2677
Preoperative Pathological Differentiation of Grade 1 and Grade 2/3 Soft Tissue Sarcomas based on Radiomics of ADC maps1The second hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Huiying Medical Technology Inc, Beijing, China
Synopsis
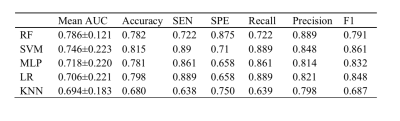
Radiomics based on ADC maps provides a new evaluation method for the preoperative pathological differentiation of Grade 1 and Grade 2/3 soft tissue sarcomas. By comparing the performance of five classifiers (random forests, logistic regression, Multi-Layer Perceptron, k-nearest neighbor, and support vector machine), we found that random forests model achieved the best result (AUC: 0.802 (95% CI: 0.659-0.881), sensitivity:0.722, specificity:0.875) on ADC maps, that can serve as a quantitative tool to differentiation of Grade 1 and Grade 2/3 soft tissue sarcomas. And the radiomics features have the capability in reflecting the Ki67 index
Purpose
To explore the value of radiomics features for preoperatively predicting the pathological differentiation of both grade1 and grade2/3 soft tissue sarcomas using apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) maps and the capability in reflecting the Ki67 index.Introduction
Soft tissue sarcomas (STSs) are heterogeneous neoplasm, which only accounts for about less than 1% of all neoplasm [1]. We have seen an increase of STSs in the overall incidence in recent years [2], partly due to the improvements in histological and imaging technologies [3]. Despite growing experience in the diagnosis and treatment of STSs, an earlier and more accurate diagnosis of STSs leading to a more tailored management strategy. The FNCLCC grading system is being widely used and is a tripartite system [4]. D Reynoso et al [5] mentioned that both the AJCC and CAP recommendations bifurcate the tripartite FNCLCC system into high grade (combining the FNCLCC intermediate- and high-grade categories) and low grade (the FNCLCC low-grade category).D R Lucas et al[6] mentioned that neoadjuvant chemotherapy is usually included in the treatment plans for high-grade STS. The two-scale system of low and high grades is a more appropriate method in neoadjuvant chemotherapy research. So far, the differentiation between grade1 and grade2/3 soft tissue sarcomas rely mainly on pathological analysis from core needle biopsy or surgically removed specimens. The results of preoperative biopsy could be compromised due to tumor heterogeneity, especially the larger ones. Therefore, there is a need for a non-invasive method that can help distinguish grade1 and grade2/3 soft tissue sarcomas before surgery. Radiomics is an emerging research method for assessing tumor heterogeneity by extracting high-throughput features from medical imaging [7].Methods
This retrospective study enrolled 54 patients with a postoperative pathological diagnosis of soft tissue sarcoma including 59 independent lesions (30 low-grade and 36 high-grade lesions) who had undergone 3.0T magnetic resonance imaging before surgery. ADC maps were collected to extract the radiomics features. For each radiomic feature, the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) was calculated to quantify reproducibility between the test-retest scans. The least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) algorithm was used to reduce the features and select valuable ones for preoperative pathological diagnosis. Then five classifiers including random forests, logistic regression, Multi-Layer Perceptron, k-nearest neighbor, and support vector machine algorithm were trained using the 4-fold cross validation strategy to separate the soft tissue sarcomas with grade1 and grade2/3. These five models were evaluated by the receiver area under the operating characteristics curve (AUC). The association between the selected features and the Ki-67 index was also investigated respectively using Spearman correlation.Results
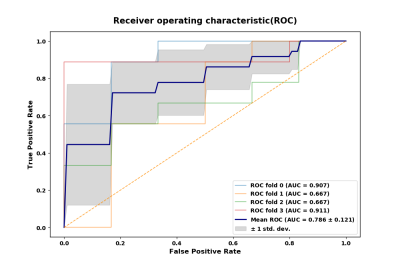
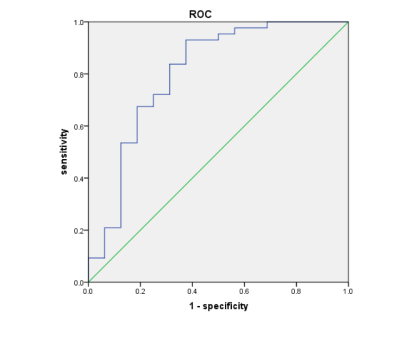
1395 quantitative imaging features were extracted from ADC maps. Because of the unclear lesion margin on the ADC maps, 61 shape-based features were excluded. And then there were 1302 features with an excellent reproducibility (ICC higher than 0.8) were included in the further selection process. After Lasso feature selection algorithm was used and 5 features with the largest coefficient were selected to build the radiomics model. The model that used random forest machine classification method achieved the best performance among the five methods (Table 1), with AUC values of 0.786±0.121, accuracy of 0.782 in test set (Fig.1). A correlation was observed between the three of selected features (logarithm_glcm_Idn, square_gldm_DependenceEntropy and 12 lbp-2D_firstorder_InterquartileRange) and Ki-67 index. The highest AUC (0.802) was found for the feature “square_gldm_DependenceEntropy” of the ROC curve with a threshold of 10% Ki67 index (Fig.2).Conclusions
Radiomics features from ADC maps could be used as candidate biomarkers for distinguishing grade1 and grade2/3 soft tissue tumors noninvasively before surgery and have the capability in reflecting the Ki67 index.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians 2019;69(1):7-34.
[2] Jemal A, Tiwari RC, Murray T, Ghafoor A, Samuels A, Ward E, et al. Cancer statistics, 2004. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians 2004;54(1):8-29.
[3] Kollar A, Rothermundt C, Klenke F, Bode B, Baumhoer D, Arndt V, et al. Incidence, mortality, and survival trends of soft tissue and bone sarcoma in Switzerland between 1996 and 2015. Cancer Epidemiol 2019;63:101596.
[4] Guillou L, Coindre JM, Bonichon F, Nguyen BB, Terrier P, Collin F, et al. Comparative study of the National Cancer Institute and French Federation of Cancer Centers Sarcoma Group grading systems in a population of 410 adult patients with soft tissue sarcoma. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 1997;15(1):350-62.
[5] Reynoso D, Subbiah V, Trent JC, Guadagnolo BA, Lazar AJ, Benjamin R, et al. Neoadjuvant treatment of soft-tissue sarcoma: a multimodality approach. J Surg Oncol 2010;101(4):327-33.
[6] Lucas DR, Kshirsagar MP, Biermann JS, Hamre MR, Thomas DG, Schuetze SM, et al. Histologic alterations from neoadjuvant chemotherapy in high-grade extremity soft tissue sarcoma: clinicopathological correlation. The oncologist 2008;13(4):451-8.
[7] Kumar V, Gu Y, Basu S, Berglund A, Eschrich SA, Schabath MB, et al. Radiomics: the process and the challenges. Magn Reson Imaging 2012;30(9):1234-48.
Figures