3410
Improving 7T Cervical Spine (C-spine) MRI using the Uniform Combined Reconstruction (UNICORN) Algorithm1Siemens Medical Solutions USA, Inc., Rochester, MN, United States, 2Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, United States, 3Siemens Healthcare AG, Zurich, Switzerland, 4SCMI, Swiss Center for Musculoskeletal Imaging, Zurich, Switzerland, 5Department of Radiology, Balgrist University Hospital, University of Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland
Synopsis
Ultra-high field (UHF) 7T MRI provides high spatial resolution with significantly better signal-to-noise ratio compared to 3T and C-spine imaging at 7T is being pursued at a few research sites across the globe. MRI of the C-spine at 7T is challenging due to multiple factors. Recently, an algorithm ‘Uniform Combined Reconstruction’ (UNICORN) was used to correct receive-coil intensity inhomogeneity and improve the uniformity and overall image quality of 7T knee MRI. In this work, we present preliminary results from the application of UNICORN to C-spine imaging and demonstrate the utility of UNICORN in improving uniformity of C-spine MRI at 7T.
Introduction
MRI has become the preferred method to evaluate cervical spine (C-spine) disorders such as degenerative changes, disc herniation, spinal cord affection or tumor. The anatomy of C-spine includes subtle structural features that can be better visualized using high spatial resolution MRI (avoiding partial volume effects). Ultra-high field (UHF) 7T MRI provides high spatial resolution with significantly better signal-to-noise ratio compared to 3T and C-spine imaging at 7T is being pursued at a few research sites across the globe (1,2). MRI of the C-spine at 7T is challenging due to multiple factors including transmit (B1) non-uniformity, inhomogeneous receive-coil sensitivity profile, main magnetic field (B0) inhomogeneity and the complexity in optimizing transmit-Receive (Tx/Rx) RF coils for C-spine imaging at UHF (2,3). Parallel transmit (PTx) methodologies, specialized B0 shimming approaches and novel RF pulses are being used to address some of the challenges in obtaining uniform 7T C-spine imaging (2). Recently, an algorithm ‘Uniform Combined Reconstruction’ (UNICORN) was used to correct receive-coil intensity inhomogeneity and improve the uniformity and overall image quality of 7T knee MRI (4). In this work, we present preliminary results from the application of UNICORN to C-spine imaging and demonstrate the utility of UNICORN in improving uniformity of C-spine MRI at 7T.Methods
Imaging was performed on 2 subjects using a custom C-spine Tx/Rx coil (a single-channel transmit, 8-channel phased-array receive coil, Rapid Biomedical, Rimpar, Germany) at 7T on a MAGNETOM Terra (Siemens Healthineers, Erlangen, Germany) under the guidelines of an Institutional Review Board.Proton density (PD)- and T1-weighted MR images were acquired using a 2D turbo-spin-echo (TSE) sequence. The sequence parameters for PD-weighted TSE imaging were: in-plane reconstructed voxel size=0.29×0.29mm2 (in-plane acquisition voxel size= 0.58×0.58mm2), field-of-view=175mm×185mm, slice-thickness= 2.5mm, slice-gap=0.375mm (15% distance factor), TE=36ms, TR= 4000ms, receive-BW=195Hz/pixel, echo-train length= 4 echoes and refocusing flip-angle= 180°. The sequence parameters for T1-weighted TSE imaging were: in-plane reconstructed voxel size=0.29×0.29mm2 (in-plane acquisition voxel size= 0.58×0.58mm2), field-of-view=175mm×185mm, slice-thickness= 2.5mm, slice-gap=0.375mm (15% distance factor), TE=9ms, TR= 1000ms, receive-BW=195Hz/pixel, echo-train length= 3 echoes and refocusing flip-angle= 180°.
The series acquired (imaged volumes) were retrospectively processed using a prototype implementation of the UNICORN algorithm. The uniformity of the images before and after UNICORN correction was compared across different slices of the imaging volume using same window-width and window-level visualization. Additionally, the histograms of the intensities in the complete 3D volume were compared before and after UNICORN correction was applied.
Results and Discussion
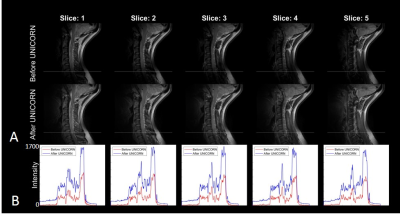
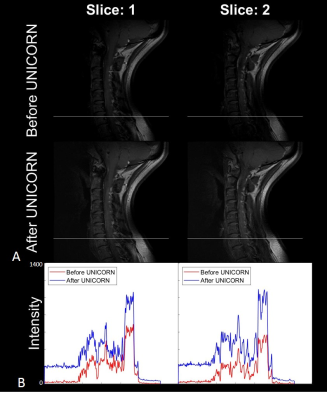
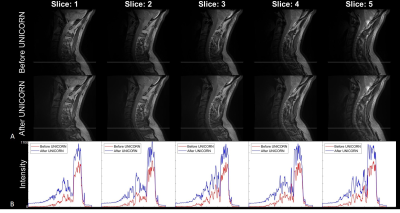
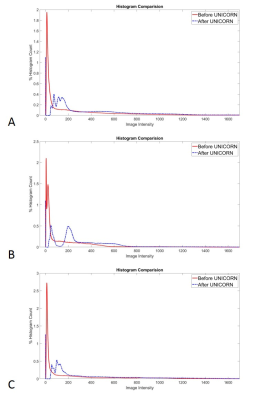
Figures 1 to 3 demonstrate the utility of UNICORN correction in improving signal uniformity of proton density (PD) weighted and T1 weighted C-spine MRI at 7T in 2 different subjects. Intensity profiles of the MR images across the inferior region of the field-of-view shown before and after UNICORN correction demonstrate the improvement in intensity uniformity achieved by UNICORN.Figure 4 shows the comparison of histograms of MRI intensity before and after UNICORN normalization for the complete image volumes shown in the Figures 1 to 3, respectively. Improved contrast (wider width of the histogram around the mode of the foreground) and improved luminosity (higher histogram counts at higher intensity values) are demonstrated by the histograms of the UNICORN images.
Conclusion
UNICORN has the potential to improve uniformity of C-spine MRI at 7T.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Sigmund EE, Suero GA, Hu C, Mcgorty K, Sodickson DK, Wiggins GC, et al. High-resolution human cervical spinal cord imaging at 7T. NMR Biomed. 2012 Jul;25(7):891–9.
2. Barry RL, Vannesjo SJ, By S, Gore JC, Smith SA. Spinal cord MRI at 7T. Neuroimage. 2018;
3. Zhao W, Cohen-Adad J, Polimeni JR, Keil B, Guerin B, Setsompop K, et al. Nineteen-channel receive array and four-channel transmit array coil for cervical spinal cord imaging at 7T. Magn Reson Med. 2014;72(1):291–300.
4. Chebrolu VV, Kollasch PD, Deshpande V, Grinstead J, Howe BM, Frick MA, et al. Uniform combined reconstruction of multichannel 7T knee MRI receive coil data without the use of a reference scan. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2019; doi: 10.1002/jmri.26691
Figures