4335
Comparison of iShim, RESOLVE, and ss-EPI diffusion-weighted MR imaging with high b value at 3T MR in the evaluation of uterine malignancy1Department of Imaging Diagnosis, National Cancer Center/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Science and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China, 2MR Scientific Marketing, Diagnostic Imaging, Siemens Healthcare Ltd, Beijing, China
Synopsis
In the evaluation of uterine malignancy, conventional DWI based on single-shot echo-planar imaging (ss-EPI) is prone to imaging artifacts, including susceptibility artifacts from gas, imaging blurring, which limit its diagnostic value, especially in detecting and staging uterine malignancy. The purpose of this study is to compare the detection of uterine malignancy and image quality among DWI based on integrated slice-specific dynamic shimming (iShim), readout segmentation of long variable echo trains (RESOLVE) and ss-EPI sequence. Our results indicated that iShim DWI showed better image quality than ss-EPI and RESOLVE DWI in the terms of subjective image scores and objective quantitative metrics.
Introduction
In the evaluation of uterine malignancy, conventional DWI based on single-shot echo-planar imaging (ss-EPI) is prone to imaging artifacts, including susceptibility artifacts from gas in the rectum, imaging blurring, geometric distortion. All these artifacts limit its diagnostic value, especially in detecting and staging uterine malignancy. The purpose of this study is to compare the detection of uterine malignancy and image quality among DWI based on integrated slice-specific dynamic shimming (iShim), readout segmentation of long variable echo trains (RESOLVE) and ss-EPI sequence. Our results indicated that iShim DWI showed better image quality than ss-EPI and RESOLVE DWI in the terms of subjective image scores and objective quantitative metrics.Methods
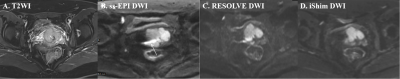
Seventeen patients with uterine malignancy (cervical cancer: 11 cases; endometrial cancer: 6 cases; all pre-treatment) underwent DWI based on iShim, RESOLVE and ss-EPI sequences with two b values (50 and 1000s/mm2) at a 3T whole-body MR scanner (MAGNETOM Prisma, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany). Without awareness of histological diagnosis and the types of image sequences, two radiologists (5 and 8 years’ experiences in interpreting gynecological cancers) independently assessed the three sets of DW images for the depiction of lesion with a 4-point scale (1 = poor and severely blurred depiction; 2 = moderate depiction; 3 = clear depiction with slight depiction; 4 = excellent depiction without blurring), susceptibility artefact with a 5-point scale (1 = severe artifacts; 2 = moderate artifacts; 3 = mild artifacts; 4 = minimal artifacts; 5 = no artifacts) and geometric distortion. Specifically, geometric distortion was evaluated by comparing lesion anteroposterior (AP) length and left-right (LR) width derived from both T2W images and three different sets of DW images using paired-sample t test. In addition, regions of interest (ROIs) were manually drawn to measure the signal intensity of the tumor (SItumor), the uterine myometrium nearby the lesion (SImyo) and the standard deviation (SD) of the background signal intensity. The contrast-to noise ratio (CNR) was defined by the following formula: CNR=(SItumor-SImyo)/SD and the signal intensity ration was calculated by the following formula: Ratio=SItumor/SImyo. The subjective image quality score, CNR and signal intensity ratio were compared using Friedman test. A value of P<0.05 was considered as statistically significant.Results
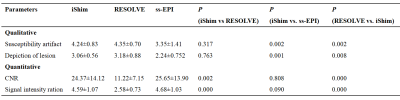
Regarding to qualitative comparisons, both iShim and RESOLVE was significantly superior to ss-EPI (P=0.001), whereas there were no significant differences between RESOLVE and iShim (P=0.332 in susceptibility artifact and P=0.773 in the depiction of lesion). Considering geometric distortion, both AP and LR length on iShim, RESOLVE and ss-EPI did not reveal any significant differences from T2W images (all P>0.05). Additionally, the CNR and signal intensity ratio between tumor and adjacent uterine myometrium of iShim (24.37±14.12 and 4.59±1.07) and ss-EPI (25.65±13.90 and 4.68±1.03) were significantly higher than RESOLVE (11.22±7.15 and 2.57±0.73, all P< 0.05), but there were no significant differences between iShim and ss-EPI (P=0.760 and P=0.771, respectively).Discussion and Conclusion
Susceptibility artifact, image blurring and spatial distortion are common in conventional DWI due to its intrinsic defects resulting from long EPI readout and corresponding low bandwidth in the phase encoding direction. In our study, both iShim and RESOLVE DWI showed better performance in reducing magnetic susceptibility artifacts and delineating lesions, which are critical for staging uterine malignancy, especially for evaluating FIGO stage IIB or above in patients with cervical cancer and FIGO stage II in patients with endometrial cancer. Additionally, the CNR and signal intensity ratio of iShim and ss-EPI have been improved compared to RESOLVE DWI. Therefore, we speculated carefully that the iShim DWI could be used to optimize image quality in terms of reducing magnetic susceptibility artifacts and imaging blurring, and at the same time improving DW images’ CNR and signal intensity ratio. In conclusion, DW imaging based on iShim may be a clinical promising technique for the purpose of evaluating lesions in patients with uterine malignancy.Acknowledgements
This research did not receive any specifific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profifit sectors.References
1 Vandecaveye V, Dresen R, De Keyzer F: Novel imaging techniques in gynaecological cancer. CURR OPIN ONCOL 2017;29:335-342.
2 Xia CC, Liu X, Peng WL, Li L, Zhang JG, Meng WJ, Deng XB, Zuo PL, Li ZL: Readout-segmented echo-planar imaging improves the image quality of diffusion-weighted MR imaging in rectal cancer: Comparison with single-shot echo-planar diffusion-weighted sequences. EUR J RADIOL 2016;85:1818-1823.
3 Liney GP, Holloway L, Al HT, Sidhom M, Moses D, Juresic E, Rai R, Manton DJ: Quantitative evaluation of diffusion-weighted imaging techniques for the purposes of radiotherapy planning in the prostate. Br J Radiol 2015;88:20150034.
4 Zhang H, Xue H, Alto S, Hui L, Kannengiesser S, Berthold K, Jin Z: Integrated shimming improves lesion detection in Whole-Body Diffusion-Weighted examinations of patients with plasma disorder at 3 t. INVEST RADIOL 2016;51:297-305.
Figures