2515
Quantitative assessment of the pancreas in healthy subjects using DWI, IVIM, and 3D mDixon-quant: correlation with age, gender and BMI1The first affiliated hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
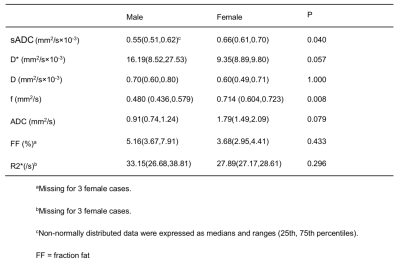
This study measured the quantitative imaging metrics of the pancreas using DWI, IVIM, and 3D mdixon-quant sequences in healthy subjects and correlated these quantitative metrics with age, gender and BMI. This study showed that there were noticeable differences in sADC, f between genders (p<0.05). It shows that pancreatic cells of male are closely arranged, cell gap is reduced, and water diffusion is limited and pancreatic perfusion reduce,which may be because pancreatic fat content of male overweigh that of female(5.16% vs.3.68%).
Introduction
At present, pancreatic fibrosis and steatosis are important pathological processes of pancreatic injury repair caused by acute and chronic pancreatitis, pancreatic tumor and other diseases[1]. Novel quantitative MR imaging techniques such as DWI, IVIM, 3D mdixon-quant[2-3] can provide in vivo characterization of tissues and have the potential to be non-invasive biomarkers to diagnose certain solid organ pathologies. Quantitative imaging metrics can also be used to monitor the course of therapy in clinical trials. However, there are lack of data on normal quantitative metrics of the pancreas and their correlation with biometric parameters (e.g., age, gender and BMI).Materials and methods
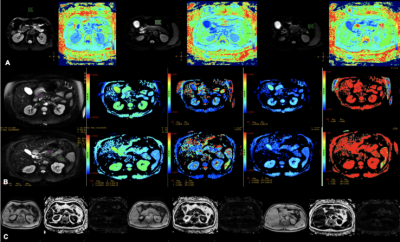
13 normal subjects (8 males and 5 females, 22 - 73 years, mean age 53.31 ± 13.56 years; BMI range, 18.73 – 27.43 kg/m2 , mean BMI, 23.29 ± 2.84 kg/m2) were included in this study, and underwent upper abdomen MRI scans (including DWI, IVIM, 3D mDIXON Quant) on a 3.0T Ingenia CX scanner (Philips Heathcare, The Netherlands).). The sequence parameters were: 3D mDIXON Quant sequence:FOV=375mm, TR/TE=6.0/1.05ms, voxel size 2.3mm×1.8mm, slice thick 5.0/-2.5. DWI:FOV=450mm, TR/TE=7700/74ms, voxel size 3.7mm×6.3mm, slice thick 6.0/0. IVIM: FOV=400mm, TR/TE=3000/91ms, voxel size 3.0mm×2.5mm, slice thick 7.0/1.0. On ISP workstation, 2D region of interest (ROI) with the size of 25-100 mm2 were placed on the head, body and tail regions of the pancreas on DWI ( Fig. A), IVIM (Fig. B) and 3D mDIXON Quant (Fig. C), avoiding blood vessels, pancreatic duct and abdominal adipose tissue as much as possible. The mean value of the three ROIs was calculated as the value of the whole pancreas. The Mann–Whitney U test was used to compare between subgroups divided by age, gender and BMI. This study has been approved by the local IRB.Results
There were no difference between age and BMI and imaging parameters of ADC, sADC, D*,D, f, FF and R2* (P>0.05)(Table 1 and 2). However, there were noticeable difference between gender and ADC Standard and f (p<0.05). D*,D,FF and R2* were similar in both genders (P>0.05)(Table 3).Discussions
This study showed that there were significant differences in sADC,f between genders (p<0.05). It shows that pancreatic cells of male are closely arranged, cell gap is reduced, and water diffusion is limited and pancreatic perfusion reduce[4],which may be because pancreatic fat content of male overweigh that of female(5.16% vs.3.68%)[3].Conclusion
This study measured the ADC, sADC, D*,D, f, FF and R2* of the pancreas in healthy subjects. The value of sADC and f of male pancreas are lower than that of female, and D*,D,FF and R2* were similar in both genders. However, no difference was seen between age and BMI and imaging parameters of ADC, sADC, D*,D, f, FF and R2*.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement foundReferences
1Temel Tirkes, Dhiraj Yadav,et al.Magnetic resonance imaging as a non‑invasive method for the assessment of pancreatic fbrosis (MINIMAP): a comprehensive study design from the consortium for the study of chronic pancreatitis[J]. Abdominal Radiology, 2019, 44: 2809–2821.
2Christophe Cassinotto, Matthieu Feldis, et al.MR relaxometry in chronic liver diseases: Comparison of T1 mapping, T2 mapping, and diffusion-weighted imaging for assessing cirrhosis diagnosis and severity[J]. European Journal of Radiology, 2015, 84:1459–1465.
3Yoon Jeong Hee, Lee Jeong Min, Lee Kyung Bun et al. Pancreatic Steatosis and Fibrosis: Quantitative Assessment with Preoperative Multiparametric MR Imaging[J]. Radiology, 2016, 279: 140-50.
4Tirkes Temel,Yadav Dhiraj,Conwell Darwin L et al. Magnetic resonance imaging as a non-invasive method for the assessment of pancreatic fibrosis (MINIMAP): a comprehensive study design from the consortium for the study of chronic pancreatitis, diabetes, and pancreatic cancer[J]. Abdom Radiol (NY), 2019, 44: 2809-2821.
Figures