2686
Optimizing Metal Related Artifact Reduction MRI at 3T: Circular versus Elliptical Radiofrequency Pulse Polarization
Iman Khodarahmi1, John Kirsch2, Gregory Chang1, and Jan Fritz3
1New York University School of Medicine, New York, NY, United States, 2Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, United States, 3Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore, MD, United States
1New York University School of Medicine, New York, NY, United States, 2Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, United States, 3Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore, MD, United States
Synopsis
Clinical metal artifact reduction techniques address B0 inhomogeneity-induced artifacts; whereas other source of artifacts, such as B1 inhomogeneity remain unaddressed. However, B1 inhomogeneity can be reduced by implementing an elliptical polarization of the radiofrequency pulse. In an in-vitro setup of hip arthroplasty implants, we show that MRI with elliptical pulse polarization results in stronger metal artifact reduction and overall superior image quality than circular polarization without increase in SAR values.
INTRODUCTION
Metal artifact reduction sequence (MARS) techniques have advanced visualization of the periprosthetic tissues by focusing on B0 magnetic field distortion as a source of metal-related artifacts.1-3 However, B1 radiofrequency (RF) pulse inhomogeneities resulting from induced eddy currents at the surface of metal implants also play major roles in causing artifacts and degradation of image quality. Therefore, we investigated the effects of circular and elliptical polarizations of the RF pulse on metal-related artifacts of total hip arthroplasty implants during MARS MRI at 3T.METHODS
Experiments were conducted on a clinical 3T MRI system (Magnetom Skyra, Siemens Healthineers) with a two-channel whole-body transmit system. A cobalt-chromium total hip arthroplasty implant system with polyethylene liner immersed in a standard ASTM gel phantom was used in this in-vitro study. The phantom system simulated a 40-year-old human torso with a height of 180 cm and weight of 80 kg. The position of the implant within the scanner bore was similar to the hip implant location of patients with similar weight. Clinical MARS MRI sequences including high-bandwidth turbo spin echo (HBW-TSE), Slice Encoding for Metal Artifact Correction (SEMAC),4 and compressed sensing (CS) SEMAC 5 were acquired in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes using proton density weighting. Each image was acquired twice with circular (CP) and elliptical (EP) RF pulse polarizations while keeping other sequence parameters identical. For EP, the second RF transmit channel had half the amplitude of the first channel and a phase offset of 130°. After anonymization and randomization, the metal artifacts of CP and EP images were quantified using manual segmentation. Additionally, two observers independently ranked the two polarities for overall image quality and extent of metal artifact reduction. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered significant for all statistical analyses.RESULTS
Sample paired CP and EP images are shown in figure 1. Scanner estimated whole-body specific absorption rates (SAR) were lower for all image planes and pulse sequences acquired in EP mode, by approximately 32%. On quantitative analysis, metal artifacts were significantly smaller on EP images compared to the corresponding CP images of the same location and pulse sequence (paired t-test: p < 0.02 for all pulse sequences). The overall metal artifact volume (including implant itself) on axial HBW-TSE images was 19% lower for EP (510 cm3) compared to CP (608 cm3) (Figure 2). Readers chose image quality of EP in 56% (95% CI: 51%-61%) and CP in 7% (95% CI: 4%-9%) of the cases with significantly superior image quality of EP (signed test: p-value < 0.001 for all pulse sequences). The metal artifact reduction ability was more effective about the femoral shaft as compared to the femoral head-polyethylene liner-acetabular cup ensemble (Figure 3).DISCUSSION
For hip arthroplasty implants, imaging with elliptical RF pulse polarization results in stronger metal artifact reduction and overall superior image quality than circular polarization without increase in SAR values. The effect is related to the more homogeneous B1 field that is created with elliptical polarization. The femoral shaft benefits the most from this effect due to its more off-center location within the magnet bore and its longer dimension along the B0 field. Switching to elliptical polarization for 3T MARS MRI of metal containing body parts may eventually hold promise for improved in-vivo clinical imaging.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
- Fritz J, Lurie B, Miller TT, et al. MR imaging of hip arthroplasty implants. Radiographics. 2014;34(4):E106-32.
- Khodarahmi I, Nittka M, Fritz J. Leaps in Technology: Advanced MR Imaging after Total Hip Arthroplasty. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2017;21(5):604-615.
- Hargreaves BA, Worters PW, Pauly KB, et al. Metal-induced artifacts in MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;197(3):547-55.
- Sutter R, Ulbrich EJ, Jellus V, et al. Reduction of metal artifacts in patients with total hip arthroplasty with slice-encoding metal artifact correction and view-angle tilting MR imaging. Radiology. 2012;265(1):204-14.
- Fritz J, Ahlawat S, Demehri S, et al. Compressed Sensing SEMAC: 8-fold Accelerated High Resolution Metal Artifact Reduction MRI of Cobalt-Chromium Knee Arthroplasty Implants. Invest Radiol. 2016;51(10):666-76.
Figures
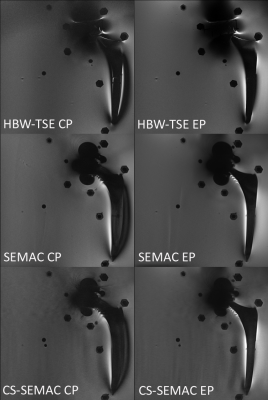
Figure 1. EP mode results
in less metallic implant-induced artifacts than CP mode using different metal
artifact reduction sequence MRI techniques, including high receiver bandwidth
(HBW), conventional Slice Encoding for Metal Artifact Correction (SEMAC), and
compressed sensing (CS) accelerated SEMAC.
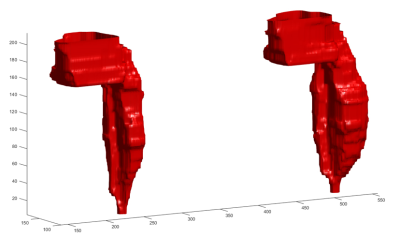
Figure 2. Overall artifact
volume including the implant itself using axial high-bandwidth turbo spin echo
images was 19% lower for EP (left) compared to CP (right).
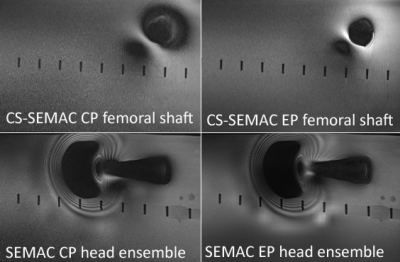
Figure 3. The metal artifact reduction effects of the
elliptical polarization are more strongly affecting the femoral shaft (top row)
as compared to the femoral head ensemble (bottom row.)