4311
Novel practical SNR determination method for MRI using combined largest b-value and echo time (COLBET)1Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Kanazawa University, Kanazawa, Japan
Synopsis
We developed a novel practical SNR measurement method using combined the largest b-value and echo time (COLBET). The COLBET method makes it possible to simply and practically perform image SNR quantitation including the long T2 region in human with parallel imaging.
Introduction
Image signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of MRI is the key indicator for quality assurance and control, as well as for acceptance testing or the performance evaluation of new hardware.1,2 Some methods for accurate SNR quantitation have previously been reported such as the background method and the image subtraction method.3-5 However, the background method is not applicable when using parallel imaging or image non-uniformity correction5 and the subtraction method is difficult for in vivo SNR measurement.6, 7 Therefore, our research group proposed a simple SNR measurement method using double echo with the longest second echo time (DELSET) for simple SNR measurement for human image even with parallel imaging,8 but this method could not apply to the long T2 regions (e.g., cerebrospinal fluid and cystic lesion) in human. To resolve this problem, we developed a novel practical method using combined the largest b-value and echo time (COLBET).Materials and methods
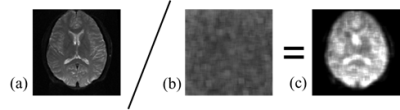
The COLBET method was performed as follows (Fig. 1). We first obtained a signal image using the objective pulse sequence. Then, we obtained the noise image of this sequence using diffusion gradient with the largest b-value and the longest TE, but other sequence parameters were completely the same as the signal image including the mechanical preparation parameters (e.g., receiver gain and transmitting power). The image SNRs was calculated from the mean signal intensity in the region of interest (ROI) in the signal image divided by signal standard deviation in the ROI (or noise map) in the no signal image after the necessary corrections to the Rayleigh noise distribution and the sum-of-squares algorithm for the multichannel coils.8 We evaluated SNRs of single-shot echo planar imaging of the brain in a healthy volunteer with array coil and obtained by the COLBET and DELSET methods. The imaging parameters were used with 73.1 ms TE and 3000 ms TR for signal image; and 1000 ms TE, 3000 ms TR, and 10000 s/mm2 b-value for noise image.Results and discussion
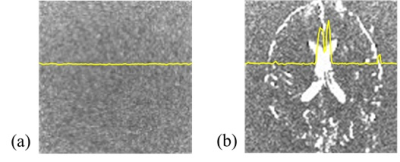
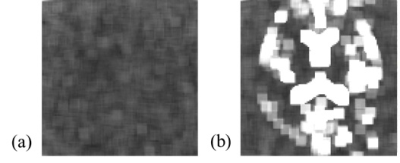
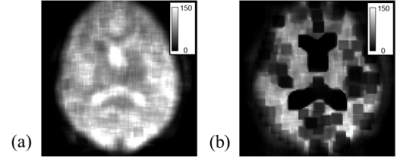
The COLBET method could obtained perfect noise image, but the DELSET method could not completely delete the cerebrospinal fluid signal (Fig. 2). Therefore, compared with the COLBET method, the DELSET led the incorrect result in the cerebrospinal fluid space in the noise and SNR maps (Figs. 3 and 4). While, the COLBET method enabled to evaluate the SNR even in the long T2 region, with parallel imaging, and in human (Fig. 4a).Conclusion
The COLBET method makes it possible to simply and practically perform image SNR quantitation including the long T2 region in human with parallel imaging.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Jackson E, et al., Maryland: American Association of Physicists in Medicine. One Physics Ellipse College Park; 2010.
2. National Electrical Manufactures Association (NEMA). NEMA Standards Publication MS 1-2008; 2008.
3. Henkelman RM, Med Phys. 1985; 12: 232-3.
4. Kaufman L, Kramer DM, Crooks LE, et al., Radiology. 1989; 173: 265-7.
5. Pruessmann KP, Weiger M, Scheidegger MB, et al., Magn Reson Med. 1999; 42: 953-62.
6. Dietrich O, Raya JG, Reeder SB, et al., J Magn Reson Imaging. 2007; 26: 375-85.
7. Goerner FL, Clarke GD. Med Phys. 2011; 38: 5049-57.
8. Ohno N, et al., Br J Radiol. 2018; 91: 2017652.
Figures