2563
The combination use of APT and R2* enhances the differentiation of endometrial carcinoma and endometrial benign lesions1Department of Radiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Amide proton transfer (APT) and mDixon - Quant techniques have been applied in clinical work, but few studies have been conducted in female pelvic system. We discussed the value of APT combined with R2* in differentiating endometrial cancer from benign endometrial lesions. The AUC, sensitivity and specificity of APT combined R2* were 0.925, 88% and 100%, respectively.
INTRODUCTION
The etiology of endometrial lesions is not clear, and the endometrial condition changes with the menstrual cycle.The clinical manifestations of endometrial carcinoma and endometrial benign lesions are more similar, so how to make an accurate diagnosis of endometrial lesions is particularly important. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is increasingly being applied for diagnosing endometrial diseases and as a problem-solving tool when there is a diagnostic dilemma, but differentiate endometrial carcinoma from benign remains challenging [1]. APT weighted MRI uses the presence of low-concentration solutes (such as mobile proteins and peptides) in tissues or tumors that contain abundant amide chemical constituents to produce an MR signal that directly correlates with cell proliferation [2]. Modified Dixon (mDixon) Quant technique with six echoes, seven fat peaks and T2* correction was found to enable robust water-fat separation and to have high quality fat and R2* quantification[3] .APT and mDixon -Quant techniques have been applied in clinical work, but few studies have been conducted in female pelvic system. In this study, we would like to explored the value of APT combined with R2* in the differential diagnosis of endometrial carcinoma and endometrial benign lesions.METHODS
Data of 8 cases of endometrial carcinoma and 5 cases of endometrial benign lesions (4 cases of endometrial polyps and 1 case of endometrial hyperplasia) confirmed by surgery and pathology were retrospectively analyzed. All patients received 3.0T routine MRI,APT and mDIXON -- Quant scans on a 3.0T MRI (Ingenia CX, Philips Healthcare, Best, the Netherlands) equipment before surgery. Table 1 lists the detail of scan parameters. According to the lesion area of endometrium on T2WI and DWI, the ROI in the lesion area was drawn on the APT -T2WI fusion images by two observers who were blindly to the pathological results. Then the APT value was recorded . ROI was also plotted in the corresponding region of mDIXON - Quant imaging to obtain the R2* value of the lesion. Intra-group correlation coefficient (ICC) was used to test the consistency of measurement results between the two observers. The rank sum test was used to analyze the difference of each parameter between the two groups, and the AUC was calculated to evaluate the diagnostic efficacy. For all tests, values of P <0.05 were considered to indicate statistical significance.RESULTS
The results of parameter values and consistency test were measured by two observers in the two groups, and the numerical consistency was good in each group (Table 2), ICC>0.75. APT value and R2* in the endometrial carcinoma group were both larger than those in the benign group, with statistically significant differences (P<0.05). Specific results were shown in Table 3 and Figure 1. The AUC values of APT, R2* and their combination were shown in Table 4.DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSIONS
APT value is affected by changes in protein concentration and PH value [4]. Tumor cells of endometrial carcinoma are metabolically active and their protein concentration is higher than that of benign endometrial lesions, so APT value is high, which is consistent with our results of this study that APT value of endometrial carcinoma group is higher than that of benign endometrial lesions. Deoxyhemoglobin, hemosiderin, noremoglobin and other paramagnetic substances can increase the R2* value [5]. In this study, the R2* value of the endometrial carcinoma group was higher than that of the endometrial benign lesion group, and the reason may be that the concentration of paramagnetic substances in the endometrial carcinoma tissues increased [6].The combination of APT and R2* can improve the diagnostic ability of discriminating endometrial carcinoma from endometrial benign lesions, which has certain clinical application value.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement.References
[1] Park BK, Kim B, Park JM, Ryu JA, Kim MS, Bae DS, Ahn GH. Differentiation of the various lesions causing an abnormality of the endometrial cavity using MRI imaging: emphasis on enhancement. Patterns on dynamic studies and late contrast-enhanced T1-weighted images. Eur Radiol. 2006;16:1591–1598.
[2] He YL, Li Y, Lin CY, et al. Three-dimensional turbo-spin-echo amide proton transfer-weighted MRI for cervical cancer: a preliminary study. J Magn Reson Imaging 2019. DOI: 10.1002/jmri.26710
[3] Kühn JP, Hernando D, Meffert PJ, et al. Proton-density fat fraction and simultaneous R2* estimation as an MRI tool for assessment of osteoporosis. Eur Radiol 2013;23:3432–3439.
[4] Ray KJ, Simard MA, Larkin JR, et al. Tumor pH and Protein Concentration Contribute to the Signal of Amide Proton Transfer Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Cancer Res 2019; 79:1343-1352.DOI:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-2168
[5]İdilman İS,Gümrük F,Haliloğlu M.The Feasibility of Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Quantification of Liver, Pancreas, Spleen, Vertebral Bone Marrow, and Renal Cortex R2* and Proton Density Fat Fraction in Transfusion-Related Iron Overload.Turk J Haematol 2016;33:21-27.DOI:10.4274/tjh.2015.0142
[6] Yang X.The Role of Metabolic Syndrome in Endometrial Cancer: A Review.FrontOncol 2019;9:744.
Figures

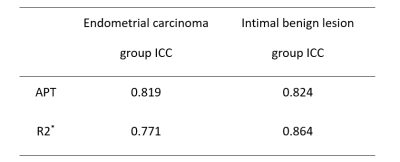
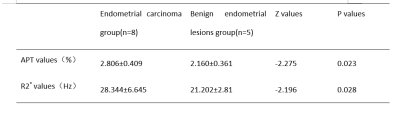
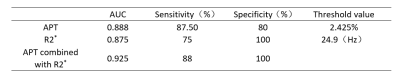
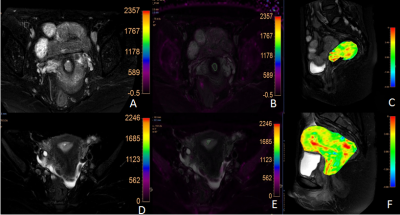
Figure 1:A-C a 55-year-old patient with endometrial carcinoma (pathologic type: endometrial adenocarcinoma) (A-B)The mDIXON -- Quant post-processed R2* original image and pseudo-color image have a value of 32.67Hz. (C)APTw image, APT value 3.3%.D-F a 51-year-old patient with endometrial polyps (D-E)mDIXON - Quant reprocessed R2* original and pseudo-color images, with a value of 24.47Hz. (F)APTw image, APT value 2.35%.