4313
Whole-Tumor Histogram Analysis of Breast Lesions Based on Simultaneous Multi-slice Readout-segmented Echo-planar Imaging1Department of Radiology, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China, 2Application Development, Siemens Shenzhen Magnetic Resonance Ltd., Shenzhen, China, 3Application Predevelopment, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany
Synopsis
This study compared the diagnostic performance of the ADC derived from the diffusion-weighted readout-segmented EPI DWI accelerated with SMS technique (SMS rs-EPI DWI) with that derived from the conventional rs-EPI DWI on breast lesions using whole-tumor histogram analysis. Our results showed that the SMS technique can increase the spatial resolution of the rs-EPI DWI sequence without prolonging the scan time. It can also improve the diagnostic performance of the derived ADC map based on whole-tumor histogram analysis in distinguishing benign and malignant breast lesions.
Background and Purpose
Readout-segmented echo-planar imaging (rs-EPI) could outperform single-shot echo-planar imaging (ss-EPI) with higher spatial resolution and less geometric distortion 1, 2. However, rs-EPI is limited by its lower acquisition efficiency compared to ss-EPI. The simultaneous multi-slice (SMS) technique, which could help improve the acquisition speed by simultaneously exciting multiple slices with a single multiband RF pulse, has been reported in many studies3-6. The present study applied the SMS technique on the diffusion-weighted rs-EPI (SMS rs-EPI DWI) sequence to further increase the spatial resolution without prolonging the scan time, and compared the diagnostic performance of the ADC map from SMS rs-EPI DWI with that from the conventional rs-EPI DWI (NOSMS rs-EPI DWI) in the differentiation between benign and malignant breast lesions using whole-tumor histogram analysis.Materials and methods
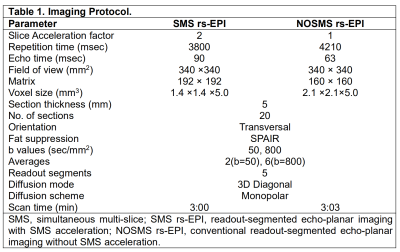
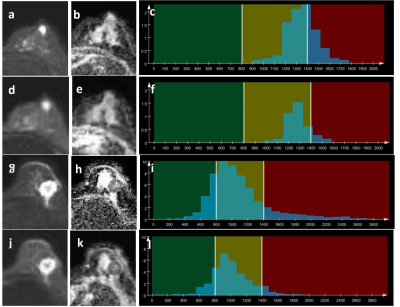
This retrospective study included 185 patients (185 breast lesions in total) who had undergone breast MRI on a 1.5T scanner (MAGNETOM Aera, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) before treatment. NOSMS rs-EPI DWI and prototype SMS rs-EPI DWI sequences were performed using the parameters shown in Table 1. Two independent radiologists evaluated the whole-volume-based histogram parameters (i.e., mean, SD, median, 5th and 95th percentiles, skewness, and kurtosis) of the breast lesion in the ADC map by using a prototype MR Multiparametric Analysis software (Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany). Student’s t test, Mann–Whitney U test, Pearson’s chi-squared test, and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves combined with regression models were used for the statistical analysis.Results
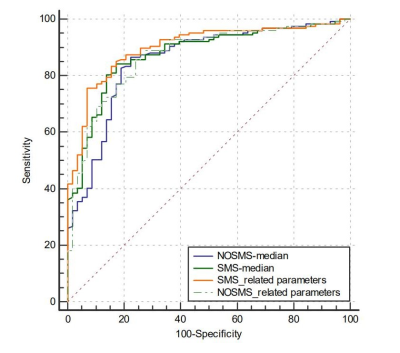
ADCmedian of both SMS rs-EPI and NOSMS rs-EPI had the highest AUC in their own histogram parameter groups (0.876, 0.855, respectively). ADCmean, SD, median, 5th and 95th percentiles, and skewness of SMS rs-EPI and ADC mean, median, 5th and 95th percentiles, and skewness of the NOSMS rs-EPI were significantly different between the malignant and benign groups (all P < 0.05). Higher SD, kurtosis, and skewness and lower mean, median, 5th and 95th percentiles of ADC were found in malignant breast lesions compared with those in benign breast lesions. The AUCs for the combination of all significant parameters of ADC with SMS rs-EPI (0.901; sensitivity 75.6%, specificity 93.1%) were higher than that with NOSMS rs-EPI (0.871; sensitivity 85.8%, specificity 75.9%), though they did not differ significantly (Z = 1.821, P = 0.0687).Discussion and Conclusions
Sufficient spatial resolution is crucial for the whole-tumor histogram or texture analysis. By utilizing the SMS technique, we can increase the spatial resolution of diffusion-weighted images with rs-EPI without prolonging the scan time. The results of the present study demonstrated that the diagnostic performance of the whole-tumor histogram-derived parameters of the ADC maps with SMS rs-EPI sequence was improved compared to that with NOSMS rs-EPI, in distinguishing benign and malignant lesions. In conclusion, whole-tumor histogram analysis of the ADC maps from the SMS rs-EPI DWI sequence could be a useful diagnostic tool for breast tumors.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Bogner W, Pinker-Domenig K, Bickel H, et al. Readout-segmented Echo-planar Imaging Improves the Diagnostic Performance of Diffusion-weighted MR Breast Examinations at 3.0 T. Radiology.263(1):64-76.
2. Ju KY, Hun KS, Joo KB, et al. Readout-Segmented Echo-Planar Imaging in Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in Breast Cancer: Comparison with Single-Shot Echo-Planar Imaging in Image Quality. Korean Journal of Radiology Official Journal of the Korean Radiological Society.15(4):403-.
3. Taron J, Martirosian P, Kuestner T,et al. Scan time reduction in diffusion-weighted imaging of the pancreas using a simultaneous multislice technique with different acceleration factors: How fast can we go?
4. Phi Van VD, Becker AS, Ciritsis A,et al. Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Analysis of Abdominal Organs: Application of Simultaneous Multislice Acquisition. Invest Radiol. 2018;53(3):179-85.
5. Filli L, Ghafoor S, Kenkel D, et al. Simultaneous multi-slice readout-segmented echo planar imaging for accelerated diffusion-weighted imaging of the breast. Eur J Radiol. 2016;85(1):274-8.
6. Ohlmeyer S, Laun FB, Palm T, et al. Simultaneous Multislice Echo Planar Imaging for Accelerated Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Malignant and Benign Breast Lesions. Invest Radiol. 2019;54(8):524-30.
Figures