LA strain and strain rate measurements were determined from five randomly selected rTOF and five control subjects.Results
RV volumes, RA end-systolic volume (RAESV) were increased, and RAEF decreased, in rTOF patients versus control (Tables 1 and 2). LA strains were significantly reduced in rTOF versus controls even as LA EF were comparable (60±5% vs. 63±4%, P=0.06) (Table 3). LA reservoir strain has good negative correlation with RA end-diastolic volume index (r=-0.51, p<0.001) and RAESV index in rTOF group (r=-0.49, p=0.002). LA strains and strain rates have good reproducibility in Intra-observer and inter-observer analyses (Table 4).Conclusions
LA strains were reproducible from feature tracking CMR in pediatric rTOF. The data showed abnormal LA strain and strain rate in pediatric rTOF. These findings may suggest LA diastolic dysfunction from chronic RV and RA dilations in rTOF, even at early stage after initial repair.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
- Stokke T M, Hasselberg N E, Smedsrud M K, et al. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 2017, 70(8):942-954.
- Kutty S, Shang Q, Joseph N, et al. International Journal of Cardiology, 2017;248:136-142.
- Dick A, Schmidt B, Michels G, et al. European Journal of Radiology, 2017, 89:72.
- Leng S, Tan RS, Zhao XD, et al. Validation of a rapid semi-automated method to assess left atrial longitudinal phasic strains on cine cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging. Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, 2018;20:71.
Figures
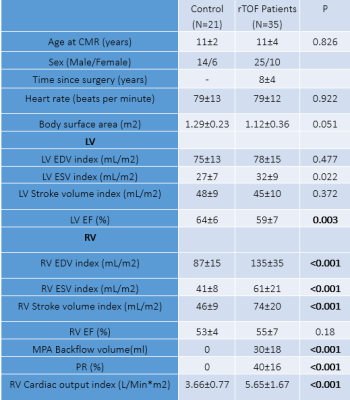
Fig 1.Characteristics of cardiac function and ventricular strain in rTOF
patients
and control group
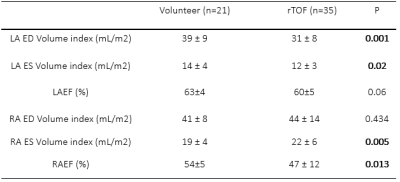
Fig 2.Comparisons of Left
and right atrial function between repaired TOF and control groups.
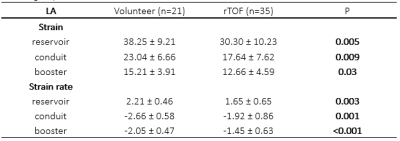
Fig 3.Comparisons of average
peak strain and peak strain rate between repaired TOF and control groups.
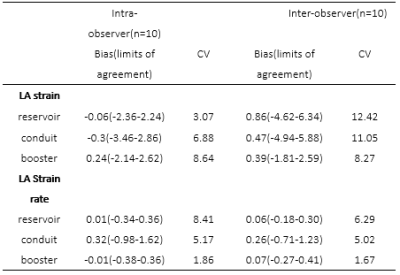
Fig 4.Intra-observer and inter-observer
variability of LA strain and strain rate in rTOF and control cases.
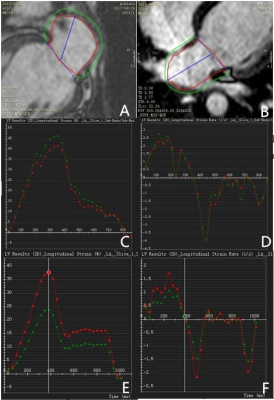
Fig 5.The circle shows epi
and endo atrial in two chamber view (Figure A) and four chamber view (Figure B)
in volunteer case. LA performance can be quantified by measuring global
longitudinal strain and global peak strain rate (SR) during cardiac cycle in
rTOF patient (Figure C and D) volunteer (Figure E and F).