2618
The Value of Oral Paramagnetic Contrast Agent in Eliminating Gastrointestinal Interference with DWIBS1The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
The present study aims to explore the effect of oral paramagnetic contrast agent on image quality of Diffusion weighted Whole body Imaging with Background body signal Suppression(DWIBS).This study confirmed that the oral paramagnetic contrast agent could eliminate gastrointestinal interference without affecting the diagnostic efficacy of DWIBS images.
Objective
To study the effect of oral paramagnetic contrast agent on Diffusion weighted Whole body Imaging with Background body signal Suppression (DWIBS) image quality and its parameters.Introduction
DWIBS has emerged as a powerful diagnostic tool since it was first described for clinical imaging in 2004 by Takahara and colleagues[1].However, the quantitative potential of DWIBS has not yet been fully exploited.Materials and methods
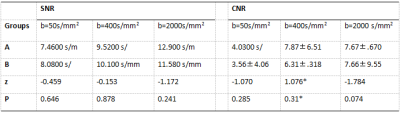
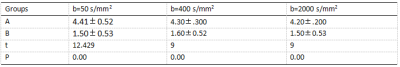
15 volunteers, (28.73±11.58) years of age, were divided into Group A (n=15) and Group B (n=15). Group B volunteers were asked to take ferric ammonium citrate effervescent granules (ferric ammonium citrate, FAC) 20 minutes after abdominal DWIBS scanning, while Group A volunteers fasted 20 minutes before the scan. The DWIBS scan (xx stations in total) were taken on a 3.0 T MR scanner (Ingenia CX, Philips Healthcare, Best, the Netherlands) with TR/TE = 2848/77ms, FOV= 300x450 mm2, voxel size = 3.5x3.8 mm2, slice thickness = 6mm, and b values = 0, 800, 1500, and 2000 s/mm2. Signal to noise Ratio (SNR) and Contrast to noise Ratio (CNR) of the liver were calculated in images with b values of 50, 400 and 2000 s/mm2, and the Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) of the liver was measured for consistency test. Paired t test or Wilcoxon test wasperformed for the measured values in groups A and B. The influence of gastrointestinal signals on the surrounding structure was scored on a 3-point scale, and the consistency test was performed for the two groups A and B, and Kappa test was performed.Results
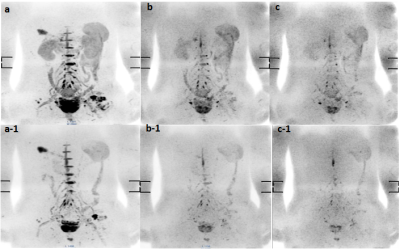
There was no significant difference in SNR and CNR of DWIBS images between group A and group B (both P were >0.05,Table 1). There was a significant difference in the effect of gastrointestinal signals on the surrounding structure (P = 0.00,Table2).FAC has obvious effect on suppressing intestinal signals on DWIBS(Figure 1).ADC values of groups A and B were (0.54±0.18) ×10-3mm2/s and (0.58±0.18) ×10-3mm2/s, respectively. After paired sample t test, t=-1.657 and P=0.132>0.05, the difference was not statistically significant.Discussion and Conclusion
FAC is a paramagnetic substance, whose active component is Fe5+. Five electrons with no spin distance produce spin magnetic moment under the action of the external magnetic field, which increases the local magnetic field, reduces the uniformity, and dephases the precession proton, thus shortening the T2 relaxation time. The spin magnetic moment creates a magnetic field that promotes energy conversion, increases longitudinal relaxation, and shortens T1, thereby altering the surrounding signals. Previous studies[2,3] have confirmed that FAC can be applied to Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography(MRCP)and Magnetic Resonance Urography(MRU), effectively inhibiting fluid signals in the stomach, duodenum and small intestine, and the shape changes of the pancreatic bile duct caused by the lesions and the ureteral lesions on both sides of the renal portal area are more clear.In the clinical practice of IVIM, image quality and ADC value are affected by many factors. Xielifen et al. [4] have shown that gadolinium contrast injection can reduce the SNR of DWI with low b-value in the liver, increase the CNR of liver lesions with medium b-value, and do not affect the SNR of liver lesions. The present study showed that paramagnetic contrast agent FAC does not affect ADC value. FAC not only inhibits gastrointestinal signals, but also retains ADC value accuracy, which is expected to enhance the clinical application of DWIBS.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Takahara T, Imai Y, Yamashita T, et al. Diffusion weighted whole body imaging with background body signal suppression (DWIBS): technical improvement using free breathing, STIR and high resolution 3D display. Radiat Med 2004;22(4):275–82.
[2] WEN Peng,YUChanglu,ZHANGXiang,etal.Application of oral ferric ammonium citrate effervescent granules in positioning of gallstones in MRCP examination.Int J Med Radiol 2016,39(4):358-360.
[3] ZHANG Lina,XUKe,RENKe,etal.Preliminaryevalution of the gastrointestinal signals elimination in 3D-MRU by using Ferric ammonium citrate.ChinClin Med Imaging 2010,21(5):328-342.
[4] XIE Lifen, LIU Zaiyi, LIANG Changhong.Effect of Gadolinium Contrast Media on IntravoxelIncoherent Motion MRI of Abdominal Solid Organs.Chinese Journal of Medical Imaging 2015 ,23(2): 114-119, 124.
Figures