3405
Mitigating artifacts from eye-motion in interleaved multi-shot DWI1Philips Healthcare, Bangalore, India, 2Philips Healthcare, Tokyo, Japan
Synopsis
A novel approach for mitigating artifacts from localized motion of the eye, during interleaved multi-shot diffusion weighted imaging, is presented. A 2D cylindrical spatial saturation pulse is used to suppress signal from the orbit region, thereby significantly suppressing the ghost artifacts from eye movement in low b-value images. The saturation being localized to the orbit region does not influence the surrounding tissues. Placement of such a cylindrical pulse on the orbit region is relatively straight forward. In addition, the total scan time is not significantly affected by the cylindrical pulse saturation.
Introduction
Diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) is one of the primary techniques used in MRI for evaluating tissue damage in-vivo. Single-shot echo-planar imaging (SSH EPI) methods are typically used for acquiring diffusion weighted images, due to short acquisition times. SSH EPI methods, however, suffer from geometric distortion, adversely affecting their diagnostic quality. For distortion, while shorter readout times help in reducing distortion in EPI, this in-turn limits the spatial resolution that can be achieved. To overcome this, multi-shot imaging techniques were introduced which allow collection of the required k-space in multiple segments, with each segment having a short readout time. However, with data acquisition in multiple shots, data consistency from shot-to-shot becomes an important parameter to address[1], for obtaining artifact free images. Navigator based methods[2] or self navigated methods[3] have been used to correct for shot-to-shot variations arising from bulk patient motion. However, effects of involuntary/voluntary motion of local tissue between the shots, like that of the eye, can lead to anatomy-specific data inconsistencies, leading to ghost artifacts in interleaved multi-shot techniques. This is especially true in low diffusion weighting (low b-value) images where there is sufficient signal from the vitreous humor of the eye. Data consistency based reconstruction approaches may help in mitigating artifacts related to localized tissue motion[4]. However, this can lead to SNR penalty. Conversely, spatial saturation of the signal from the eye could help in mitigating ghosts from the eye[5]. However, due to the rectilinear nature of the spatial 1D saturation bands, it could suppress signal from other regions due to the curvature of the brain. Hence, a more localized spatial saturation of the orbit region, using a two dimensional (2D) cylindrical spatial saturation pulse[6], was evaluated for artifact mitigation from eye-motion in an interleaved multi-shot DWI technique.Materials and Methods
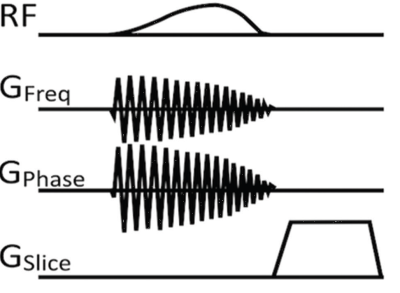
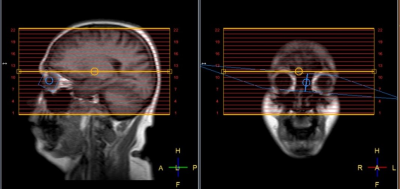
Two adult healthy volunteers underwent neuroimaging on a Philips 1.5T Prodiva system after obtaining an informed consent. The volunteers were instructed to move their eyes intermittently during the scan session. Data was acquired using a navigator based interleaved multi-shot DWI sequence without and with cylindrical spatial saturation of the eye-balls. Figure 1 shows the scheme of 2D cylindrical spatial saturation method. The cylindrical spatial saturation is based on a 2D spiral radio-frequency pulse with gradients in both frequency and phase directions and a spoiler gradient in the slice direction that enables a cylindrical saturation along the right-left anatomical direction. The cylindrical spatial saturation pulse is played between the fat suppression pre-pulse and the excitation of each shot. Following imaging parameters were used: TR/ TRwithSaturation/TE – 4063/4787/105 ms, 2 shot, 1.5 x 1.5 x 5 mm3, b=0 and 1000, 22 slices, scan-time -1:38 min, scan-timewithSaturation -1:55 min. A 2D cylindrical spatial saturation pulse (9.2ms duration) with diameter of 25mm and flip angle 90o was used in the orbit region. Figure 2 shows the placement of the cylindrical pulse on the eye-balls. Image quality was assessed for artifacts in both acquisitions.Results
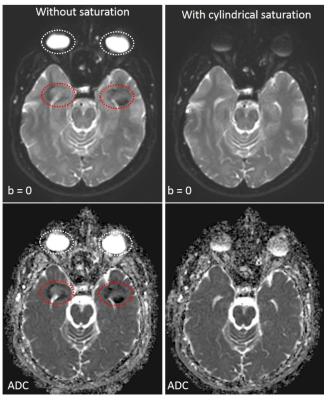
Ghost artifacts from eye-movement were clearly visualized in multi-shot DWI without cylindrical spatial saturation of the eyeballs. The ghosts were significantly suppressed using 2D cylindrical spatial saturation (Figure 3).Discussion
In this work we found that a 2D cylindrical spatial saturation pulse successfully mitigates the artifacts from eye-movement in interleaved multi-shot diffusion weighted imaging of brain. The 2D cylindrical pulse does not cause any significant impact on the scan time. Since the saturation is localized to the orbit region, this solution does not influence the other tissue regions, thereby the image quality remains unchanged relative to a no-motion case. Placement of such a 2D cylindrical saturation pulse is relatively straight forward compared to the spatial 1D saturation bands. Even though the profile of the cylindrical spatial saturation is susceptible to magnetic field inhomogeneity, the pulse does not seem to negatively affect the image quality. The usage of the 2D cylindrical spatial saturation pulse for interleaved multi-shot diffusion may be extended to other anatomies like suppression of cardiac pulsation in breast diffusion or urinary bladder motion in prostate diffusion.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Wu W, Miller KL. Image formation in diffusion MRI: A review of recent technical developments. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2017 Sep;46(3):646-662.
[2] Jeong HK, Gore JC, Anderson AW. High-resolution human diffusion tensor imaging using 2-D navigated multishot SENSE EPI at 7 T. Magn Reson Med. 2013 Mar1;69(3):793-802.
[3] Chen NK, Guidon A, Chang HC, Song AW. A robust multi-shot scan strategy for high resolution diffusion weighted MRI enabled by multiplexed sensitivity-encoding (MUSE). Neuroimage. 2013 May 15;72:41-7.
[4] Winkelmann R, Börnert P, Dössel O. Ghost artifact removal using a parallel imaging approach. Magn Reson Med. 2005 Oct;54(4):1002-9.
[5] Chou MC, Wang CY, Liu HS, Chung HW, Chen CY. Pseudolesions arising from unfolding artifacts in diffusion imaging with use of parallel acquisition: origin and remedies. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007 Jun-Jul;28(6):1099-101.
[6] Yoneyama M, Nakamura M, Ozawa Y, Obara M, Okuaki T, Tatsuno S, Sashi R, Sawano S, Van Cauteren M. Cylindrical Inversion Pulse for the Reduction of Cardiac Motion Artifacts in Contrast-enhanced Breast MRI. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2018 Jan10;17(1):80-85.
Figures