2518
Predicting the resectability and pathological grading of pancreatic cancer by intra voxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging1Changzhou First People's Hospital, Changzhou, China, 2Clinical Science, Philips Healthcare, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
The resectability and pathological grade of pancreatic cancer are important for prognosis of patients. We try to predict the pathological grade and the resectability of pancreatic cancer by quantitative IVIM-DWI. Comparing the IVIM parameters of resectable and unresectable pancreatic cancer, poorly differentiated and highly-moderately differentiated pancreatic cancer, we found that poorly differentiated pancreatic cancer had lower f value than highly-moderately differentiated pancreatic cancer, and resectable pancreatic cancer had higher d, f values than unresectable pancreatic cancer. The quantitative IVIM parameters can predict the resectability and pathological stage of pancreatic cancer, which can be helpful for assessment of resectability.
Introduction
The pancreatic cancer has the characteristics of strong proliferation and invasion, while the tumor cells in the local focus grow infiltratively.As a result,it is very important to evaluate pathological grading, judge whether surgical resection can be performed, make individualized treatment plan, and improve survival rate and prognosis by early diagnosis and evaluation of pancreatic cancer.Purpose
The pancreatic cancer has the characteristics of strong proliferation and invasion, while the tumor cells in the local focus grow infiltratively.As a result,it is very important to evaluate pathological grading, judge whether surgical resection can be performed, develop individualized treatment plan, and improve survival rate and prognosis by early diagnosis and evaluation of pancreatic cancer.So far, a number of studies have reported that ADCslow and f as the quantitative parameters for IVIM-DWI can distinguish high-moderately differentiated and low differentiated pancreatic cancel and predict the pathological stage of pancreatic cancer before operation.However, it remains unknown whether the resectability of pancreatic cancer can be predicted by IVIM-DWI quantitative parameters.Therefore, the main goal of this study was to explore the application of intra voxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging (IVIM-DWI) in predicting the resectability and pathological grading of pancreatic cancer before surgery.Materials and Methods
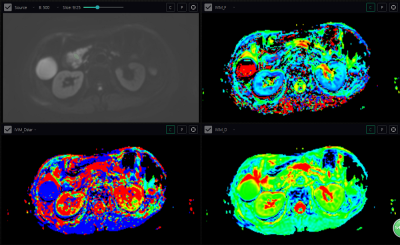
From November 2018 to August 2019, participants(39 participants;median age, 68 years;eighteen women) with biopsy-proven pancreatic cancer were prospectively recruited to undergo IVIM-DWI with 10 b values(including 0,10,20,40,60,80,100,150,200,500) at 3.0T MRI(Ingenia,Philips healthycare ,Netherlands) before pancreatectomy.IVIM-DWI sequence was used to acquire quantitative parameters maps(D, diffusion coefficient; D*,pseudodiffusion coefficient; f, perfusion fraction).The corresponding scan parameters were of field-of-view 380 mm×298 mm, matrix size 128 mm×298 mm,repetition time (TR) 1261 ms,echo of time(TE) 69 ms,The scan time was 10-14 minutes.Participants were categorized into poorly and highly-moderately differentiated or resectable and unresectable pancreatic cancer groups according to pathology.All statistical analyses were performed in SPSS software. Interobserver reliability was assessed with intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC).T-test was used to compare the differences of parameters between the resectable and unresectable groups, poorly differentiated and moderately differentiated pancreatic cancer. The predicted value and diagnostic effectiveness of each parameter value were evaluated by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis of the subjects.Significance threshold was set as p<0.05.Results
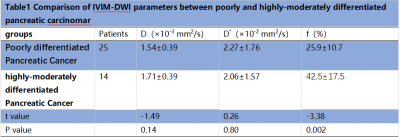
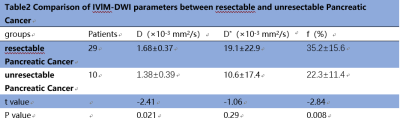
The f values of poorly differentiated pancreatic cancer (25.9%±10.7%) were lower than that of highly-moderately differentiated pancreatic cancer(42.5%±17.5%),P<0.05.There was no significant difference in D、D* value between poorly differentiated and highly-moderately differentiated pancreatic cancer[(1.54±0.39)×10-3 mm2/s,(2.27±1.76)×10-2 mm2/s;(1.71±0.39)×10-3 mm2/s,(2.06±1.57)×10-2 mm2/s;respectively)]. The D, f values of resectable pancreatic cancer[(1.68±0.37)×10-3 mm2/s, 35.2%±15.6%)]was higher than that of unresectable pancreatic cancer[(1.38±0.39)×10-3 mm2/s, 22.3%±11.4%), P<0.05, The AUCs of the f value for predicting pathological grade of pancreatic cancer was 0.79. The AUCs of D and f values to distinguish the resectability of pancreatic cancer were 0.71 and 0.73, respectively. There was no significant difference in D* value between resectable and unresectable pancreatic carcinoma[(2.29±1.91)×10-2 mm2/s,(1.74±1.06)×10-2 mm2/s, respectively)]. The AUC of D* values to distinguish the resectability of pancreatic cancer and the pathological grade of the pancreatic cancer were 0.69 and 0.55,respectively.Conclusion
IVIM quantitative parameters especially the D and f values could predict the resectability and pathological stage of pancreatic cancer, which can be helpful for preoperative evaluation of the pancreatic cancer.It may be more important to evaluate the resectability of the pancreatic cancer than the pathological grade for the prognosis of the patients.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Luciani A,Vignaud A,Cavet M,et al. Liver cirrhosis:intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging-pilot study[J]. Radiology,2008,249:891-899.
[2] Shen YN, Bai XL, Li GG, et al. Review of radiological classifications of pancreatic cancer with peripancreatic vessel invasion: are new grading criteria required[J]. Cancer Imaging, 2017, 17(1):14.
[3] Hoshimoto S, Hishinuma S, Shirakawa H, et al. Reassessment of the clinical significance of portal-superior mesenteric vein invasion in borderline resectable pancreatic cancer[J]. Eur J Surg Oncol, 2017, 43(6):1068-1075 .
[4]Ma W, Zhang G, Ren J, Pan Q, Wen D, Zhong J, Zhang Z, Huan Y. Quantitative parameters of intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion weighted imaging (IVIM-DWI): potential application in predicting pathological grades of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Quant Imaging Med Surg 2018;8(3):301-310. doi: 10.21037/qims.2018.04.08.
[5]Lee HJ, Rha SY, Chung YE, Shim HS, Kim YJ, Hur J, Hong YJ, Choi BW. Tumor perfusion-related parameter of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging: correlation with histological microvessel density. Magn Reson Med 2014;71:1554-8.
[6] Apte MV, Park S, Phillips PA et al (2004) Desmoplastic reaction in pancreatic cancer: role of pancreatic stellate cells. Pancreas 29:179–187.
[7] Jaster R,Emmrich J.Crucial role of fibrogenesis in pancreatic diseases.Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol,2008,22(1):17-29.
[8] Erkan M,Hausmann S,Michalski CWj et a1.How fibrosisinfluences imaging and surgical decisions in pancreatic cancer.Front Physiol,2012,3:389.
[9] Wang Y'Chen ZE,Nikolaidis P'et a1.Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of pancreatic adenocarcinomas:association with histopathology and tumor grade.J Magn Reson Imaging,2011,33(1):136-142.
[10] Lim JE, Chien MW, Earle CC. Prognostic factors following curative resection for pancreatic adenocarcinoma: a population based, linked database analysis of 396 patients. Ann Surg 2003;237:74-85. [11] Wasif N, Ko CY, Farrell J, Wainberg Z, Hines OJ, Reber H, Tomlinson JS. Impact of tumor grade on prognosis in pancreatic cancer: should we include grade in AJCC staging? Ann Surg Oncol 2010;17:2312-20.