2930
Effect of DNA methylation levels of dopamine D4 receptor gene on GABA concentrations in the mPFC in children with primary nocturnal enuresis1Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, China
Synopsis
In the current study we investigated the effect of DRD4 DNA methylation levels on the GABA concentrations in mPFC in PNE children.
Our results suggested the DNA methylation level of DRD4 is associated with increased GABA concentrations in the mPFC in PNE children. The effects of epigenetic variation of the DRD4 DNA on GABA concentrations in mPFC may help us understand the epigenetic susceptibility of the DRD4 DNA methylation to PNE.
INTRODUCTION
Recent studies have shown that the genotype of dopamine D4 receptor (DRD4) were associated with structural and functional abnormalities in children suffer from primary nocturnal enuresis (PNE). However,the effect of DRD4 DNA methylation levels on concentrations of gamma amino butyric acid (GABA)in the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) is important but remained to unknown. Hence we carried investigation to explore the effect of DRD4 DNA methylation levels on the GABA concentrations in mPFC in PNE children.METHODS
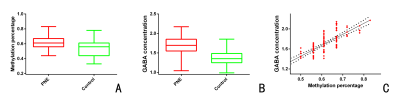
Epigenetic and GABA MRS data were acquired from 107 PNE patients (9.0–13.9 years, with a median age of 11.5 years) and 104 healthy controls (9.1–14.0 years, with a median age of 11.3 years) . Methylation levels were assayed for the island of 18 CpG sites in the DRD4 receptor gene. The DRD4 DNA methylation percentage was calculated for each subject.MEGA-PRESS sequence was applied to measure GABA spectra (TR/TE=2000/68ms, Dynamic scans =320,Spectral BW (Hz) =2000,total scan time= 10 min 56 sec) using a 3T MRI scanner (Ingenia, Philips Healthcare) while subjects were at rest. The 40×30×24 mm MRS voxel was placed in the mPFC. MRS data were post-processed using Gannet 3.0 software package (https://github.com/richardedden/Gannet3.0/). The GABA+ concentrations (CSF-corrected) were calculated.
Comparisons of GABA concentrations in the mPFC and percentages of DRD4 DNA methylation were performed using the Mann–Whitney U test method between groups. Spearman’s correlation analysis was performed to explore the relationship between GABA concentrations in the mPFC and percentages of DRD4 DNA methylation.
RESULTS
Percentages of DRD4 DNA methylation of the PNE group were significantly higher than those of the healthy control group (Z = 4.488, P <0.001). GABA concentrations of the PNE group were significantly higher than those of the healthy control group in the mPFC (Z = 9.793, P <0.001). The GABA concentration of mPFC also showed a significant positively correlation with the percentage of DRD4 DNA methylation within PNE group (r = 0.791, P < 0.001).DISCUSSION
This research showed the PNE children exhibit increased GABA concentrations in mPFC. Hypothesis is raised that the DRD4 DNA methylation may lead to down regulation of DRD4 transcription. Thus, the DNA methylation-related decrease in the DRD4 receptor may weaken the inhibition of depolarization evoked by Calcium-dependent GABA release, causing increased GABA concentrations in the mPFC.The mPFC is an important node of the default mode network and is also the central node in the functional architecture of the sleep cycle that contains the majority of neurons controlling the sleep ‘active’ and ‘inactive’ states. Therefore, the increased mPFC GABA concentration may affect the switching between sleep/waking .
It has also been shown that the anterior thalamic radiation, which connects the medial prefrontal cortex and the thalamus, is responsive to bladder filling, so the increased GABA concentration of mPFC may also inhibit the processing of afferent signals from the bladder to cortex and result in nocturnal enuresis.
CONCLUSION
Our results suggested the DNA methylation level of DRD4 is associated with increased GABA concentrations in the mPFC in PNE children, and more validation tests with more cases and other measurement aspects are needed. The effects of epigenetic variation of the DRD4 DNA on GABA concentrations in mPFCs may help us understand the epigenetic susceptibility of the DRD4 DNA methylation to PNE.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Yu B, Chang N, Lu Y, Ma H, Liu N, Guo Q. Effect of DRD4 receptor -616 C/G polymorphism on brain structure and functional connectivity density in pediatric primary nocturnal enuresis patients. Sci Rep. 2017 Apr 27;7(1):1226.
[2] Wang X, Zhong P, Yan Z. Dopamine D4 receptors modulate GABAergic signaling in pyramidal neurons of prefrontal cortex. J Neurosci. 2002 Nov 1;22(21):9185-93.
[3] Wong CC, Caspi A, Williams B, Craig IW, Houts R, Ambler A, Moffitt TE, Mill J. A longitudinal study of epigenetic variation in twins. Epigenetics. 2010 Aug 16;5(6):516-26.
[4] Chen X, Fan X, Hu Y, Zuo C, Whitfield-Gabrieli S, Holt D, Gong Q, Yang Y, Pizzagalli DA, Du F, Ongur D. Regional GABA Concentrations Modulate Inter-network Resting-state Functional Connectivity. Cereb Cortex. 2019 Apr 1;29(4):1607-1618.
[5] Saleh MG, Rimbault D, Mikkelsen M, Oeltzschner G, Wang AM, Jiang D, Alhamud A,
Near J, Schär M, Noeske R, Murdoch JB, Ersland L, Craven AR, Dwyer GE, Grüner ER,
Pan L, Ahn S, Edden RAE. Multi-vendor standardized sequence for edited magnetic
resonance spectroscopy. Neuroimage. 2019 Apr 1;189:425-431.