2581
Application of intravoxel incoherent motion in preoperative assessment of clinicopathological features of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma1radiology, Henan Cancer Hospital, Zhengzhou, China
Synopsis
Preoperative assessment of intravoxel incoherent motion in clinicopathologic features of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. the uploaded file includes objective,method,results,conclusion,references, acknowledgements and figure.
Objective
To explore the value of intravoxel incoherent motion(IVIM) in preoperative evaluation of clinicopathological features of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC).Methods
ESCC patients who underwent esophageal cancer resection were prospectively enrolled from April 2016 to June 2017. MRI routine scan and IVIM examination were performed within one week before operation. The quantitative parameters of IVIM, including apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), diffusion coefficient (D), perfusion coefficient (D*) and perfusion score (f) were measured. The relationship between IVIM parameters and pathological parameters (infiltration depth, lymph node metastasis, differentiation degree, angiolymphatic and perineural invasion) was analyzed.The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were used to evaluate the efficacy of predicting clinicopathological features of ESCC.Results
A total of 31 patients were enrolled in the study .The difference in f value between T1+T2 and T3 was statistically significant (P = 0.03). With the f value of 0.497 as the threshold, the diagnostic efficacy of infiltration depth is highest, and the sensitivity and specificity were 55.6% and 86.4% respectively. The f value of angiolymphatic invasion group was significantly lower than that of noninvasion group, and the differences were statistically significant (P = 0.04). With the f value of 0.408 as the threshold, the diagnostic efficacy of angiolymphatic invasion is highest, and the sensitivity and specificity were 70.6% and 78.6% respectively. ADC value, D value and D* value showed no significant difference among groups.Conclusion
IVIM can be used as a new imaging modality to preoperative evaluate clinicopathological features of ESCC. f values can reflect the infiltration depth and angiolymphatic invasion of ESCC.Acknowledgements
The authors have no acknowledgements to report. No externalfunding source was involved in this investigation.References
[1] Kim T, Grobmyer SR, Smith R, et al.Esophageal cancer--the five year survivors. [J].J Surg Oncol. 2011,103(2):179-183.
[2] Hu Y, Hu C, Zhang H,et al. How does the number of resected lymph nodes influence TNM staging and prognosis for esophageal carcinoma? [J].Ann Surg Oncol. 2010,17(3):784-790.
[3] Bai B, Ma W, Wang K,, et al. Detection of D2-40 monoclonal antibody-labeled lymphatic vessel invasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and its clinicopathologic significance[J]. Cancer Biol Med. 2013,10(2):81-85.
[4] Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, et al. MR imaging of intravoxel incoherent motions: application to diffusion and perfusion in neurologic disorders[J]. Radiology, 1986, 161(2): 401-407.
[5] Edge SB, Compton CC. The American Joint Committee on Cancer: the 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging manual and the future of TNM[J]. Ann Surg Oncol,2010,17(6):1471-1474.
[6] Koh DM, Lee JM, Bittencourt LK,et al. Body Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging in Oncology: Imaging at 3 T[J]. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am,2016,24(1):31-44.
[7] Donati F, Boraschi P, Pacciardi F, et al. 3T diffusion-weighted MRI in the response assessment of colorectal liver metastases after chemotherapy: Correlation between ADC value and histological tumour regression grading[J]. Eur J Radiol. 2017,91:57-65.
[8] Chung SR, Lee SS, Kim N, et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion MRI for liver fibrosis assessment: a pilot study. Acta Radiol. 2015,56(12):1428-1436.
[9] Wang LL, Lin J, Liu K, et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MR imaging in differentiation of lung cancer from obstructive lung consolidation: comparison and correlation with pharmacokinetic analysis from dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging. Eur Radiol. 2014; 24(8):1914-1922.
[10] Chen JW, Xie JD, Ling YH, et al. The prognostic effect of perineural invasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. BMC Cancer. 2014,14:313.
[11] Lee G, I H , Kim SJ, et al. Clinical implication of PET/MR imaging in preoperative esophageal cancer staging: comparison with PET/CT, endoscopic ultrasonography, and CT[J]. J Nucl Med. 2014, 55(8): 1242-1247.
[12] Giganti F, Ambrosi A, Petrone MC,et al. Prospective comparison of MR with diffusion-weighted imaging, endoscopic ultrasound, MDCT and positron emission tomography-CT in the pre-operative staging of oesophageal cancer: results from a pilot study[J]. Br J Radiol.2016,89(1068):20160087.
[13] Wayman J, Bennett MK, Raimes SA, et a1.The pattern of recurrence of adenocarcinoma of the ocsophago-gastric junction[J].Br J Cancer, 2002, 86(8) :1223-1229.
[14] Chandarana H,Lee VS,Hecht E,et a1.Comparison of biexponential and monoexponential model of diffusion weighted imaging in evaluation of renal lesions:preliminary experience[J].Invest Radiol,2011,46(2):285-291.
[15] Cohen AD, Schieke MC, Hohenwalter MD, et al. The effect of low b-values on the intravoxel incoherent motion derived pseudodiffusion parameter in liver[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2015,73(1):306-311.
[16] Pang Y, Turkbey B, Bernardo M, et a1. Intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging for prostate cancer:an evaluation of perfusion fraction and diffusion coefficient derived from different b-value combinations[J]. Magn Reson Med,2013,69(2):553-562.
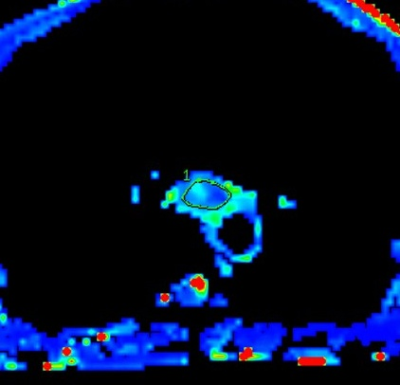
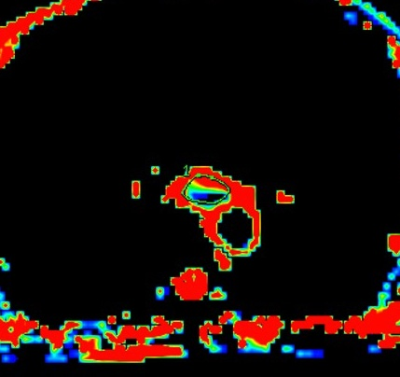
Figures