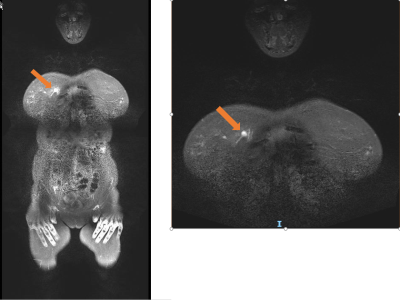
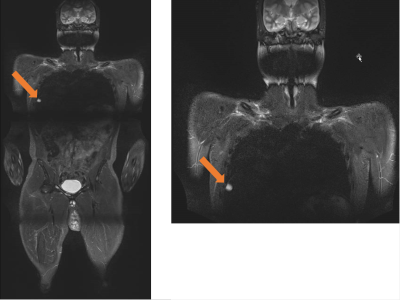
2614
Whole body MRI evaluation for adult patients with hereditary cancer syndromes1Radiology, University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics, Iowa City, IA, United States
Synopsis
Patients diagnosed with hereditary cancer syndromes (HCS) mutations are at increased risk of developing tumors. We are trying to evaluate the utility and cost-effectiveness of WB MRI for screening and monitoring adult HCS patients for new lesions (malignant or pre malignant). We retrospectively collected the data from the HCS patients who had whole-body MRI scans and are aged 18 -72 years old. Overall sensitivity and specificity of WB MRI is 100% and 87.5% and mean per patient cost responsibility per scan is $358.83 which proves WB MRI can be an effective tool for screening and surveillance of HCS patients.
INTRODUCTION
Hereditary cancer syndromes (HCS) are responsible for around 5 - 10% of cancers 1, 2. Whole body magnetic resonance imaging (WB MRI) may play a key role in screening and surveillance of adult patients with HCS without exposing patients to ionizing radiation. Our objective in this study was to assess the clinical utility of WB MRI for screening and surveillance for new lesions (malignant or pre malignant) in adult patients with HCS. Also, we wanted to assess the cost-effectiveness of WB MRI as a screening tool in patients diagnosed with HCS.METHODS
The retrospective study was approved by the Institutional Review Board. Fifty WB MRI scans of 30 patients with HCS, (21 females and 9 males) were retrospectively studied. The age of the patient population included in this study is 18 - 72 years old. These patients were screened for HCS and confirmed through genetic testing because of a personal history or family history of cancers. The syndromes included in the study are Li-Fraumeni syndrome (LFS) (N= 14), paraganglioma pheochromocytoma syndrome (N= 12), rhabdomyosarcoma (N= 1), neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) (N= 1), carcinoid syndrome (N= 1) and retinoblastoma (N= 1). The sequences acquired were short-tau inversion recovery (STIR), diffusion weighted imaging (DWI), T1-weighted imaging (T1WI) and T2 weighted imaging (T2WI) sequences. The scans were read by radiologists with 5 to 35 years of experience. Of the 50 scans, 11 scans had STIR only sequences, 16 scans had STIR and T2WI, 1 scan had STIR and T1WI, 4 scans had STIR and T1WI and T2WI and 15 scans had STIR and T1 WI and DWI sequences. The MRI findings were correlated with medical records, biopsy results and follow up imaging. Standard definitions were used for the calculation of the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV). To assess the cost effectiveness, data associated with insurance, hospital billing, and the amount patient responsible for, was collected from the electronic medical records. Mean of per patient cost responsibility for single WB MRI scan was calculated using standard definitions.RESULTS
From the 50 scans, 9 scans had suspicious findings and were followed with additional scans including ultrasound, focused MRI, CT/PET scan or biopsy. Out of the 9 suspicious lesions, one lesion was confirmed as breast cancer, another lesion was confirmed as metastatic lung mass and a third scan demonstrated multiple neurofibromas which needed further monitoring for malignant transformation. Forty-one scans were true negative, 6 scans were false positive, 3 scans were true positive and there were no false negative scans. The overall statistics of WB MRI in HCS patients is sensitivity - 100%, specificity – 87.2%, PPV – 33.3%, NPV – 100%. The statistics of WB MRI with STIR, T1WI and/or T2WI and without DWI scans in HCS patients is sensitivity - 100%, specificity – 87.5%, PPV – 42.8%, NPV – 100%. The statistics of WB MRI scans with STIR, T1WI and DWI scans in HCS patients is specificity – 86.6%, NPV -100%.Mean per patient cost responsibility for a WB MRI scan is $358.83 according to the information available in the medical records.
DISCUSSION
WB MRI is a valuable tool for imaging in HCS patients for various reasons like the multiplicity of lesions in HCS, the susceptibility of HCS patients to radiation induced mutations and need for long term monitoring 3. According to a study done by Anupindi et al., in the pediatric patient population, screening susceptible patients for early detection and following up of new lesions can have a positive impact on prognosis of HCS patient while reducing health care costs 4. In this study, the sensitivity, specificity, and NPV of WB MRI scans used as a screening and surveillance tool in the adult patients with HCS is high. These findings can be valuable to consider WB MRI scans for screening and surveillance of adult patients with HCS.The mean patient cost responsibility of $358.83 per WB MRI scan can also make WB MRI a cost-effective modality for screening and surveillance of adult patients with HCS.
CONCLUSION
WB MRI with a combination of STIR, T1WI, T2WI and DWI sequences can give morphological and functional information for HCS patients without exposing them to ionizing radiation, and low mean patient cost responsibility per scan can make WB MRI scans an affordable modality for screening and surveillance of adult patients with HCS.Acknowledgements
References
1. Niendorf, K.B, et al. A model for patient-direct screening and referral for familial cancer risk. Fam Cancer. 2016;15(4):707-716.
2. Riley, B.D, et al. Essential elements of genetic cancer risk assessment, counseling, and testing: updated recommendations of the National Society of Genetic Counselors. J Genet Couns. 2012;21(2):151-161.
3. Greer, M.C, et al. Imaging of cancer predisposition syndromes. Pediatr Radiol. 2018;48(9):1364-1375.
4. Anupindi, S.A, et al. Diagnostic Performance of Whole-Body MRI as a Tool for Cancer Screening in Children With Genetic Cancer-Predisposing Conditions. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015;205(2):400-408.
Figures