Jingjun Wu1, Ailian Liu1, Jiazheng Wang2, Xiaofang Xu2, Dahua Cui1, Lihua Chen1, Qingwei Song1, Renwang Pu1, and Bingbing Gao1
1Department of Radiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
When compared to SENSE 2, a clinical routine kidney T2WI protocol and hence the golden standard in this study, CS-SENSE with a 75% higher acceleration factor achieved comparable image quality, both qualitatively and quantitatively, while approximately halved the imaging time. CS-SENSE with acceleration factor 3.5 has the potential to replace the 2 fold SENSE acceleration as a clinical routine to increase patient comfort and throughput, which is especially beneficial for ultra-high resolution acquisitions which normally demands extended imaging time.
Purpose
To objectively evaluate the high resolution 2D T2-weighted MRI (T2WI) in kidney with high acceleration rate using a combination of compressed sensing and parallel imaging, in comparison to the standard of care clinical routine protocol.Materials and Methods
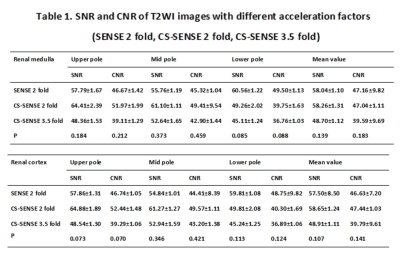
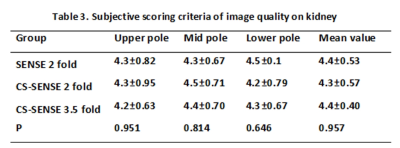
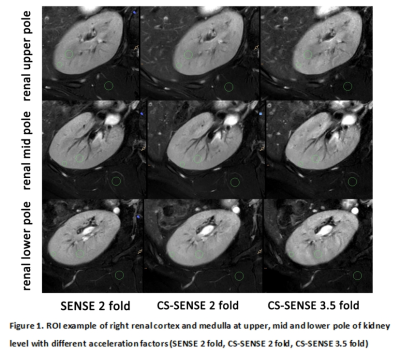
Ten healthy subjects (mean age 28.7±2.15 (22–35) years; 5 males, 5 females) were prospectively involved and underwent 3.0 T MR scan (Ingenia CX, Philips) with a 16-channel abdominal array coil. T2 weighted images of the right kidney were acquired using a 2D TSE sequence with reduced FOV and different acceleration methods and factors (SENSE 2 fold, CS-SENSE 2 fold, CS-SENSE 3.5 fold), where SENSE is the routine parallel imaging methods with acceleration factor 2 and CS-SENSE refers to a combination of compressed sensing and SENSE. Scan times were 357 s, 357 s, and 231 s for the three protocols, while all the other parameters kept same (TR/TE 1490/90 ms, FOV 140x140 mm2, resolution 0.6x0.6 mm2, slice thickness 4 mm) . All the image analysis was performed on IntelliSpace Portal (Philips). Two radiologists independently placed ROIs on renal cortex and medulla at upper, mid and lower pole of kidney level, and on the psoas muscle of the same levels, respectively (Figure 1), where the SNR and CNR (kidney to psoas muscle) were measured. Image qualities were also visually rated by the same two radiologists independently according to the Likert 5 method for the overall image impression, anatomical distortion and detail display (Table 2). The SNR and CNR values between images from different sequences were analyzed using Friedman-test. The Likert score was analyzed for consistency using Kappa coefficient. Results
There was no statistically significant difference in SNR, CNR, and the subjective scoring in all the kidney regions when compared among the SENSE 2, CS 2, and CS 3.5 groups, P values shown in Table 1 and 3.Discussion and Conclusion
When compared to SENSE 2, a clinical routine kidney T2WI protocol and hence the golden standard in this study, CS-SENSE with a 75% higher acceleration factor achieved comparable image quality, both qualitatively and quantitatively, while approximately halved the imaging time. CS-SENSE with acceleration factor 3.5 has the potential to replace the 2 fold SENSE acceleration as a clinical routine to increase patient comfort and throughput, which is especially beneficial for ultra-high resolution acquisitions which normally demands extended imaging time.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
No reference found.