4452
Brodmann atlas based non-Gaussion water diffusion analysis of normal tension glaucoma: A diffusion kurtosis imaging study1Radiology Department, Beijing Tongren Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China, 2GE Healthcare, MR Research China, Beijing, Beijing, China
Synopsis
To access the non-Gaussion water diffusion characteristic of normal tension glaucoma (NTG), we analyzed the diffusion parameters generated from diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI). The parameters derived from DKI within changed brain regions of NTG group were reduced and involved the occipital lobe. The visual cortex in NTG group had lower degree of diffusional heterogeneity and microstructural complexity compared to normal control (NC) group.
Introduction
Patients with NTG have been reported that the diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) derived parameters (e.g. fractional anisotropy, FA) of them were significantly altered in visual pathway [1]. DKI extends conventional DTI by estimating the kurtosis of the non-Gaussion water diffusion distribution, which is strongly linked to cellular microstructure. To evaluate the non-Gaussion water diffusion characteristic and cellular microstructure feature of NTG, we investigated the diffusion parameters derived from DKI.Material and Methods
A total of 24 volunteers from NC (NC group, 15 Female, 9 Male, age 47±10) group and 26 patients with NTG (16 Female, 10 Male, age 47±13) were enrolled in this study. All subjects underwent MR scans on a 3T MR scanner (Discovery MR750, GE Healthcare, USA) with an 8-channel head coil. The three-dimensional brain T1 weighted MRI and DKI (3b values: 0, 1000, 2000s/mm2, 25 diffusion directions) sequences were scanned. The DKI images were preprocessed using the following method: 1) DICOM formats were changed into NIfTI; 2) apply eddy current correction and 3) brain extraction; 4) computation of b0 mean image. The T1 image also underwent brain extraction. Then DKI and T1 of each subject were registered into the Montreal Neurological Institute (MNI) space.The diffusion parameters including mean kurtosis (MK), axial kurtosis (AK), radial kurtosis (RK) , mean diffusivity (MD), axial diffusivity (AD), radial diffusivity (RD), and FA were generated via diffusional kurtosis estimator (DKE), while the computations were speed up and simplified through a cloud platform (www.humanbrain.cn).
The Brodmann atlases (BA) were taken at the region of interest (ROI) and applied to extract the DKI parameters for each subject. Statistical analyses were performed using two sample t test function through coding in MATLAB for each parameter in each region of NTG and NC groups. P<0.05 was considered significantly different. FDR correction was also applied.
Results
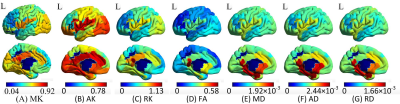
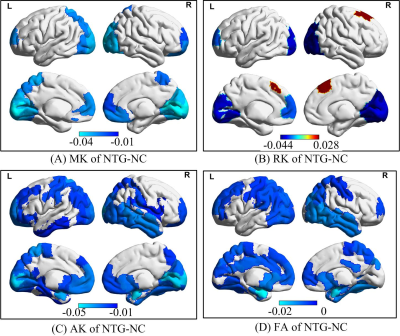
The BA region based non-Gaussion water diffusion distribution in normal controls was heterogeneous (Figure 1). The parameters of diffusion kurtosis including MK, AK and RK ranged from 0 to 1.13; FA varied from 0 to 0.58, while the diffusivity (MD, AD, RD) measures were 1.66×10-3 to 2.44×10-3. The AK values of visual cortex were obviously larger than cortexes in normal controls (Figure 1B) while that in NTG were significantly reduced compared to NC (Figure 2C).The group differences between NTG and NC in terms of MK, RK, AK and FA are shown in Figure 2. The non-Gaussion water diffusion changes of NTG mainly focused on MK, RK, AK and FA. The MK, AK, and FA values within significantly changed regions of NTG were reduced compared to NC, while RK of significant changed regions included both reduced and increased regions. In particular, the mean group difference of RK on BA8 region was increased in the NTG group.
Discussion
Studies have suggested that patients with glaucoma have significantly altered DTI-derived parameters in visual pathway [1]. In this study, we found that non-Gaussion water diffusion distribution was significantly changed in visual cortex of NTG. DKI extends conventional DTI by estimating the kurtosis of the non-Gaussion water diffusion distribution. DTI produces the standard measures such as FA and AD/RD/MD, while DKI provides those standard measures along with MK, AK, and RK. The diffusional kurtosis metrics are strongly linked to cellular microstructure, a main source of diffusional non-Gaussianity in tissues.A recent study reported that the mean MK of the optic nerves (ON), lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN), optic radiations (OR), and visual cortex in the glaucoma group were all significantly lower than those in the control group [2], which is consistent with our findings. The reduced MK, RK, AK values (blue region, Figure 2 A-C) of occipital lobe in NTG indicated that the visual cortex of NTG had a lower degree of diffusional heterogeneity and cellular microstructural complexity compared to NC. Furthermore, the group differences of RK (Figure 2B) indicated the brain compensation in NTG group since both significant increased and decreased RK values exist on brain regions.
The BA8 region includes frontal eye field, which regulates eye movements. The increased RK on BA8 of NTG may suggest that the cellular microstructural environment. The results of BA8 provide a possible evidence for the finding that unavoidable eye movements might be a cause of people with NTG. A recent study reported an increase in hemodynamic responses in the bilateral frontal cortex (including BA8 region) [3]. This suggests that the NTG may lead to cognitive problems due to alteration of microstructure and hemodynamic [4].
Conclusion
The non-Gaussion water diffusion of normal human brain is heterogeneous; significantly reduced mean, axial and radial diffusivities were found in most brain regions, including the visual cortex of NTG. In conclusion, the visual cortex in NTG group had lower degree of diffusional heterogeneity and microstructural complexity compared to NC group.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Lawlor, M., et al, 2017. Glaucoma and the brain: Trans-synaptic degeneration, structural change, and implications for neuroprotection. Survey of ophthalmology, S0039-6257, 30044-30049.
[2] Xu, Z.F., et al, 2018. Microstructural visual pathway abnormalities in patients with primary glaucoma: 3 T diffusion kurtosis imaging study. Clinical Radiology,73, 591-599.
[3] Kikuchi, A., et al, 2018. Effects of levocetirizine and diphenhydramine on regional glucose metabolic changes and hemodynamic responses in the human prefrontal cortex during cognitive tasks. Hum Psychopharmacol 33, e2655.
[4] Raman, P., et al, 2019. The Association Between Visual Field Reliability Indices and Cognitive Impairment in Glaucoma Patients. Journal of glaucoma, 28, 685-690.
Figures