2674
Diagnostic value of radiomics model based on non-enhanced MR imaging for differentiation of chondrosarcoma from enchondroma1the Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University, Zhuhai, China
Synopsis
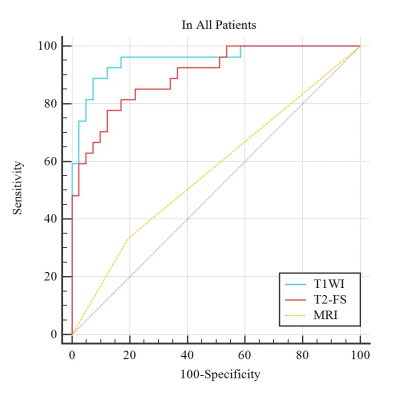
Imaging differential diagnosis between Chondrosarcoma and enchondroma is still a challenge because of their similar characteristic. Radiomics1 is a concept that images contain information reflecting underlying pathophysiology and reveal relationship between lesions through quantitative image analyses. Out study aimed to develop radiomics models based on non-enhanced MRI to differentiate chondrosarcoma from enchondroma. Sixty-eight patients were retrospectively studied. The AUC of radiomics model based on TIWI , T2WI-FS were higher than that of conventional MRI (P<0.01, 0.955, 0.901 and 0.569, respectively). Our preliminary study showed radiomics models can be used in differentiation of chondrosarcoma from enchondroma.
Purpose
To develop and validate a radiomics model based on non-enhanced magnetic resonance (MR) imaging aimed to differentiate chondrosarcoma from enchondroma.Methods
Sixty-eight patients (27 patients with chondrosarcoma and 41 patients with enchondroma) were retrospectively studied, and divided into training group (n=46) and validation group (n=22) randomly. Radiomics features were extracted from T1WI and T2WI-FS non-enhanced sequences of whole tumor by two radiologists independently, and selected by Low Variance, Univariate feature selection, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (Lasso). Intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) were performed between the two radiologists. Radiomics models were constructed by the multivariate logistic regression analysis based on features from T1WI and T2WI-FS sequences. The receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve were performed for radiomics models as well as a third radiologist (with 10 years clinical experiences in musculoskeletal radiology) using conventional MR imaging separately to determine diagnostic accuracy.Results
The ICC value for interreader agreement of radiomics features ranged from 0.779 to 0.923 which indicated excellent agreement. Ten and eleven features were selected from T1WI and T2WI-FS sequences to construct radiomics models, respectively. The area under the curves (AUC) of TIWI and T2WI-FS model were 0.990 and 0.925 in training group; 0.915 and 0.855 in validation group, respectively. There is no statistically significant differences between the two sequences-based models(P>0.05). In all cases, the AUC of radiomics model on the basis of TIWI , T2WI-FS sequences and conventional MR imaging were 0.955, 0.901 and 0.569, respectively, while the diagnostic accuracy of the two sequence-based radiomics models were higher than that of conventional MR imaging (P<0.01).Discussions
Compared with previously studies2,3, our study showed that the radiomics models based on T1WI and T2WI-FS non-enhanced MR imaging performed higher diagnostic accuracy than that of conventional MR imaging. The radiomics features comprised of histogram features, gray level co-occurrence matrix, gray level run length matrix, gray level size zone matrix and features based on filter classes, such as wavelet, square and logarithm etc. The most valuable features for differentiation were selected by Lasso to improve stability as well as reliability of the radiomics models. In addition, there was no statistically significant differences between T1WI and T2WI-FS radiomics model, which indicated both the two sequence can be used in differentiation of chondrosarcoma from enchondroma.Conclusion
The radiomics models based on T1WI and T2WI-FS non-enhanced MR imaging can be used in differentiation of chondrosarcoma from enchondroma.Acknowledgements
Potential conflict of interest: Nothing to report.References
1. Gillies RJ, Kinahan PE, Hricak H. Radiomics: Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data. Radiology. Feb 2016;278(2):563-577.
2. Fritz B, Muller DA, Sutter R, et al. Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Based Grading of Cartilaginous Bone Tumors Added Value of Quantitative Texture Analysis. Investigative Radiology. Nov 2018;53(11):663-672.
3. Lisson CS, Lisson CG, Flosdorf K, et al. Diagnostic value of MRI-based 3D texture analysis for tissue characterisation and discrimination of low-grade chondrosarcoma from enchondroma: a pilot study. European Radiology. Feb 2018;28(2):468-477.
Figures
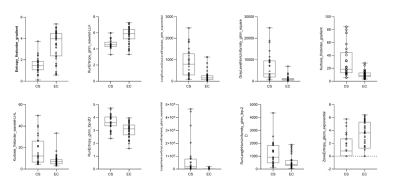
CS=chondrosarcoma; EC=enchondroma
Box plots and scatter plots for 10 radiomics features selected from T1WI sequence
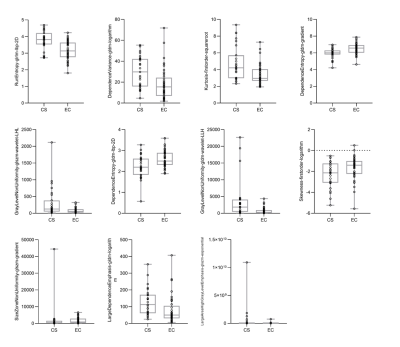
CS=chondrosarcoma; EC=enchondroma
Box plots and scatter plots for 11 radiomics features selected from T2WI-FS sequence
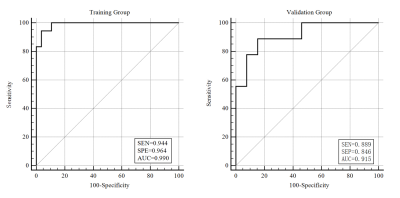
SEN=Sensitivity; SPE=Specificity; AUC=area under the curves
Receiver operating characteristic curve of radiomics model based on T1WI for differentiation of chondrosarcoma from endochondroma. The AUC of the training group (n=46) and the validation group (n=22) were 0.990 and 0.915, respectively.
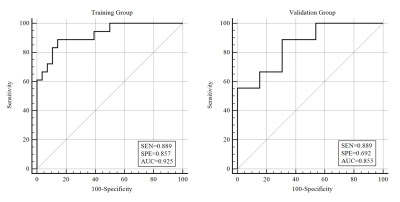
SEN=Sensitivity; SPE=Specificity; AUC=area under the curves
Receiver operating characteristic curve of radiomics model based on T2WI-FS for differentiation of chondrosarcoma from endochondroma. The AUC of the training group (n=46) and the validation group (n=22) were 0.925 and 0.855, respectively.