3072
Assessment of Diffusion Kurtosis at 3.0T as an in vivo Imaging Marker for Breast Lesions Characterization1radiology, Second Affiliated Hospital, Shantou University Medical College, China, shantou, China
Synopsis
Breast multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging (mp-MRI) is a well-established technique in breast cancer for tumor characterization, treatment strategies and post operative predicting, owing to its non-invasive nature of excellent soft-tissue contrast. Our preliminary work demonstrated that MK showed promise in characterizing breast lesions as well as predicting prognostic factors. However, due to the small samples in our previous research and few research relating to the correlation between MK and molecular subtypes, further study with larger cohort is needed to verify our initial results and explore more potential of MK in other clinical applications (assessing therapeutic response to MWA in BBLs).
Background
Background: Breast cancer (BC) has become the leading cause of women mortality nowadays.1,2 The aim of this study was to prospectively compare the diagnostic accuracy of diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI)and diffusion weighted imaging(DWI)in differentiation between malignant and benign breast lesions (BBLs) independently or jointly, and explore the correlation between functional diffusion parameters and prognostic factors, as well as molecular subtypes of breast cancer to provide clinical prognostic information for treatment planning on patients with breast neoplasm.Methods
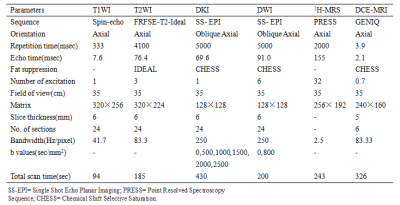
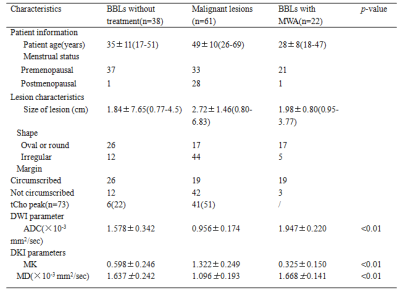
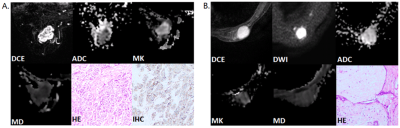
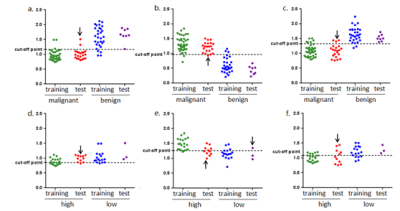
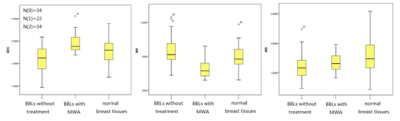
Ninety-two patients with 121 breast lesions were obtained between October 2015 and August 2019 in Radiology Department of our hospital. Eighty patients with 99 breast lesions were examined by breast MRI at 3.0 T prior to operation, including DWI and DKI. Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), mean kurtosis (MK) and mean diffusivity (MD) values in training set were compared by Mann-Whitney U test and Student’s t test. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was used to evaluate the diagnostic performance and determine the cut-off value of the imaging parameters in training set. Spearman correlation and Pearson correlation were used to evaluate the associations between imaging parameters and prognostic factors, as well as molecular subtypes of breast cancers. The ROC optimal cut-off value of the parameter screened out with the highest diagnostic accuracy for detecting breast cancer or predicting prognostic factors and molecular subtypes, was further used in validation set to verify their diagnostic accuracy. 12 patients with 22 benign breast lesions were examined in the same 3.0T MR scanner after receiving one session treatment by microwave ablation (MWA) with complete ablation, box plot was used to compare ADC, MK and MD among BBLs without treatment, BBLs with complete ablation after one session treatment by MWA and normal breast tissues, and Student’s t test was used to compare parameters in these three groups.Results
MK exhibited higher area under the curves (AUCs) for differentiation between malignant and benign lesions than did ADC and MD (0.978 vs 0.945 and 0.963, respectively, p<0.05). MK showed better correlation with histological grade compared with ADC and MD (r=0.733, -0.438 and -0.522, respectively) and showed higher AUCs in distinguishing high- and low-grade breast cancer. MK was the only parameter correlated with Ki-67 expression and luminal A breast cancer (r=0.339 and -0.518). MK was significantly lower and ADC was higher in BBLs with complete ablation after one session treatment by MWA than in BBLs without treatment.Discussion
1. DWI model assumes an ideal Gaussian distribution that water diffuse without restriction , whereas DKI model assumes that water diffusion follows non-Gaussian distribution which reflect real situation of restricted water diffusion owing to the complex microstructural environment that more likely happens in malignant lesions.32. Ki-67 expression is considered as a biomarker of cell proliferation, its high expression suggests increased cellularity, vascular hyperplasia and necrosis and high-grade tumors are characterized by active mitosis and absence of normal glandular architecture, which shows positive correlation with high Ki-67 expression tumors.4,5 All these changes indicate tumor hypercellularity and increasing microstructural complexity in breast cancers, therefore resulting in higher kurtosis and lower diffusivity in breast cancer with high histological grade and Ki-67 expression.
3. MK was significantly higher in BBLs with complete ablation compared with BBLs without treatment, this might due to less restriction of water distribution in lesions with complete necrosis after MWA.
Conlusion
MK derived from DKI showed higher diagnostic accuracy compared with ADC and MD for detecting breast cancer,6 and has the potential to evaluate the therapeutic response to MWA on BBLs. And DKI exhibited correlation with prognostic factors (histological grade, Ki-67 expression and HER2) and luminal A breast cancers, showing promise as an in-vivo and sensible imaging marker for characterizing breast lesions and providing valuable clinical information.Acknowledgements
1. National Natural Science Foundation of China (81471729, 81101102).
2.The Science and Technology, Planning Project of Guangdong Province (2016A020216025).
3.The Research Award Fund for Outstanding Young Teachers in Higher Education Institutions, Guangdong Province (YQ2015245).
References
1. Allemani, C., et al., Global surveillance of trends in cancer survival 2000-14 (CONCORD-3): analysis of individual records for 37 513 025 patients diagnosed with one of 18 cancers from 322 population-based registries in 71 countries. Lancet, 2018. 391(10125): p. 1023-1075.
2. Kuhl, C.K., The Changing World of Breast Cancer: A Radiologist's Perspective. Invest Radiol, 2015. 50(9): p. 615-28.
3. Jensen, J.H. and J.A. Helpern, MRI quantification of non-Gaussian water diffusion by kurtosis analysis. NMR Biomed, 2010. 23(7): p. 698-710.
4. Healey, M.A., et al., Assessment of Ki67 expression for breast cancer subtype classification and prognosis in the Nurses' Health Study. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2017. 166(2): p. 613-622.
5. Kamranzadeh, H., et al., Association between Ki-67 expression and clinicopathological features in prognosis of breast cancer: A retrospective cohort study. J Res Med Sci, 2019. 24: p. 30.
6. Huang, Y., et al., Diffusion Kurtosis at 3.0T as an in vivo Imaging Marker for Breast Cancer Characterization: Correlation With Prognostic Factors. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2019. 49(3): p. 845-856.
Figures