4287
A Component Projection Algorithm for eliminating the interference of Pilot Tone Signal1DL, Siemens, Shenzhen, China, 2MR Collaborations, Siemens Healthcare Ltd., Shenzhen, China, 3Beijing Institute of Technology, BeiJing, China
Synopsis
In this work, we provided a component-projection algorithm for Pilot Tone (PT) signal anti-jamming. The interference of a PT signal induced by the MR measurement can be effectively mitigated with the following procedure: the original PT signals received by the array coil are orthogonally transformed into the Eigen Space of interference signal, and the principle component of interference Eigen Space is subsequently discarded to maximally suppress the interference before the remaining components are projected into a predefined direction to combine the final PT navigator signal. Phantom and volunteer experiments demonstrated that the technique can effectively reduce the interference during scanning.
Introduction
Pilot Tone navigator signals generated by a commercial signal generator and received with MR coils could be used for respiratory navigation [1]. A novel idea is to modulate PT signal out of the bandwidth of MR signal, then same coils can be used to receive both MR signal and PT signal at same time. However, one major remaining challenge PT Navigator signal would be serious interfered MR measurement, frequent coil tune and detune make PT Navigator signal interrupted and sharp distortions, and making the successive navigator signals ambiguous and inaccurate. To address these issues, we propose a component projection algorithm with a pre-scan module to maximally mitigate the interference of PT signal induced by sequence running.Methods
As shown in [Fig1], MR measurement can seriously interfere with the PT navigator signal by frequent coil tune and detune switches. To reduce the interference during sequence running, an additional waiting period and a dummy scan was performed before each normal MR measurement, and PT signals received during this two period were divided into two parts for analyzing the interferences induced by the MR measurement.Because the first part was only a waiting period and not affected by the measurement [Fig2-(1)], the principal component (on which most of the energy distributes) in the Eigen Space can be used to represent respiratory characteristics. However, in the second part(usually less than 0.5s in time), the respiratory-induced effect was too small to be noticed [Fig2-(1)], and the principal component in the Eigen Space was primarily determined by the interferences during sequence running. This analysis would identify three important factors: the principal component direction of the pure respiratory signal, the principal component direction and the Eigen Space of the interferences. Based on the analysis, to reduce interference during MR measurement, the acquired PT signals would proceed through the process with the following three procedures [Fig2-(2)],
1.PT signals (multi-channel) are orthogonally transformed into the interferences Eigen Space;
2.Discard the principle component;
3.Project the remaining components into the principal component of respiratory characteristics
Results
Phantom and volunteer experiments were performed on a 1.5T MAGNETOM Sempra scanner (Siemens Healthcare, Shenzhen, China) with a 13-channel body matrix coil, of which four channels were used to receive Both PT and MR signals. Sequences as HASTE, TSE-BLADE, and Turbo-FLASH were used for testing in this study. As shown in Figures 3, 4, and 5, the measurement interferences induced by the MR measurement were effectively mitigated with the proposed component projection algorithm.Conclusion
In this work, we proposed a component projection algorithm to mitigate the interference of PT Signal induced by the MR measurement. The preliminary study demonstrated that the technique can effectively reduce the interference during scanning. Clinical evaluations are still needed to validate its effectiveness and stability.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] P. Speier et al. PT-Nav: A Novel Respiratory Navigation Method for Continuous Acquisition Based on
Modulation of a Pilot Tone in the MR-Receiver. ESMRMB, 129:97–98, 2015. Doi:10.1007/s10334-015-0487-2.
Figures
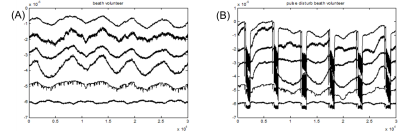
Fig1. (A) PT signals received with an array coil with no sequence running; (B) PT signals received with the same array coil during sequence running, distortions accrued since frequent coil tune and detune action
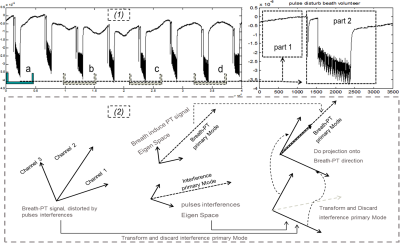
Fig2. (1) Data acquired before scanning are used for algorithm preparation (only one channel signal is displayed). The interference signal is assumed to keep the principle component direction, the algorithm calculated with (1-a) is effective for suppressing the following interferences (1,b,c or d); (2) is the flow chart of the component-projection algorithm, which is conducted in real-time.The interference were effectively suppressed by discarding the principle component of its Eigen Space.
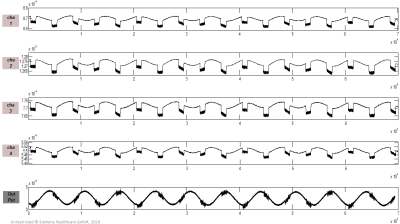
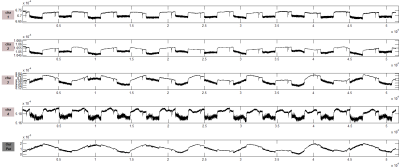
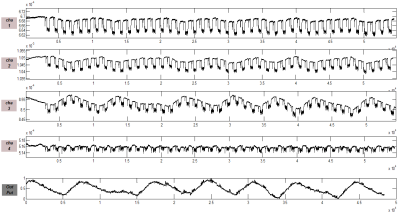
Fig5. 4-channel PT signals (with simulated breath signal) were seriously distorted during the volunteer experiments. The output PT navigator signal after the component projection algorithm is at the bottom of the figure; a 3D Turbo-FLASH protocol was used to generate interferences.