3750
Optimized dimensionality reduction for parameter estimation in MR fingerprinting via deep learning1Center for Data Science, NYU, New York, NY, United States, 2Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences and Center for Data Science, New York University, New York, NY, United States, 3Center for Biomedical Imaging, Department of Radiology, New York University School of Medicine, Center for Advanced Imaging Innovation and Research (CAI2R), Department of Radiology, New York University School of Medicine, New York, New York, NY, United States
Synopsis
We propose a deep learning approach for MR fingerprinting that jointly learns a low-dimensional representation of the fingerprints and estimates biophysical parameters from this subspace. In contrast to SVD-based projections, which are agnostic to the estimation task, the learned subspace is optimized to maximize information content about the parameters of interest. Incorporating the learned basis functions in the forward imaging operator suppresses undersampling artifacts and increases computational efficiency.
Introduction
A key element of MR fingerprinting (MRF)1 is to heavily undersample each time frame with a different k-space trajectory in order to accelerate the acquisition and make it clinically feasible. As a result, back-projecting the data into image space results in significant undersampling artifacts1. However, the fingerprints corresponding to different relaxation times have been shown to be well approximated by their projection onto a fixed low-dimensional linear subspace2. Reconstructing the time evolution of the magnetization directly in such a low-dimensional subspace virtually removes aliasing artifacts, lifting this burden from the model fitting or dictionary matching3,4. In previous approaches2,3,4, the low-dimensional subspace was obtained through a singular-value decomposition (SVD) of a precomputed dictionary. This maximizes the SNR of the subspace images, but not necessarily their information content about the underlying biophysical parameters. We propose to instead learn the low-dimensional subspace by training a neural network to first project the data and then perform parameter estimation. Training the neural network end-to-end optimizes the subspace to extract information relevant for parameter estimation.Method
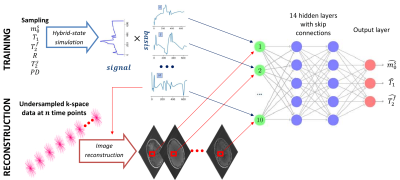
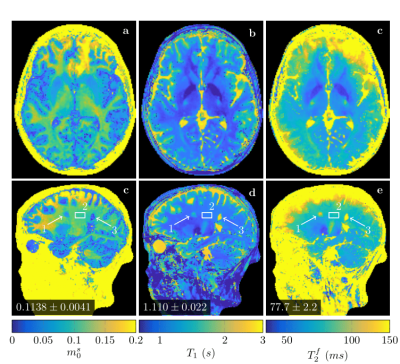
We test this concept at the example of quantitative magnetization transfer. We use the hybrid-state5 model and the pulse sequence described in Ref.6, which contains 666 TRs, each 4.5ms. We design a neural network that first projects a fingerprint onto a low-dimensional subspace, and then estimates the biophysical parameters from this subspace using 14 fully-connected layers (Figure 1). We train the network to output only 3 of our 6 model parameters, namely the fractional proton density of the semi-solid pool $$$m_0^s$$$, an apparent $$$T_1$$$, and $$$T_2^f$$$ of the free pool. As a result, the projection learned by the first layer is optimized to capture as much information as possible about those parameters. The training loss is defined as the sum of the mean squared errors of $$$m_0^s$$$ on a linear scale, and $$$T_1$$$ and $$$T_2^f$$$ on a log scale. The network weights (including the projection layer) are initialized at random. For comparison, we also trained a network with a projection onto a fixed low-dimensional subspace spanned by singular vectors of the training data, as well as a projection layer learned from an initialization with the singular vectors. The training data consists of simulated fingerprints with randomly chosen biophysical parameters and additive noise. We acquired in vivo brain data of a multiple sclerosis (MS) patient with approval of our IRB. The data has 1.2mm isotropic resolution and was acquired on a 3T Prisma scanner (Siemens, Germany). We measured 256 repetitions of the dynamic series, resulting in a total scan time of approx. 12min. We used a 3D-radial koosh-ball trajectory and incremented the polar angle and the azimuth of the spokes by multi-dimension golden means7. We reconstructed images in the learned subspace using BART8 with ESPIRiT coil-sensitivity maps9 and with locally-low rank regularization10,11.Results and Discussion
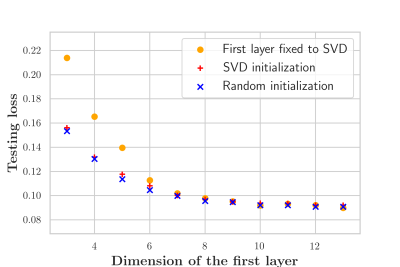
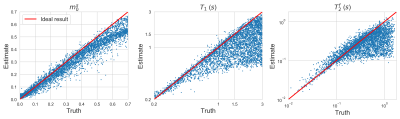
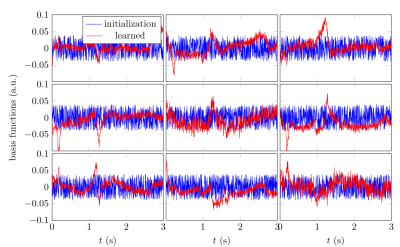
Figure 2 demonstrates that networks with a learned dimensionality reduction layer outperform networks in which this layer consists of singular vectors. While the difference of performance seems to be mainly relevant at small dimensions, the performance advantage might play a substantially bigger role for dictionaries of high rank, such as in the original MRF, which incorporates $$$B_0$$$2. The computational advantages of the proposed method are two-fold. First, learning the projection allows one to forgo the calculation of an SVD of a precomputed dictionary. Second, the memory requirements for the image reconstruction in BART scales with the square of the dimension. For the here presented data, five components require approximately 200GB, while 13 components require 1.4TB. Analyzing the error of the individual parameters (Figure 3), we observe good performance at the center of the parameter space, while we observe some biases towards high values of $$$m_0^s,T_1$$$, and $$$T_2^f$$$. As the pulse sequence was not optimized for such large values6, future work will need show to what degree this behavior originates from the acquisition and the neural network, respectively. We will further investigate if this can be improved with different network architectures and loss functions.Starting from a random initialization, we can see that the networks learn structured basis functions (Figure 4). The learned basis functions still contain residual random components, but preliminary tests indicate that those can be removed when using higher learning rates and longer training times (not shown here). As an in vivo test case, we used a network with 9 basis functions (Figure 4) to reconstruct data of an MS patient. The estimated values in a normal-appearing white matter region of interest align well with the literature12. Near the skull and the frontal sinus, $$$m_0^s$$$ and $$$T_2^f$$$ are overestimated due to $$$B_0$$$ inhomogeneities. Future work will include a correction of $$$B_0$$$13. We predict that this will increase the performance gap between the learned and SVD-based basis functions (Figure 2) as the corresponding dictionary is of considerably higher rank2,13.Conclusion
Our proposed approach enables data-driven dimensionality reduction of MR fingerprinting data by learning a low-dimensional subspace jointly with a neural network that performs parameter estimation. Incorporating the learned projection into the forward imaging operator3,14 reduces computational cost and removes undersampling artifacts. This departs from previous applications of machine learning to MR fingerprinting15,16,17,18, which heuristically treat these artifacts as noise.Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge Martin Uecker for help with the BART implementation. This research was supported by the grant NIH/NIBIB R21 EB027241. JA further acknowledges support from the Center for Advanced Imaging Innovation and Research, a NIBIB Biomedical Technology Resource Center (NIH P41 EB017183).References
1. Dan Ma, Vikas Gulani, Nicole Seiberlich, Kecheng Liu, Jeffrey L.Sunshine, Jeffrey L. Duerk, and Mark A. Griswold. Magnetic resonance fingerprinting. Nature, 495(7440):187–192, 2013. ISSN 0028-0836. doi: 10.1038/nature11971. URL http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v495/n7440/full/nature11971.html.
2. Debra; McGivney, Dan; Ma, Haris; Saybasili, Yun; Jiang, and Mark Griswold. Singular Value Decomposition for Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting in the Time Domain. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging, 33(12):2311–2322, 2014.
3. Jakob Assländer, Martijn A Cloos, Florian Knoll, Daniel K Sodickson, Jürgen Hennig, and Riccardo Lattanzi. Low rank alternating direction method of multipliers reconstruction for MR fingerprinting. Magn. Reson. Med., 79(1):83–96, jan 2018. ISSN 07403194. doi: 10.1002/mrm.26639. URL http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/mrm.26639.
4. Bo Zhao, Kawin Setsompop, Elfar Adalsteinsson, Borjan Gagoski, Huihui Ye, Dan Ma, Yun Jiang,P. Ellen Grant, Mark A. Griswold, and Lawrence L. Wald. Improved magnetic resonance fingerprinting reconstruction with low-rank and subspace modeling. Magn. Reson. Med., 79(2):933–942, 2018. ISSN 15222594. doi: 10.1002/mrm.26701.
5. Jakob Assländer, Dmitry S Novikov, Riccardo Lattanzi, Daniel K Sodickson, and Martijn A Cloos.Hybrid-state free precession in nuclear magnetic resonance. Nat. Com-mun. Phys., 2(1):73, dec 2019. ISSN 2399-3650. doi: 10.1038/s42005-019-0174-0. URL http://www.nature.com/articles/s42005-019-0174-0.
6. Jakob Assländer and Daniel K Sodickson. Quantitative Magnetization Transfer Imaging in the HybridState. In Proc. Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med. 28, page 1104, 2019.
7. Rachel W. Chan, Elizabeth A. Ramsay, Charles H. Cunningham, and Donald B. Plewes. Temporal stability of adaptive 3D radial MRI using multidimensional golden means. Magn. Reson. Med., 61(2):354–363,feb 2009. ISSN 07403194. doi: 10.1002/mrm.21837. URL http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/mrm.21837.
8. Martin Uecker, Frank Ong, Jonathan I Tamir, Dara Bahri, Patrick Virtue, Joseph Y Cheng, Tao Zhang,and Michael Lustig. Berkeley Advanced Reconstruction Toolbox. In Proc. Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med. 23, page 2802, 2015.
9. Martin Uecker, Peng Lai, Mark J. Murphy, Patrick Virtue, Michael Elad, John M. Pauly, Shreyas S.Vasanawala, and Michael Lustig. ESPIRiT - An eigenvalue approach to autocalibrating parallel MRI:Where SENSE meets GRAPPA. Magn. Reson. Med., 71(3):990–1001, 2014. ISSN 07403194. doi: 10.1002/mrm.24751.
10. Joshua D. Trzasko and Armando Manduca. Calibrationless parallel MRI using CLEAR. Conf. Rec.- Asilomar Conf. Signals, Syst. Comput., pages 75–79, 2011. ISSN 10586393. doi: 10.1109/AC-SSC.2011.6189958.
11. Tao Zhang, John M. Pauly, and Ives R. Levesque. Accelerating parameter mapping with a locally lowrank constraint. Magn. Reson. Med., 73(2):655–661, feb 2015. ISSN 07403194. doi: 10.1002/mrm.25161. URL http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/mrm.25161.
12. Richard D. Dortch, Ke Li, Daniel F. Gochberg, E. Brian Welch, Adrienne N. Dula, Ashish A. Tamhane,John C. Gore, and Seth A. Smith. Quantitative magnetization transfer imaging in human brain at 3T via selective inversion recovery. Magn. Reson. Med., 66(5):1346–1352, 2011. ISSN 07403194. doi: 10.1002/mrm.22928.
13. Vladimir A. Kobzar, Carlos Fernandez-Granda, and Jakob Assländer. Hybrid-State Free Precession forMeasuring Magnetic Resonance Relaxation Times in the Presence of B0 Inhomogeneities. In Proc. Intl.Soc. Mag. Reson. Med. 28, 2019.
14. Jonathan I. Tamir, Martin Uecker, Weitian Chen, Peng Lai, Marcus T. Alley, Shreyas S. Vasanawala,and Michael Lustig. T2 shuffling: Sharp, multicontrast, volumetric fast spin-echo imaging. Magn. Reson.Med., 77(1):180–195, 2017. ISSN 15222594. doi: 10.1002/mrm.26102
15. Elisabeth Hoppe, Gregor Körzdörfer, Tobias Würfl, Jens Wetzl, Felix Lugauer, Josef Pfeuffer, andAndreas Maier. Deep learning for magnetic resonance fingerprinting: A new approach for predictingquantitative parameter values from time series.Studies in health technology and informatics, 243:202–206, 01 2017.
16. Zhenghan Fang, Yong Chen, Mingxia Liu, Yiqiang Zhan, and Weili Lin.Deep Learning for Fast andSpatially-Constrained Tissue Quantification from Highly-Undersampled Data in Magnetic ResonanceFingerprinting (MRF): 9th International Workshop, MLMI 2018, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI2018, Granada, Spain, September 16, 2018, Proceedings, volume 11046, pages 398–405. 09 2018. ISBN978-3-030-00918-2. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-00919-946.
17. Marco Barbieri, Leonardo Brizi, Enrico Giampieri, Francesco Solera, Gastone Castellani, Claudia Testa, andDaniel Remondini. Circumventing the curse of dimensionality in magnetic resonance fingerprinting througha deep learning approach, 11 2018.
18. Ouri Cohen, Bo Zhu, and Matthew S. Rosen. MR fingerprinting Deep RecOnstruction NEtwork (DRONE). Magn. Reson. Med., 80(3):885–894, 2018. ISSN 15222594. doi: 10.1002/mrm.27198.
Figures