4555
Brain microstructural alterations of left precuneus mediate the association between KIBRA rs17070145 and working memory in healthy adults.1Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital Clinical College of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China, 2Drum Tower Hospital, Medical School of Nanjing University, Nanjing, China, 3Clinical Science, Philips Healthcare, Shanghai, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
We used voxel-based independent sample t-test to investigate differences of DKI and resting-state fMRI parametric maps between KIBRA rs17070145 polymorphism in 163 young adults. Mediation analysis was used to explore the association between the KIBRA polymorphism, brain and working memory. We observed that KIBRA C-allele carriers had increased AD, RD, MD and decreased FA, MK, RK, ALFF compared with KIBRA TT homozygotes. The MK, RK of the left precuneus mediated the association between the KIBRA polymorphism and the working memory performance. These findings may be useful in understanding the neural mechanisms of KIBRA and provide a biological pathway of gene-brain-behavior.
Introduction
KIBRA rs17070145 is found to be associated with memory function and impaired cognitive process. However, the neural mechanisms underlying the association are not fully understood. This study aimed to explore the effect of KIBRA polymorphism on brain microstructure and blood oxygenation level dependent fluctuation using the DKI and the resting-state fMRI in 163 young adults. Furthermore, we investigated whether these alterations mediate the association between the KIBRA gene and working memory performance.Methods
The study included 163 healthy, right-handed young Chinese adults (mean age: 23.0 ± 1.8 years; 53 males and 110 females). Genetic, demographic and working memory data, diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) and resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data were collected. The voxel-based independent sample t-test was used to investigate differences of DKI and resting-state fMRI parametric maps between KIBRA rs17070145 polymorphism and then extracted for mediation analysis with working memory performance.Results
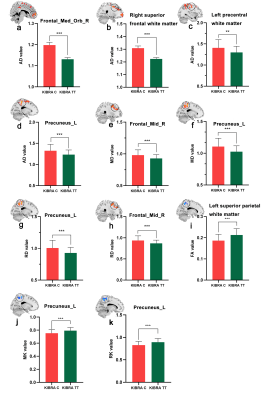
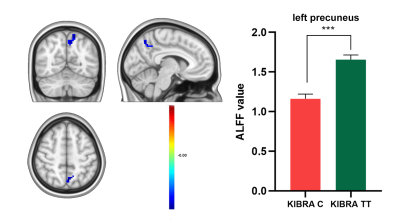
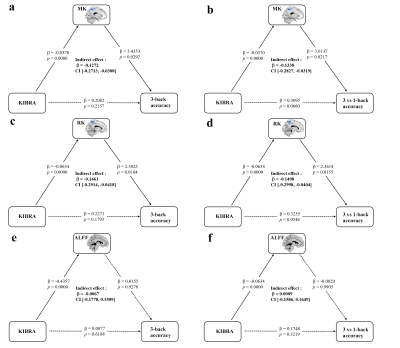
Voxel-based analysis of DKI data showed that KIBRA C-allele carriers exhibited increased AD, RD, MD and decreased FA, MK and RK compared with KIBRA TT homozygotes (Figure 1). These regions were primarily prefrontal lobe, left precuneus and the left superior parietal white matter. Meanwhile, KIBRA C-allele carriers exhibited decreased ALFF in the left precuneus than KIBRA TT homozygotes (Figure 2). Mediation analysis revealed that the DKI metrics (MK and RK) of the left precuneus mediated the association between the KIBRA polymorphism and the working memory, while the ALFF of left precuneus did not exhibit the moderating effect (Figure 3).Discussion & Conclusion
These findings provide a gene-brain-behavior pathway that KIBRA rs17070145 affects working memory via modulating the brain microstructure of the left precuneus, which may provide additional biological information than resting-stating fMRI.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81720108022, 91649116, 81571040); the social development project of science and technology project in Jiangsu Province (BE2016605, BE201707); key medical talents of the Jiangsu province, the "13th Five-Year" health promotion project of the Jiangsu province (B.Z.2016-2020); Jiangsu Provincial Key Medical Discipline (Laboratory) (ZDXKA2016020); the project of the sixth peak of talented people (WSN-138, BZ).The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.References
1. Andreas P, Stephan DA, Huentelman MJ, et al. Common Kibra alleles are associated with human memory performance. Science. 2006;314(5798):475-478.
2. John M, Matthew E, Fabio S, et al. WWC1 genotype modulates age-related decline in episodic memory function across the adult life span. Biological Psychiatry. 2014;75(9):693-700.
3. Karolina K, Lars-GRan N, Rolf A, Elias E, Lars N. KIBRA polymorphism is related to enhanced memory and elevated hippocampal processing. Journal of Neuroscience the Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience. 2011;31(40):14218-14222.
4. A M, A H, C V, HJ H, DJ dQ, A P. Association of KIBRA with episodic and working memory: a meta-analysis. American journal of medical genetics. Part B, Neuropsychiatric genetics: the official publication of the International Society of Psychiatric Genetics. 2012;null(8):958-969.
Figures