3423
Improved dual inversion recovery T2-weighted black-blood image on myocardial MRI using zoomed technique1Tokyo Metropolitan Police Hospital, Nakano, Japan, 2Philips healthcare, Tokyo, Japan, minato, Japan
Synopsis
The conventional Dual Inversion Recovery T2-weighted Black Blood (c-DIR-BB) on myocardial MRI is useful for the clinical diagnosis. One of the problems of c-DIR-BB is aliasing artifact, resulting in degradation of image quality. The zoomed method for improved aliasing artifact, orthogonal selection (i.e. phase / slice direction) excites to suppress tissue signals outside with a smaller FOV in phase encoding direction. Hence the DIR-BB using zoomed methods was improved image quality by orthogonal select excitation RF pulse.
Introduction
Conventional Dual Inversion Recovery T2-weighted Black Blood (c-DIR-BB) on myocardia MRI is useful for the clinical evaluation of myocardial edema, myocardial infarction and cardiomyopathy. Aliasing artifact on c-DIR-BB is concerned by the heart orientation and physique, and the expanding field of view (FOV) is able to suppress for aliasing artifact1-2. However, this method is often cause to extend scan time and degrade image quality with breath-hold failure. As a method for improved aliasing artifact, orthogonal selection (i.e. phase / slice direction) excites to suppress tissue signals outside with a smaller FOV in phase encoding direction3-5. This method zoomed-DIR-BB(z-DIR-BB).Purpose
In this study, we estimated the aliasing artifact to compare between the c-DIR-BB and z-DIR-BB.Methods
Using a 3.0Tesla (T) achieva clinical MR scanner R 5.6.1 (Philips medical systems) 32ch cardiac torso coil. The common following parameter: FOV = 250×250~64 (minimum), aquision = cartesian, scan mode = M2D, profile order = linear, slice thickness (mm)/gap = 8.0/0.8, ACQvoxel MPS(mm)=1.25×1.65, TR(ms) = 2beats, flip angle=90, TE(ms) = 80, Echo space=6.8~7.9, SENSE factor = 2.0, NSA = 1, scantime(s) = 10-15 (depend on heart beats), phase-encoding = AP, the different parameters both c-and z-DIR-BB was fold-over-suppression (rest: c-DIR-BB, zoom: z-DIR-BB).On the experiment1 (Ex1), the phantom image of c- and z-DIR-BB was obtained by the variable FOV (25-100%) for the phase direction. It was evaluated quantity of aliasing artifacts using line profile and coefficient of variation (CV) by measured from signal intensity (SI)and standard diviation.On the experiment2 (Ex2), seven health volunteers underwent myocardial MRI of the c- and z-DIR-BB images. The contrast ratio (CR) of the volunteer images was calculated by measured from the SI on four segments (anterior, inferior, septum, lateral) of the myocardium and left ventricle blood(CRmyocardial/blood).Results
On the Ex1, Line profile of c-DIR-BB showed clearly signal change at small-FOV. However, z-DIR-BB showed almost no change for all FOVs. CV changed significantly c-DIR-BB for small FOV. However, z-DIR-BB showed almost no change for all FOVs. On the Ex2, Each CRmyocardial/bloodfor four segments was equivalent.Discussion
c-DIR-BB was adopted an 90-and 180 degree pulse for slice-direction.Therefore, aliasing artifact occurred with signal from outside for small FOV. Zoom-DIR-BB was adopted an orthogonal RF pulses with 90- with the slice-selection gradient for phase direction and 180- with slice-selection gradient for slice-direction. Therefore, z-DIR-BB was possible to improve aliasing artifact than c-DIR-BB for small FOV. Furthermore, this arrangement RF pulse excited only in the phase encoding step range of the imaging section, possible to suppress of signals outside on the FOV.Conclusion
We suggested zoom-DIR-BB was possible to improve the image quality (i.e. aliasing artifact ) without extend scan time.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Pedro F Ferreira,Cardiovascular magnetic resonance artefacts:Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance2013,15:41
2.Sarah A. Peel, MS, Accelerated Aortic Imaging Using Small Field of View Imaging and Electrocardiogram-Triggered Quadruple Inversion Recovery Magnetization Preparation journal of magnetic resonance imaging 34:1176–1183 (2011)
3.Hussain T, Clough RE, Cecelja M, et al. Zoom Imaging for Rapid Aortic Vessel Wall Imaging and Cardiovascular Risk AssessmentJ Magn Reson Imaging 2011;34:279–285.
4.Randolph M setser, High resolution imaging of the right ventricle using ZOOM MRI Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance volume 12, Article number: M8 (2010)
5.Raja Muthu Pillai , Navigator guided high-resolution single-shot black-blood (BB) TSE images using zoom and sensitivity encoding (sense) on a 32 channel RF system.Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance volume 12, Article number: O73 (2010)
Figures
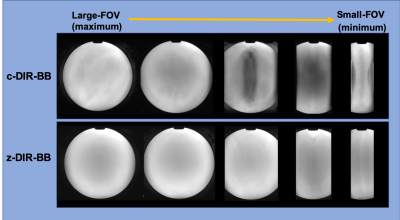
Figure1.The phantom study images. The c-DIR-BB occurred to aliasing artifact with signal from outside by small FOV.However, the z-DIR-BB was improved image quality without aliasing artifact.
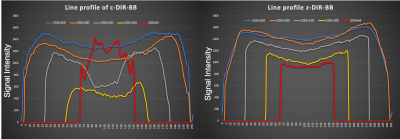
Figure2.Line profile of c- and z-DIR-BB.c-DIR-BB showed clearly signal change at small-FOV. However, z-DIR-BB showed almost no change for all FOVs.
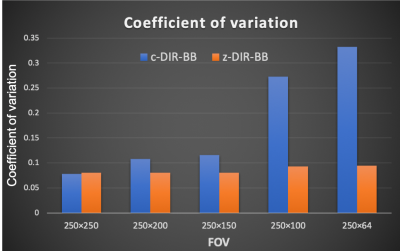
Figure 3.The graph of Coefficient of variation for phantom.CV changed significantly c-DIR-BB for small FOV. However, z-DIR-BB showed almost no change for all FOVs.
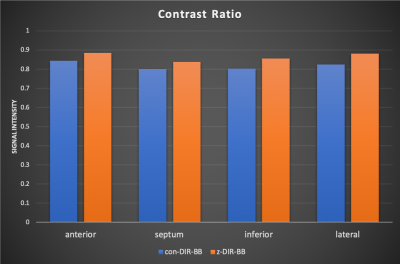
Figure 4.The graph of contrast ratio(CR).The CR was calculated by measured from the SI on four segments (anterior, inferior, septum, lateral) of the myocardium and left ventricle blood.Each CRmyocardial/blood for four segments was equivalent.
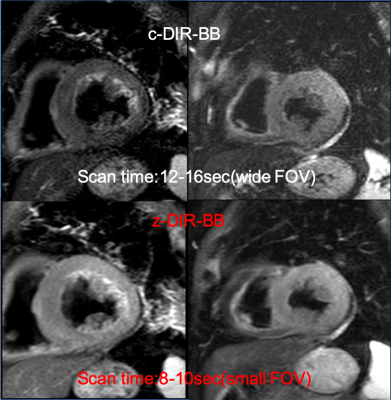
Figure 5. The Healthy volunteer images of c- and z-DIR-BB.The c-DIR-BB of expanding FOV was cause to extend scan time.However,The z-DIR-BB was possible to improve the image quality without extend scan time for small FOV.