2583
Diffusion Weighted whole body Imaging with Background body signal suppression with three b value for tumorlike lesion detection in abdomen1first Affiliated hospital of Dalian medical university, Dalian, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China, Beijing, China
Synopsis
The purpose of this study was to evaluate image quality of diffusion weighted whole body Imaging with background body signal suppression (DWIBS) sequence using different b values (b=0,800 and b=0,800,1500) for predicting tumor or tumorlike lesions in abdomen. The results showed index ADC image with b=0,800 depicted more lesions than b=0,1500, including false positive lesions. The ADC value of b=0,800, 1500 is less than that of b=0, 800, indicating tumor’s precise ADC value is lower than we thought before.
Introduction
Diffusion weighted whole body imaging with background body signal suppression (DWIBS) is kind of protocol for quick whole-body lesion detection1. DWIBS as a clinical tool in the management of oncological patients for initial and metastasizing tumor detection is limited mostly by the relatively long-up to 60 minutes-scan time2. In the present study, we aimed to detect abdominal lesions using DWIBS with three b values (0,800,1500), and apply as clinical protocol in abdominal disease.Methods
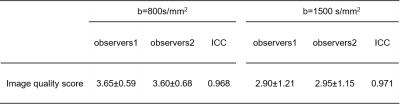
This study was approved by the institutional ethics committee of the hospital. The study was retrospective. We recruited 15 patients with abdominal tumor or tumorlike lesion who underwent MR scan with DWIBS sequence from March to September 2019 in our hospital. The image parameters were showed in table1. The lesions included hepatic hemangioma, hepatic carcinoma, gastric stromal tumor, rectal cancer, cervical cancer, prostatic cancer and multiple myeloma. Totally twenty lesions were found. The lesions on T2WI were set as reference. On one hand, we subjectively evaluated the image quality using a four-points scale: 1, poor; 2, fair; 3, good; 4, excellent; and the results were compared with one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). Two radiologists who were unaware of the clinical, surgical, and histological findings analyzed the MR images independently. On the other hand, we quantitatively analyzed the ADC values of lesions depicting in two different ADC maps at b=0, 800 and b=0, 800, 1500 s/mm2. This two group of ADC values were compared with paired T-test.Results
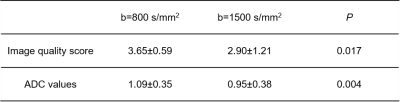
The intra-class correlation coefficient (ICC) showed excellent consistency between two radiologists (0.938 to 0.944 for all measurements) (table 2). Significant difference was found for image quality scale (P=0.017) and ADC values (P=0.004) between two group of b values (table 3). On index ADC images with b=0, 800, both image quality scale and ADC values were higher than that of ADC images with b=0, 800,1500.Discussion and Conclusion
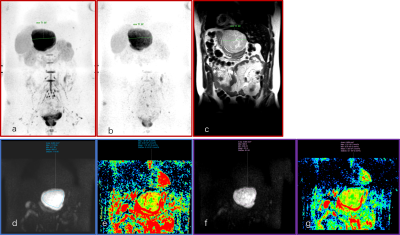
The results of this study showed that index ADC image derived from b=0, 800 detecting more lesions than that of b=0,1500. Lesions on T2-weighted images and index ADC image (b=0, 800) were similar in size, shape and boundary, part of lesions on index ADC image (b=0,1500) became smaller in size, blurred shape and boundary. The ADC value of b value=0,800, 1500 s/mm2 was preferred over 800 s/mm2 for lesion detection. Diffusion weight image with different b values reflects the random microscopic motion of water molecules (either intra-cellular or extracellular) and the microcirculation of blood3. As b value goes up, the ADC maps reflect less tissue diffusivity and more tissue microcapillary perfusion4. Thus, there are false positive lesions on index ADC image (b=0, 800) image. We suggest to use b values of 800 and 1500 for lesion detection in abdomen.Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to department of radiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, supports this study. The authors thank all patients who participated in this study.References
1. Kenkel, D.; Wurnig, M. C.; Filli, L.; Ulbrich, E. J.; Runge, V. M.; Beck, T.; Boss, A., Whole-Body Diffusion Imaging Applying Simultaneous Multi-Slice Excitation. Rofo 2016, 188 (4), E1.
2. Koo, J. H.; Kim, C. K.; Choi, D.; Park, B. K.; Kwon, G. Y.; Kim, B., Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging for the evaluation of prostate cancer: optimal B value at 3T. Korean J Radiol 2013, 14 (1), 61-9.
3. Le Bihan, D.; Turner, R.; Moonen, C. T.; Pekar, J., Imaging of diffusion and microcirculation with gradient sensitization: design, strategy, and significance. J Magn Reson Imaging 1991, 1 (1), 7-28.
4. Michielsen, K.; Dresen, R.; Vanslembrouck, R.; De Keyzer, F.; Amant, F.; Mussen, E.; Leunen, K.; Berteloot, P.; Moerman, P.; Vergote, I.; Vandecaveye, V., Diagnostic value of whole body diffusion-weighted MRI compared to computed tomography for pre-operative assessment of patients suspected for ovarian cancer. Eur J Cancer 2017, 83, 88-98.
Figures