2562
Quantitative identification of endometrial carcinoma and endometrial polyp by T2 mapping1The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 3Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
T2 mapping is a novel MRI sequence that enables quantitative assessment of various diseases. However, its potential for diagnosis of endometrium diseases has not been explored,andit may also help differential diagnosisof endometrial carcinoma and endometrial polyp.In this study, the T2mapping was used for quantitative analyses of endometrial carcinoma and endometrial polyp. Results shown that endometrial carcinoma was associated with significant higher T2 values than endometrial polyp, therefore, it is feasible to use T2 mapping for discrimination of endometrial carcinoma and endometrial polyp.
INTRODUCTION
T2 mapping has been applied in quantitative assessment of various diseases in tissues such as heart, nerve and bone joints. It has a special application in evaluating diffuse cardiomyopathy (such as edema and fibrosis) and also benefits diagnoses of diseases including myocarditis and myocardial infarction [1]. Endometrial carcinoma is a malignant tumor of epithelium, while endometrial polyps are the most common benign endometrial lesions. It can be difficult to distinguish the two types of endometrial lesions on conventional MR images due to similar signals. Ghosh, et al [2] argued that the T2 mapping could predict biological behaviors of endometrial tumors, and it may work for discrimination of endometrium benign and malignant lesions. In this study, the possibility ofT2 mapping for differential diagnoses ofendometrial carcinoma and endometrial polyps was investigated.METHODS
Data of 8 patients with endometrial carcinoma (group A) and 7 patients with endometrial polyps(group B)confirmed by operation and pathology were retrospectively analyzed. All patients received MR examinations on a 3.0T MR scanner (Ingenia CX, Philips Healthcare, Best, the Netherlands)before surgery. Scanning parameters for the T2 mapping sequence included: FOV=360mm, TR=3.5s, flip angle = 90°, voxel size = 1.3×1.0×4.0mm3, slice thick = 8cm, and scanduration = 1′58″). T2 values for both groups were measured by two observers using double-blind methods. ROIs (diameter≥1.0cm) were placed on three adjacent layers of the largest cross section of the lesions (avoid heterogeneous areas).Mean values of the T2 values of the three layers were calculated and recorded. Intra-group correlation coefficient (ICC) was used to test the measurement consistency between the two observers. Difference in T2 values (mean values by the two observers) between the two groups was analyzed by the Mann-Whitney u test, and the diagnostic efficacy was evaluated by the ROC analysis.RESULTS
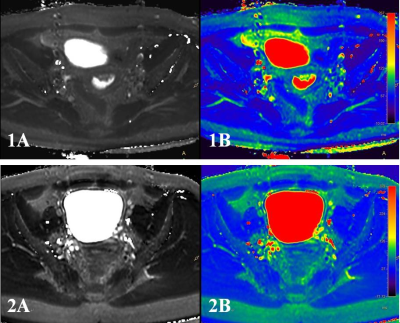
Measurements of T2 values by the two observers were in good agreement for both the two groups (endometrial carcinoma: ICC = 0.882, endometrial polyps: ICC = 0.889). T2mapping images of two patients with different lesions are shown in Figure 1. T2 values measured forthe endometrial carcinoma and the endometrial polyps were (73.069±7.629) and (99.687±32.804)ms, respectively. T2 values for group A (patients with endometrial carcinoma) group were significantly lower (Z=-1.967,P=0.049) than those of group B (patients with endometrial polyps). The AUC of the T2 value was 0.804, the sensitivity was 87.5%, specificity was 85.7%, with a cut-off value of 77.950 ms.DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSIONS
T2 values for the lesion of endometrial carcinoma were significant lower than those for endometrial polyps. This may be due to the complex composition of endometrial cancer and its less content of water. A conclusion can be drawn that T2mapping may serve as an effective tool for discrimination of endometrial carcinoma and endometrial polyps with high sensitivity and specificity.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement.References
[1] Hamlin SA, Henry TS, Little BP, et al. Mapping the future of cardiac MR imaging: case-based review of T1 and T2 mapping techniques. Radiograohics. 2014;34(6):1594-1611.
[2] Ghosh A, Singh T, Bagga R, et al. T2 relaxometry mapping in demonstrating layered uterine architecture: parameter optimization and utility in endometrial carcinoma and adenomyosis: a feasibility study. BrJRadiol.2018;91(1081):20170377.