3852
BOLD Responses in the Rat Auditory Pathway Upon the Cessation of Sound1Champalimaud Research, Champalimaud Centre for the Unknown, Lisboa, Portugal
Synopsis
Auditory offset responses due to cessation of auditory stimuli have been previously described, suggesting the existence of a dedicated auditory offset pathway. These responses are of major importance in auditory perception, as temporal cues like sound duration can be crucial for sound identification and interpretation. Still, studies on the subject are scarce compared to classic auditory onset responses. Here, we investigate the BOLD dynamics upon the cessation of sound using BOLD fMRI in the rat. We find differences between Onset and Offset paradigms suggesting negative BOLD responses observed in the latter are likely due to an active process.
Introduction
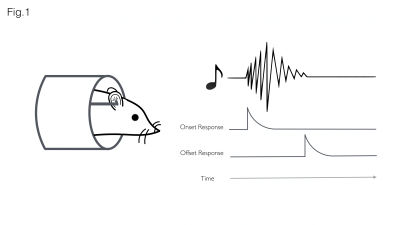
Accurate representation of changes in sound over time requires encoding of both sound onsets (appearances) and sound offsets (disappearances) by the auditory system (Fig. 1). Previous studies found that 10–30% of auditory neurons selectively respond to the termination of stimuli, suggesting the existence of a dedicated ‘offset pathway’ in the brain1. Despite the potential functional significance, off-responses have received little attention compared to on-responses, due to reduced prevalence2,3 saliency4, or because detecting the termination of a sound is more challenging than its initiation5.In recent years, fMRI has been used to characterize the auditory pathway in humans6, rats (tonotopy7,8, sound pressure level encoding9 or laterality10), and, very recently, mice11. The purpose of this study was to investigate whether fMRI could be used to investigate offset responses in the rat auditory pathway.
Methods
Animal experiments were preapproved by the institutional and national authorities and were carried out according to European Directive 2010/63.Animal preparation and auditory stimulation setup: Female adult Long Evans rats (n=5) (7-9 weeks, 250-350g) were kept under medetomidine anaesthesia while oxygen levels were kept at ~28% with the help of an oxygen sensor. Temperature and respiration rates were monitored and remained stable throughout the experiment. Custom made earpieces were inserted into both ears of the animal, projecting sound directly into the ear canal. The rest of the ear was occluded with Vaseline-doused cotton to isolate external sounds.
MRI experiments: All experiments were conducted on a Bruker BioSpec 9.4T (Bruker, Karlsruhe, Germany) equipped with an 86mm volume coil for transmittance and a 4-element array cryogenic coil (Bruker, Fallanden, Switzerland) for signal reception, and a gradient system capable of producing up to 660mT/m isotropically.
fMRI acquisition: A multislice GE-EPI was used for the fMRI acquisitions, with the following parameters: TR/TE=1000/15msec, in plane resolution=250×250µm2, slice thickness=1mm, 800 repetitions, 8 slices.
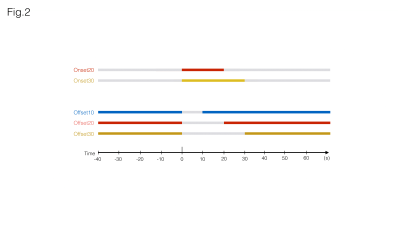
Auditory Stimulation: Broadband (5-45kHz) white noise at 80dB (calibrated to achieve a linear frequency response output) was presented monoaurally into the animal’s right ear. Five different paradigms (Fig.2) were selected for this study
“Onset20” – 20s sound ON, 90s sound OFF
“Onset30” – 30s sound ON, 90s sound OFF
“Offset10” – 90s sound ON, 10s sound OFF
“Offset20” – 90s sound ON, 20s sound OFF
“Offset30” – 90s sound ON, 30s sound OFF
For each experiment, five blocks of each paradigm were presented to the animals. All experiments were separated by a 5min resting period.
Data analysis: Image processing and data analysis were performed in MATLAB® (Mathworks, Natick, Massachusetts, EUA). Pre-processing steps included manual outlier detection (<0.5% of data), motion regression and detrending (polynomial fit of resting periods) for time-course analysis.
Results
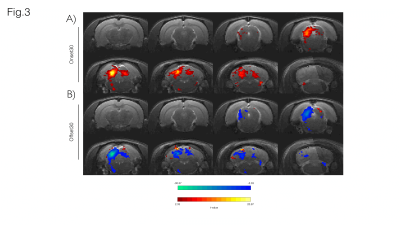
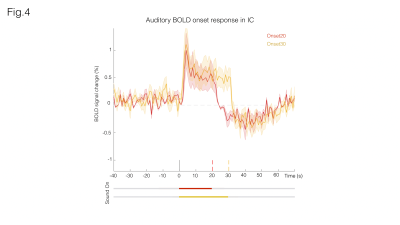
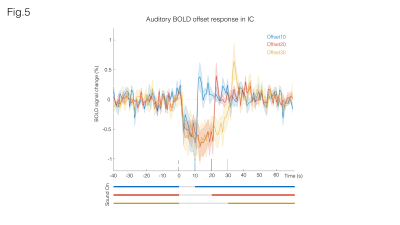
Fig. 3A shows sound onset responses, evidencing positive BOLD in the prominent auditory pathway regions. Fig. 3B shows maps acquired upon the cessation of sound, exhibiting negative BOLD responses with similar relative intensity between different structures.To further investigate these responses, we focus on signals from an ROI in the Inferior Colliculus (Figs.4/5). Onset responses (Fig.4) show an increase in BOLD signal peaking around 3s after the stimulus is presented, followed by a plateau that lasts for the duration of the sound. Upon the cessation of sound, a clear undershoot is observed. By contrast, responses to offset paradigms (Fig.5) evidence peak negative BOLD around 15s after the disappearance of the sound, with a consistent increase and return to “baseline” observed while no sound is present (particularly more noticeable in the Offset30 paradigm).
Discussion
Several mechanisms have been previously suggested for sound offset responses, from temporal filtering as a result of the excitation/inhibition interactions12,13,14, post- stimulus suppression15,16, to post-inhibitory rebound17 or facilitation18. Reported prevalence of offset responses in IC ranges from 9%19 to 70%18, with onset and offset responses tending to overlap20. By characterizing the BOLD dynamics upon the cessation of sound, we’ve presented a first step into the study of auditory offset responses via BOLD fMRI.The positive BOLD undershoot occurring at sound cessation in the onset experiments and the overall dynamics observed upon auditory offsets, which evidenced marked peaks with timings commensurate with the offset duration (Figs4/5), may suggest an active process is involved in offset BOLD response and that the decrease in signal is not only due to the absence of activation but also to some mechanism driving BOLD signal in the opposite direction – perhaps an inhibitory21 or negative feedback response22. Our findings will be extended soon to analysis of the entire pathway. Multimodal approaches may assist in further investigating this phenomenon.
It is important to note that despite our efforts to seal the ears entirely, the animals cannot be considered to be in a state of complete silence due to leakage of the inherent acquisition noise in the MRI. Silent pulse sequences24,25,26 may assist in deconfounding scanner noise effects in the future.
Conclusions
We have provided a first characterization (to our knowledge) of offset responses in the rat using BOLD fMRI. BOLD response differences between Onset and Offset paradigms likely suggest that the negative BOLD responses observed in the latter are likely due to an active process.Acknowledgements
This study was supported by funding from the European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme (Starting Grant, agreement No. 679058) and Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia (Portugal), project PD/BD/128297/2017. The authors acknowledge the vivarium of the Champalimaud Centre for the Unknow, a facility of CONGENTO which is a research infrastructure co-financed by Lisboa Regional Operational Programme (Lisboa 2020), under the PORTUGAL 2020 Partnership Agreement through the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) and Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia (Portugal), project LISBOA-01-0145-FEDER-022170.References
[1] Kopp-Scheinpflug, C., L. Sinclair,J., Jennifer F. Linden, J. (2018), When Sound Stops: Offset Responses in the Auditory System, Trends Neurosci., https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2018.08.009
[2] Phillips, D. P., Hall, S. E., & Boehnke, S. E. (2002). Central auditory onset responses, and temporal asymmetries in auditory perception. Hearing Research. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-5955(02)00393-3
[3] Young, E. D., & Brownell, W. E. (1976). Responses to tones and noise of single cells in dorsal cochlear nucleus of unanesthetized cats. Journal of Neurophysiology. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.1976.39.2.282
[4] Cavaco, S., & Lewicki, M. S. (2007). Statistical modeling of intrinsic structures in impacts sounds. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.2729368
[5] Sohoglu, E., & Chait, M. (2016). Neural dynamics of change detection in crowded acoustic scenes. NeuroImage. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.11.050
[6] Wessinger, C., Buonocore, M., Kussmaul, C., Mangun, G. (1997), Tonotopy in human auditory cortex examined with functional magnetic resonance imaging, Human Brain Mapping, https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0193(1997)5:1<18::AID-HBM3>3.0.CO;2-Q
[7] Cheung, M. M., Lau, C., Zhou, I. Y., Chan, K. C., Cheng, J. S., Zhang, J. W., … Wu, E. X. (2012). BOLD fMRI investigation of the rat auditory pathway and tonotopic organization. NeuroImage. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.01.087
[8] Cheung, M. M., Lau, C., Zhou, I. Y., Chan, K. C., Zhang, J. W., Fan, S. J., & Wu, E. X. (2012). High fidelity tonotopic mapping using swept source functional magnetic resonance imaging. NeuroImage. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.03.031
[9] Zhang, J. W., Lau, C., Cheng, J. S., Xing, K. K., Zhou, I. Y., Cheung, M. M., & Wu, E. X. (2013). Functional magnetic resonance imaging of sound pressure level encoding in the rat central auditory system. NeuroImage. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.09.069
[10] Lau, C., Zhang, J. W., Cheng, J. S., Zhou, I. Y., Cheung, M. M., & Wu, E. X. (2013). Noninvasive fMRI Investigation of Interaural Level Difference Processing in the Rat Auditory Subcortex. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0070706
[11] Blazquez Freches, G., Chavarrias, C., & Shemesh, N. (2018). BOLD-fMRI in the mouse auditory pathway. NeuroImage. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.10.027
[12] Grothe, B. (1994). Interaction of excitation and inhibition in processing of pure tone and amplitude-modulated stimuli in the medial superior olive of the mustached bat. Journal of Neurophysiology. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.1994.71.2.706
[13] Burger, R. M., & Pollak, G. D. (1998). Analysis of the role of inhibition in shaping responses to sinusoidally amplitude-modulated signals in the inferior colliculus. Journal of Neurophysiology. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.1998.80.4.1686
[14] Takahashi, H., Nakao, M., & Kaga, K. (2004). Cortical mapping of auditory-evoked offset responses in rats. NeuroReport. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.wnr.0000134848.63755.5c
[15] Kiang, N. Y., Pfeiffer, R. R., Warr, W. B., & Backus, A. S. (1965). Stimulus coding in the cochlear nucleus. Transactions of the American Otological Society. https://doi.org/10.1177/000348946507400216
[16] Kadner A., Berrebi, A.S. (2008), Encoding of temporal features of auditory stimuli in the medial nucleus of the trapezoid body and superior paraolivary nucleus of the rat., Neuroscience, DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.11.008
[17] Felix, R. A., Fridberger, A., Leijon, S., Berrebi, A. S., & Magnusson, A. K. (2011). Sound rhythms are encoded by postinhibitory rebound spiking in the superior paraolivary nucleus. Journal of Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2450-11.2011
[18] Akimov A., Egorova M, Ehret G. (2017), Spectral summation and facilitation in on- and off-responses for optimized representation of communication calls in mouse inferior colliculus. Eur. J. Neurosci., DOI: 10.1111/ejn.13488
[19] Kasai, M. et al. (2012) Distinct neural firing mechanisms to tonal stimuli offset in the inferior colliculus of mice in vivo. Neurosci. Res. 73, 224–237
[20] Xie, R., Gittelman, J. X., & Pollak, G. D. (2007). Rethinking tuning: In vivo whole-cell recordings of the inferior colliculus in awake bats. Journal of Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2865-07.2007
[21] Sten, S., Lundengård, K., Witt, S. T., Cedersund, G., Elinder, F., & Engström, M. (2017). Neural inhibition can explain negative BOLD responses: A mechanistic modelling and fMRI study. NeuroImage. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.07.002
[22] Klingner, C. M., Ebenau, K., Hasler, C., Brodoehl, S., Görlich, Y., & Witte, O. W. (2011). Influences of negative BOLD responses on positive BOLD responses. NeuroImage. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.01.028 [
23] Antunes, F. M., & Malmierca, M. S. (2014). An overview of stimulus-specific adaptation in the auditory thalamus. Brain Topography. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-013-0342-6
[24] Schmitter, S., Diesch, E., Amann, M., Kroll, A., Moayer, M., & Schad, L. R. (2008). Silent echo-planar imaging for auditory FMRI. Magnetic Resonance Materials in Physics, Biology and Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-008-0132-4
[25] Schwarzbauer, C., Davis, M. H., Rodd, J. M., & Johnsrude, I. (2006). Interleaved silent steady state (ISSS) imaging: A new sparse imaging method applied to auditory fMRI. NeuroImage. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.08.025
[26] Perrachione, T. K., & Ghosh, S. S. (2013). Optimized design and analysis of sparse-sampling fMRI experiments. Frontiers in Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2013.00055
Figures