2793
Brachial plexus imaging using DANTE-SPACE: comparison with conventional T2-SPACE at 3T1radiology, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, 2MR Collaborations, Siemens Healthcare, Shenzhen, China, Shenzhen, China, 3MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthcare, Wuhan, China
Synopsis
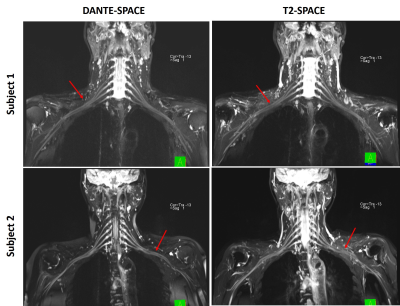
Three-dimensional high-resolution visualization of brachial plexus using T2-weighted SPACE (T2-SPACE) sequence has very high clinical value for the evaluation of brachial plexopathy. However, conventional T2-SPACE is limited by the lack of relative contrast between nerves and their surrounding tissues. In contrast to T2-SPACE, DANTE-SPACE has been proposed with superior blood flow suppression and might be a potential alternative to address its shortcoming. The objective of this study was to evaluate the T2-weighted DANTE-SPACE for its capability to diagnose brachial plexus due to its superior blood flow suppression.
Introduction
Magnetic resonance neurography (MRN) has been increasingly used to further evaluate cases of suspected or established brachial plexopathy, but it is limited by the lack of relative contrast between nerves and their surrounding tissues [1]. In recent years, three-dimensional (3D) T2-weighted variable-flip-angle turbo spin-echo (SPACE) has been proposed as a black-blood technique that permits more direct visualization of the brachial plexus [2]. However, this technique has limited capacity due to the high signal within veins due to slow venous flow and the insufficient contrast between nerves and their surrounding tissues [2]. Recently, a new blood flow suppression technique using the delay alternating with nutation for tailored excitation (DANTE) pulse train has been used in SPACE sequence providing good suppression of slow flow and less signal loss [3]. The combination of DANTE and SPACE may be complementary for suppressing flow, especially in the context of slow venous flow suppression [3]. Based on the aforementioned considerations, the goal of this study was to evaluate the T2-weighted SPACE with DANTE preparation for its capability to imaging brachial plexus due to its superior blood flow suppression without reducing nerve signal.Materials and Methods
This study was approved by the institutional ethics committee. Twenty healthy volunteers (7 males,13 females, average age 31.0) were consecutively enrolled and underwent brachial plexus examinations on a 3T scanner with a 20-channel head coil and an 18-channel body matrix coil (MAGNETOM Skyra, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany), The optimized parameters for T2-weighted DANTE-SPACE with DANTE preparation included: FA=21o; pulse trains number=150; RF gap=1.13ms, spoiler moment=18000(mT/m*sec). The parameters for the SPACE readout included: 3D coronal imaging with a resolution of 1.0 × 1.0 × 1.2mm3, FOV=400mm2, TR/TE=3600/206ms, turbo factor=100, GRAPPA factor=2, bandwidth=539Hz/pixel. Conventional T2-weighted SPACE with the same parameters was also conducted for comparison. All images were graded by two radiologists with >10 years’ experience in MR neurography on a 4-point scale(4 points indicated intact, continuous, and clear visualization of the brachial plexus and its main branches without venous interference; 3 points indicated that the majority of the brachial plexus and its branches were displayed continuously and with some slight venous interference which had no impact on evaluation; 2 points indicated that the majority of the brachial plexus and its branches were displayed and clearly with some moderate venous interference which had impact on evaluation; 1 point indicated the majority of the brachial plexus structure was not displayed and there was serious venous interference). Quantitative contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) between the nerves and their surrounding tissues were calculated for all the subjects and compared between DANTE-SPACE and T2-SPACE methods. Image quality scores and CNRs between the two methods were compared using t test. Statistical significance was defined as p < 0.05.Results
In contrast to T2-SPACE, the images obtained by the proposed DANTE-SPACE method had better CNR (210.5±45.34 vs. 148.3±54.51, p = 0.005) between the nerves and their surrounding tissues. Furthermore, the proposed DANTE-SPACE method provided a superior image quality score compared to the T2-SPACE technique (3.54 ± 0.49 vs. 1.97± 0.35, p = 0.005).Conclusion
The preliminary clinical study suggested that the combination of DANTE and SPACE can be complementary for suppressing flow, and may outperform SPACE to provide excellent venous blood signal suppression. T2-weighted DANTE-SPACE can effectively improve the delineation of the brachial plexus by inhibiting the high signal from veins, and has the potential to be used in clinics for diagnosing pathology of the brachial plexus without the use of contrast agents.Acknowledgements
Many thanks to Department of Radiology, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology.
Many thanks to MR Collaborations, Siemens Healthcare, Shenzhen, China