3487
Comparing the performance of optimized support vector machine model in predicting efficacy of chemo-radiotherapy for advanced rectal cancer with and without a paired-difference up-sampling strategy under small sample size
Jie Kuang1, QingLei Shi2, Gaofeng Shi1, Xu Yan3, and LI Yang1
1The Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, China, 2Siemens Healthcare, MR Scientific Marketing, Beijing, China, 3Siemens Healthcare, MR Scientific Marketing, Shanghai, China
1The Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, China, 2Siemens Healthcare, MR Scientific Marketing, Beijing, China, 3Siemens Healthcare, MR Scientific Marketing, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
In this study, we evaluated the effect of paired-difference analysis (PDA) up-sampling strategy on the performance of optimized support vector machine model (SVM) in predicting efficacy of chemo-radiotherapy for advanced rectal cancer. A higher accuracy and robustness was gained for the model adopted the PDA method in predicting the efficacy of treatment, which means that the PDA method can be used as an up-sampling strategy in improving the performance of some machine learning models.
Purpose
Due to the difficulties of collecting patient data in clinical situations, we adopted a paired-difference analysis (PDA) method as an up-sampling strategy, and intended to evaluate the effect of this method in improving the accuracy and robustness of the model in predicting the treatment effect of non-metastatic locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC) treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy-radiation therapy based on radiomics signatures coming from apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) maps.Materials and Methods
This retrospective study included 55 patients (male 32; female11; age range: 28 to 77 years; mean age: 56.77±12.66) with non-metastatic LARC (adenocarcinoma 38, including 6 cases of poorly differentiation, 30 cases of moderately differentiation, 2 cases of highly differentiation, 4 cases of adenocarcinoma with a small amount of mucinous adenocarcinoma, and 1 case of mucinous adenocarcinoma; pathological stage: low grade 30 cases, high grade 13 cases) scanned from March 2017 to May 2018. All patients were received concurrent chemoradiotherapy and surgical treatment, with an interval range of 49 to 54 days (mean: 51 days), and all underwent MR examinations at a 3T scanner (MAGNETOM Skyra, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) before and after chemo-radiotherapy treatment within one month. According to curative effect, patients were divided into treatment effective group (TRG0 6 cases; TRG1 8 cases; TRG2 19 cases) and treatment ineffective group (TRG3 10 cases). The inclusion criteria of the study cohort were as follows: (a) MRI scan was performed within 1 week before CRT and within 1-2 weeks after CRT, and the scanned sequence included high-resolution T2WI and DWI (b-values 50 and 800); (b) postoperative pathological data and tumor regression level (TRG) record were complete.Radiomics signatures were extracted using an open source tool named Pyradiomics (https://pyradiomics.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html). In order to evaluate the effect of paired-difference analysis (PDA) up-sampling strategy on model, the performance of the model were compared under the condition of with and without PDA method. Considering the characteristics of different machine learning models, a support vector machine (SVM) was used as the classifier, which is an effective and robust classifier to build the model. The kernel function has the ability to map the features into a higher dimension to search the hyper-plane for separating the cases with different labels. Here we used the linear kernel function because it was easier to explain the coefficients of the features for the final model. After comparing the diagnostic performance of models trained with different methods in normalization, dimensional reduction, and features selection, a normal-0-center unit method, a pearson correlation coefficients (PCC), and an recursive feature elimination (RFE) were used for the model with PDA, and a normal-0-center unit, a principle component analysis (PCA) and a RFE were used for the model without PDA in data preparation.
The performance of the model was evaluated using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis. The area under the ROC curve (AUC) was calculated for quantification. The accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV) were also calculated. All above processes were implemented with FeAture Explorer (FAE, v0.2.5, https://github.com/salan668/FAE) on Python (3.6.8, https://www.python.org/).
Result
We found that the model with and without PDA method can get the highest AUC based on 8 and 16 features on the validation and testing data set. The AUC and the accuracy are (0.819 vs 0.534) and (0.891 vs 0.800), respectively. In this point, The AUC and the accuracy of the model achieve (0.934 vs 0.767) and (0.984 vs 0.769) on testing data set. The sensitivity and specificity were (0.800 vs 0.700) and (1.000 vs 1.000) on the testing data, with (0.9831 vs 0.500) and (1.000 vs 1.000) for the NPV and PPV. The selected features were shown in Table 1, and the ROC curve was shown in Figure 1.Discussions
In clinical situations, considering the difficulties of data collection, a method of up-sampling is very important. In this study, we proposed a paired-difference analysis (PDA) method of up-sampling, which can achieve an effect of large sample size. In this method, firstly, six patients with typical effective effect (TRG0 6 cases) and three patients with typical ineffective effect were selected and regarded as templates. Then, differences were done between each template and the other patients among each group. Finally, these differences of radiomics signatures (paired-case) were used to train and test the diagnostic ability of the trained model. Through PDA analysis, we gained 147 paired-case differences as the training data set (13/134 = positive/negative) and 63 paired-case differences as the independent testing data set (5/58 = positive/negative). Through comparing the performance of the SVM with and without PDA method, we evaluated the feasibility of this method in improving the accuracy and robustness of the model via the effect of up-sampling and improving the generalization ability of the model. To prove the performance of the model further, we applied cross validation with 5-folder on the data set.Conclusions
Under the conditions of small sample size, the PDA method can be used as an up-sampling strategy that can improve the accuracy and robustness of the model in predicting the treatment effect of non-metastatic locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC) treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy-radiation therapy based on radiomics signatures coming from apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) maps.Acknowledgements
References
Figures
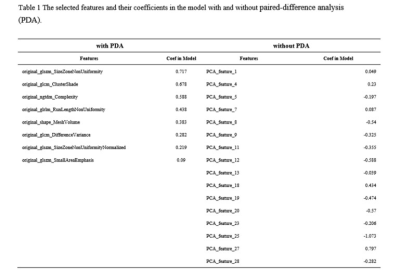
Table 1 The selected features and
their coefficients in the model with and without paired-difference analysis (PDA).
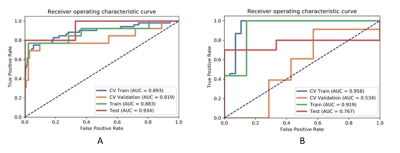
Figure
1 The
AUC values of ROC on CV training, CV validation, training and testing data with
(A) and without (B) PDA method. The AUC values of the model with PDA method
demonstrated better performance. CV train: average of k-1 folder of training
data set in k-folder cross validation; CV validation: the average of k-1 folder
of validation data set in k-folder cross validation. PDA: paired-difference
analysis.
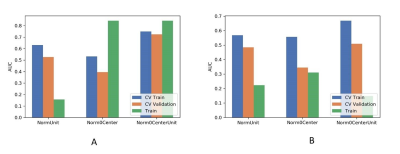
Figure
2 Effects of three normalization method on CV training and CV validation data,
and the corresponding AUCs with (A) and without (B) PDA method. CV train: the
average of k-1 folder of training data set in k-folder cross validation; CV
validation: the average of k-1 folder of validation data set in k-folder cross
validation. PDA: paired-difference analysis.
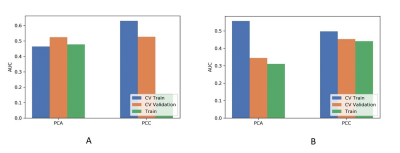
Figure
3 Effects of two dimensional reduction methods on CV training and CV validation
data, and the corresponding AUCs with (A) and without (B) PDA method. CV train:
the average of k-1 folder of training data set in k-folder cross validation; CV
validation: the average of k-1 folder of validation data set in k-folder cross
validation. PDA: paired-difference analysis.
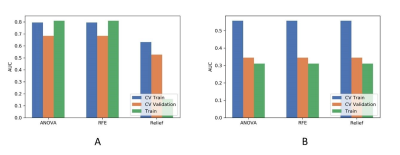
Figure
4 Effects of three feature selective methods on CV training and CV validation
data, and the corresponding AUCs with (A) and without (B) PDA method. CV train:
the average of k-1 folder of training data set in k-folder cross validation; CV
validation: the average of k-1 folder of validation data set in k-folder cross
validation. PDA: paired-difference analysis.
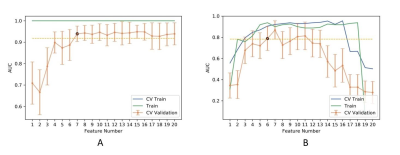
Figure
5 The number of selected features and the corresponding AUCs on CV training and
CV validation, and all training data with (A) and without (B) PDA method. CV
train: the average of k-1 folder of training data set in k-folder cross
validation; CV validation: the average of k-1 folder of validation data set in
k-folder cross validation. PDA: paired-difference analysis.
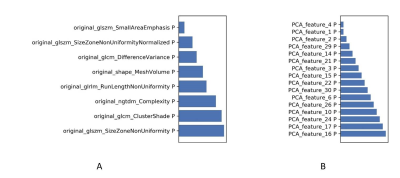
Figure
6 The selected features and their contributions on the model with (A) and
without (B) PDA method. PDA: paired-difference analysis.