3234
High-Efficient Metabolic Nano-Theranostics for MR Imaging and Cancer Therapy1Radiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China, 2Electronic information engineering, University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing, China, 3GE Healthcare, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
In order to realize the nanotheranostics and reduce the toxicity of nanotheranostics agents to healthy tissues/organs, we constructed a novel nanotheranostics agents (Gd-DTPA-CS@β-CD@Dox) for MR imaging and Cancer treatment. Renal-clearable nanocomposites made it possible to overcome the long-term toxicity by accumulation in healthy living body. High uptake of the as-synthesized Gd-DTPA-CS@β-CD@Dox was achieved due to the longer blood circulation time. Moreover, the nanotheranostics agents possessed excellent performance in MRI. The nanotheranostics agents demonstrated a PH sensitive drug release. Such functional nanotheranostics agents applicable in highly integrated bio-modal imaging and multiple therapeutic functions may have great prospects in clinical practice.
Introduction
The simultaneous diagnosis and treatment of cancer remain one of the biggest challenges in the clinic.1-2 The rapid development of nanomedicine brings new hope for the integration of cancer diagnosis and treatment. Researchers modify materials to construct stable, efficient and safe functional nanocomposites.3 And then, functional nanocomposites combined with anticancer drugs and highly accurate cancer diagnostic probes are applied to diagnosis and treatment of cancer.4 Therefore, multi-functional nanoparticles drug delivery systems have become a global research topic. When the multifunctional nanocomposites with imaging and treatment are delivered to cancer cells, they need to work in a very complex environment and overcome biological barrier in vivo. Small molecular drugs or small-sized nano-drugs can be easily cleared out of the body by kidney filtration in the blood circulation, difficult to effectively enrich the tumor site.5 However, the time of the blood circulation time for the drug can be prolonged by the appropriate surface modification of nanoparticles with appropriate size. Meanwhile, the tissue has high uptake of diagnostic and therapeutic reagents.3-5Methods
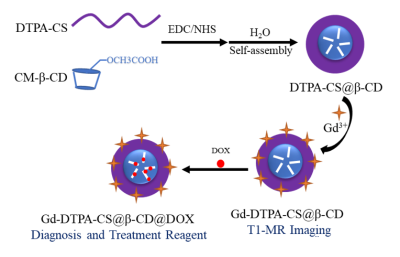
In this study, we constructed a novel and versatile diagnosis and treatment integration nanocomposite (Figure1). First, we activated carboxymethyl β-cyclodextrin(β-CD) by EDC/NHS and then modified it onto hydrophilic DTPA-chitosan(DTPA-CS) by amidation reaction. DTPA-CS@β-CD nanoparticles with core-shell structure were prepared in aqueous solution by electrostatic self-assembly. The Gd3+ was chelated to DTPA-CS@β-CD to obtain Gd-DTPA-CS@β-CD nanocomposites with super-paramagnetic. In addition, the hydrophobic anticancer drug Dox was encapsulated into Gd-DTPA-CS@β-CD by host-guest interaction to obtain drug-Dox nanocomposites (Gd-DTPA-CS@β-CD@Dox). The biological toxicity of Gd-DTPA-CS@β-CD was evaluated by the MTT assay and histological analysis of viscera sections. Furthermore, We observed the cellular uptake of Gd-DTPA-CS@β-CD@Dox by confocal laser microscopy, and then evaluated the ability of Gd-DTPA-CS@β-CD@Dox to enter cells and the Dox release ability in the micro-environment of cancer cells.Results
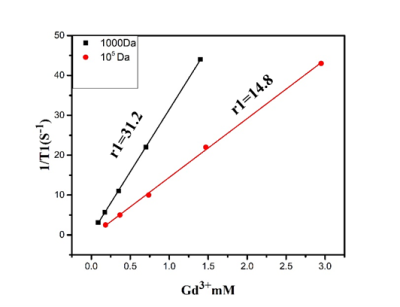
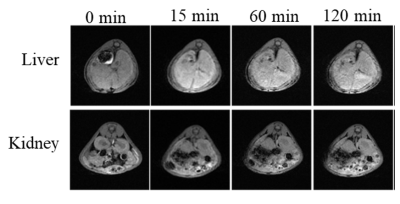
The representative transmission electron microscope (TEM) imaging of DTPA-CS@β-CD exhibits Core-shell DTPA-CS@β-CD nanocomposites were successfully synthesized. As shown in Figure 2, in vitro magnetic resonance imaging experiments indicated that Gd-DTPA-CS@β-CD nanocomposites had a high relaxation efficiency about 31.2 mM-1S-1 and were higher than the value of the pure Gd-DTPA complex. The application of T1 MRI in vivo for small animals was also demonstrated by the Kunming mouse after intravenous injection with 2 mg/mL Gd-DTPA-CS@β-CD nanocomposites. Meanwhile, the positive-contrast enhancement of Gd-DTPA-CS@β-CD nanocomposites were researched by transversal MRI in vivo. Furthermore, Figure 3 showed the imaging effect of the liver area was significantly enhanced 15 minutes after intravenous injection with Gd-DTPA-CS@β-CD nanocomposites, and until 120 min, it still showed good contrast effect. The imaging effect of the kidney area was also markedly increased. The above results suggest that Gd-DTPA-CS@β-CD contrast agent could reach mice quickly and had good stability in the vivo, keeping a long imaging time. After a period of time, the nanocomposites could be metabolized by liver and kidney. Confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) observation showed that the Gd-DTPA-CS@β-CD@Dox nanocomposites were efficiently taken up by cancer cells, which indicated good bio-compatibility thus can be practically employed for bio-imaging and drug delivery.Discussion and Conclusion
In summary, we developed a novel renal-clearable multi-functional theranostic Gd-DTPA-CS@β-CD@Dox nanocomposites for MR imaging and cancer therapy. The relaxation rate of nanocomposites and the effect of MR imaging in the liver and kidney confirmed that it was an efficient, stable, safe and high specificity MR contrast agent. Meanwhile, Gd-DTPA-CS@β-CD@Dox can be swallowed up by cancer cells,and the anticancer drug Dox can be released in the cancer cell micro-environment. In particular, Gd-DTPA-CS@β-CD was relatively low toxicity for small animals, which was confirmed by MTT assays and histological analyses. More importantly, these nanocomposites could be metabolized by liver and kidney in vivo, avoiding long-term toxicity. Therefore, the nano-theranostic with efficient magnetic resonance imaging and cancer treatment may have a great application potential in clinical practice.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Wei Q, Chen Y, Ma X, et al. High-Efficient Clearable Nanoparticles for Multi-Modal Imaging and Image-Guided Cancer Therapy. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(2): 1704634.
2. Ma Y, Huang J, Song S, et al. Cancer‐targeted nanotheranostics: recent advances and perspectives[J]. Small, 2016, 12(36): 4936-4954.
3. Guo J, Li D, Tao H, et al. Cyclodextrin‐Derived Intrinsically Bioactive Nanoparticles for Treatment of Acute and Chronic Inflammatory Diseases[J]. Advanced Materials, 2019,1904607.
4. Song S, Chong Y, Fu H, et al. HP-β-CD Functionalized Fe3O4/CNPs-Based Theranostic Nanoplatform for pH/NIR Responsive Drug Release and MR/NIRFL Imaging-Guided Synergetic Chemo/Photothermal Therapy of Tumor[J]. ACS applied materials & interfaces, 2018, 10(40): 33867-33878.
5. Zhang M, Liu X, Huang J, et al. Ultra-small graphene oxide based T1 MRI contrast agent for in vitro and in vivo labeling of human mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine, 2018, 14(7): 2475-2483.