4124
MR guided blood-brain-barrier opening induced by focus ultrasound on Non-human primate1Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology,Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, China, 2The Shenzhen College of Advanced Technology, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, China, 3Research center for medical AI, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, China
Synopsis
Magnetic Resonance Imaging(MRI) is highly recommended for estimation of the feasibility and safety of BBB opening. We opened BBB in three different deep brain areas of an non-human primate with a single element ultrasound transducer working at 300kHz without detectable edema, hemorrhage and abnormal behavior. We found that the BBB in gray matter was easier to be disrupted than that in white matter, suggesting that for a local BBB opening in deep brain on non-human primate and human subjects, array transduces with relative large assemble surface are required to avoid the BBB disruption in cerebral cortex.
Purpose
Verifying the feasibility and safety of BBB opening on Non-human primate in deep brain induced by a single element focused ultrasound transducer based on MRI.Introduction
The blood-brain barrier(BBB )is a selectively permeable boundary structure between the systemic circulation and parenchyma of the central nervous system. BBB maintains the microenvironment stability and at the same time limiting the pharmaceutical passage during chemical therapy. Non-invasively BBB opening has great potential in treatment of central nervous system-related diseases, Magnetic Resonance Imaging(MRI) is highly recommended for estimation of the feasibility and safety of BBB opening.Studies demonstrated that low-power ultrasound pulses combined with microbubbles can temporarily opening BBB, which has been investigated in multiple species: prominently small rodent models with fewer studies in Non-human primate and human subjects[1].This work aimed to verify the feasibility and safety of BBB opening in multiple areas of deep brain on a macaque with MRI.Method
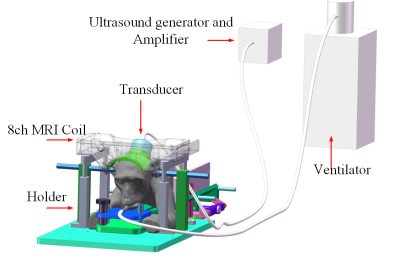
The experiment was under the approval of the Institutional Review Board. The monkey was anesthetized and maintained with a ventilator, lie in a holder on the MRI bed with respiratory and blood oxygen monitoring and warmed with hydrothermal blanket, as shown in Fig. 1. The macaque was first scanned with T1-weighted FSE sequence with parameters TR/TE = 700/13 ms; echo length:3; Average = 2; spatial resolution: 0.3×0.3×2.5mm . The sonication was then carried out by a single element spherical transducer of 300kHz with a bolus of microbubble (Sonovue, with 0.15ml/kg) intravenously injection from leg at the beginning of sonication. The depth of focus is 50mm and the theoretical geometric focus by -6dB attenuation is 10.8mm×1.4mm.The peak power of sonication was about 0.36Mpa(calibrated in water), with 1% duty cycle in 1 second interval, and the sonication lasted for 2 minutes[2.3]. After sonication, contrast enhanced agent Gd-DTPA was injected for T1-weighted MRI. T1-weighted FSE sequence was scanned using the protocol mentioned above. T2*-weighted GRE (TR/TE =600/16 ms; flip angle= 30°) and T2-weighted FSE(TR/TE = 5000/90 ms; flip angle= 145°,echo length:16 ) sequences were used for edema and hemorrhage detection [3-5]. A custom-built 8 channel head array for monkey was used for signal reception in this study[6].Three times of BBB opening experiments were carried out with the same ultrasound parameters at different zones (one in the middle of front lobe, the other two in right parietal lobe) of the same macaque. The interval between each experiment was more than two weeks.
Results
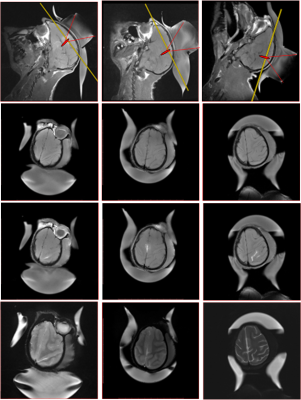
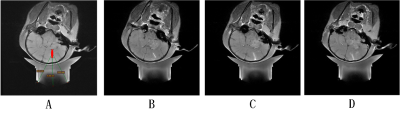
The BBB was safely opened in all three areas of the macaque with the same ultrasound parameters without hemorrhage, edema and behavioral abnormalities found in all three experiments. As shown in Fig. 2, significant signal enhancement on T1 weighted images after Gd-DTPA injection verifies the BBB opening and no detectable hemorrhage and edema on T2* weighted images and T2 weighted image.The threshold of BBB opening in gray matter area seems lower than that in white matter area.As shown in Fig.3, the focal of ultrasound targeted in white area in deep brain, while in three contiguous slices of T1 weighted MRI for one experiment, the contrast-enhanced signal can be found in each slice and is mainly distributed in gray matter area and sulcus gyrus, the pattern of enhanced pixels is consistent with that of sulcus gyrus rather than the focus. However, the signal enhancement in white matter area is very little.
Discussion
BBB opening is easily accessible and relatively safe by ultrasound combined with microbubble in our experiments,while quantitative evaluation and standardization which need further research are critical for clinical translation of this technology. Besides the safety verification of anatomical structures, the effects of BBB opening on neurological function need to be further studied for the safety estimation. The opening of BBB in a specific area of deep brain may require array transducer with large element assemble surface, which can make the ultrasonic energy sharply attenuated outside the focus area, so as to prevent the BBB opening on the path of sonic beaming.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NSFC of Grant No. 81527901References
1. Meng Y, Pople CB, Lea-Banks H, et al. Safety and efficacy of focused ultrasound induced blood-brain barrier opening, an integrative review of animal and human studies. Journal of controlled release : official journal of the Controlled Release Society 2019;309:25-36
2. Hynynen K, McDannold N, Vykhodtseva N, Jolesz FA. Noninvasive MR imaging-guided focal opening of the blood-brain barrier in rabbits. Radiology 2001;220(3):640-646.
3. McDannold N, Livingstone M, Top CB, Sutton J, Todd N, Vykhodtseva N. Preclinical evaluation of a low-frequency transcranial MRI-guided focused ultrasound system in a primate model. Phys Med Biol 2016;61(21):7664-7687.
4. Downs ME, Buch A, Sierra C, et al. Long-Term Safety of Repeated Blood-Brain Barrier Opening via Focused Ultrasound with Microbubbles in Non-Human Primates Performing a Cognitive Task (vol 10, e0125911, 2015). PloS one 2015;10(6).
5. Lipsman N, Meng Y, Bethune AJ, et al. Blood-brain barrier opening in Alzheimer's disease using MR-guided focused ultrasound. Nat Commun 2018;9.
6. Jo Lee, et al., Development of an 8channel head array for MRI guided monkey ultrasound stimulation, 27th ISMRM,2019, 5616
Figures