2527
The value of ESWAN in diagnosis and differential diagnosis of endometrial carcinoma and endometrial polyp1Department of Radiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
Synopsis
Enhanced T2* weighted angiography (ESWAN) has been applied in the diagnosis of female pelvic tumor, but no study on the differentiation of endometrial cancer and related benign lesions by ESWAN has been found. We investigated the value of ESWAN multiple quantitative parameters in the identification of endometrial carcinoma and endometrial polyps.
INTRODUCTION
Endometrial carcinoma (EC) is one of the three major malignant tumors of female reproductive system and is the source of epithelial tissue. Endometrial polyp (EP) is formed by transitional growth of the local endometrial membrane and protrusion into the uterine cavity. Currently, biopsy is a commonly used examination method in clinical practice, but due to the limited sample size, it is sometimes unable to be accurately characterized, and cervical or vaginal stenosis of some patients is not suitable for this examination [1]. ESWAN technology can reflect the change of blood oxygen content in tissues according to the difference of magnetic sensitivity between tissues, and obtain quantitative parameters such as magnitude value, phase value, R2* value and T2* value [2]. Previous studies have shown that ESWAN has been applied in the diagnosis of uterine sarcoma [3] and has certain value in the identification of ovarian malignant epithelial tumors [4].METHODS
Data of patients with EC or EP diagnosed by surgical pathology and who underwent routine MRI and ESWAN from June 2012 to July 2019 were retrospectively analyzed. Finally, EC 25 cases (including 23 cases of endometrial adenocarcinoma, 2 cases of serous adenocarcinoma) and EP 20 cases were enrolled. Two observers measured the parameters of the two groups of patients without knowing the pathological results. Intra-group correlation coefficient (ICC) was used to test the consistency of the two observers' measurement results for each parameter. The independent sample t-test was used to analyze the difference of each parameter between the two groups, and the ROC curve was used to evaluate the diagnostic efficacy.RESULTS
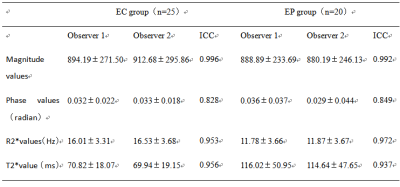
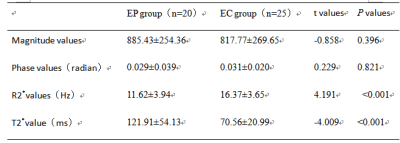
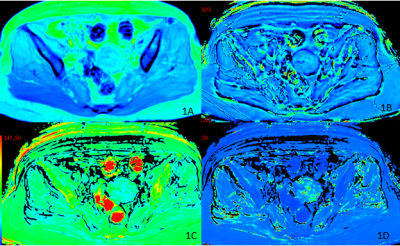
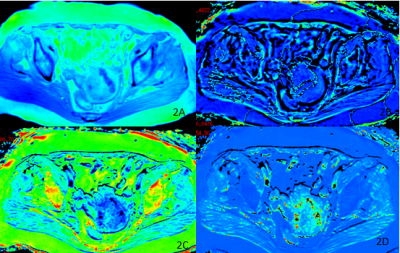
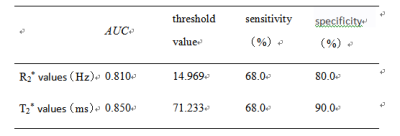
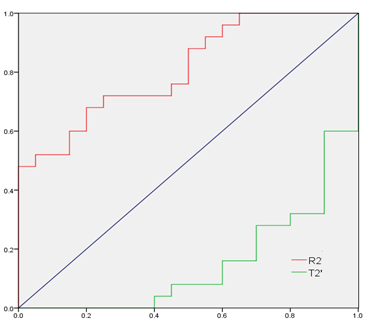
The two observers measured the magnitude, phase, R2* and T2* values and the consistency test results of the two groups of lesions. The numerical consistency of each group was very good, ICC>0.75, as shown in table 1. The R2* value of EC group was larger than that of EP group, and the T2* value was smaller than that of EP group, with statistically significant differences (P<0.05). There was no significant difference between the magnitude and phase values between the two groups (P>0.05), and the specific results were shown in table 2, figure 1 and 2. The diagnostic efficacy of R2* and T2* values for lesions in the two groups was shown in table 3 and figure 3.DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSIONS
When the blood metabolites deoxyhemoglobin, hemosiderin, noremoglobin and other paramagnetic substances phase out the magnetic field, T2* value decreases and R2* value increases [5]. In this study, the R2* value of EC group was larger than that of EP group and the T2* value was smaller than that of EP group. The reason may be that EC was in a relatively hypoxic state [6], and the concentration of paramagnetic substance increased, resulting in a decrease in T2* value and an increase in R2* value. Multiple quantitative parameters of ESWAN can effectively identify EC and EP, and provide a basis for clinical treatment, which is worth popularizing and applying.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement.References
[1] Zhu Y, Liu Z, Du M, et al. Macrophages in patients with recurrent endometrial polyps could exacerbate Th17 responses [J]. ClinExpPharmacolPhysiol, 2018, 45(11):1128-1134.
[2] Zeng C, Du S, Han Y, et al. Optic radiations are thinner and show signs of iron deposition in patients with long-standing remitting-relapsing multiple sclerosis: an enhanced T2*-weighted angiography imaging study. EurRadiol, 2018, 28(10):4447-4454.
[3]Takeuchi M,Matsuzaki K. Clinical utility of susceptibility-weighted MR sequence for the evaluation of uterine sarcomas.Clin Imaging 2019;53:143-150.
[4] Han X,SunM,WangM,etal.The enhanced T star weighted angiography (ESWAN) value for differentiating borderline from malignant epithelial ovarian tumors.Eur J Radiol 2019;118:187-193.
[5]Xin JY,GaoSS,LiuJG,etal.The value of ESWAN in diagnosis and differential diagnosis of prostate cancer: Preliminary study.MagnReson Imaging 2017;44:26-31.
[6] Yang X.The Role of Metabolic Syndrome in Endometrial Cancer: A Review.FrontOncol 2019;9:744.
Figures