2512
Effect of Compressed SENSE on 3D mDixon Sequences for Liver Imaging : A Comparative Study with 3D Vane Sequences1The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
The challenging problem of MR living examination is how to obtain images with diagnostic image quality in a shorter scan time. The purpose of this study is to explore the value of 3D mDixon sequence using compressed SENSE (CS) technology in liver examination. Compared with free-breathing mDixon with 3D Vane sequence, breath-hold (BH) 3D mDixon SENSE factor 2 and BH 3D mDixon CS factor 2 sequence can effectively improve the signal-to-noise ratio, contrast-to-noise ratio of the image and the image quality, and significantly shorten the scanning time.
Purpose
To investigate the effect of compressed SENSE technology on 3D mDixon sequences for liver imaging.Introduction
T1-weighted image (T1WI) is very important in liver magnetic resonance imaging for the anatomical display of liver lobes, hepatic ducts and blood vessels. Breath holding sequence and free breathing sequence are widely used in T1WI. Combined with breath-hold (BH) or respiratory triggering techniques, the respiratory motion artifact could be significantly reduced and relatively high quality images could be obtained. Free breathing (FB) radial sampling sequence could reduce motion artifacts compared with cartesian sequence but it does not fundamentally solve the problem of rapid scanning.It is an important problem that MR examination is faced with that how to obtain the image that meets the needs of clinical diagnosis in a shorter time.Methods
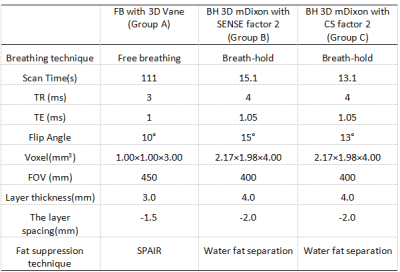
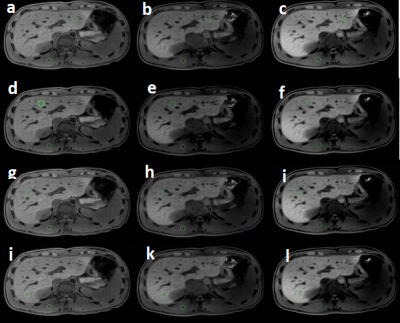
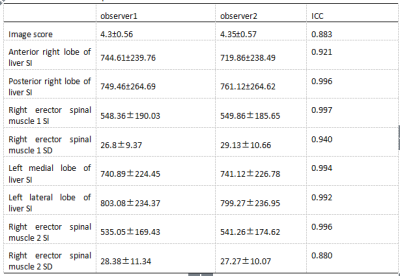
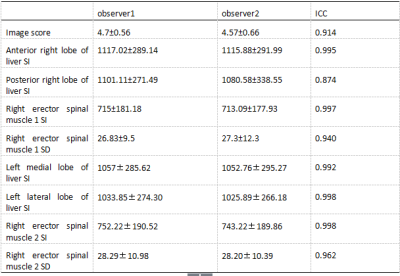
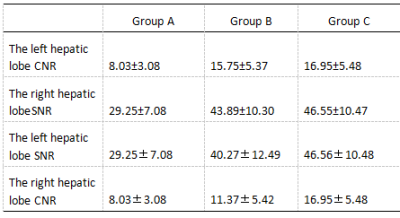
The upper abdominal MRI scans were performed on 23 healthy volunteers using mDixon T1WI sequences combined with FB pseudo-golden-angle Radial Stack-of-stars acquisitions (3D Vane) [2], BH mDixon T1WI sequence combined with SENSE factor 2 and BH mDixon T1WI sequence combined with CS factor 2, and were divided into groups A, B and C respectively. The liver image quality of the acquired mDixon images in 3 groups were subjectively scored by two observers.The intra-class correlation coefficient (ICC) method was used to confirm the measurement stability between the two observers.The signal intensity and standard deviations values were measured at the liver and erector spinae in all groups and performed consistency tests to calculate the image signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR)using independent samples Kruskal-Wallis test. The SNR, CNR and image quality scores of the anterior and posterior segments of the right hepatic lobe of the three groups were analyzed statistically between the groups using kappa test.Results
The two observers have good consistency between SNR, CNR and image scores measurement of the three groups. The SNR, CNR and image quality scores of group B and group C were significantly higher than those of group A (P<0.05)(Table1,2,3. The SNR and CNR of the left and right segments of the left hepatic lobe in the group were significantly higher than those in the A group (P<0.05). The quality scores and SNR and CNR of the posterior segment of the right hepatic lobe and the left and right hepatic lobe in the B and C groups. There was no significant difference in the difference (P>0.05).(Table4) Compared to BH 3D mDixon with SENSE factor 2 sequence, BH 3D mDixon with CS factor 2 sequence has reduced scan time by approximately 13.2%.Discussion and Conclusion
BH 3D mDixon with SENSE factor 2 and CS factor 2 sequences not only greatly shorten the scanning time when compared with FB mDixon with 3D Vane, but also effectively improve the SNR, CNR and image quality of the liver image. 3D mDixon combined with compressed SENSE technique (CS factor 2) could further accelerate the scan and has a great potential for abdominal clinical application.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Niendorf T, Sodickson DK. Highly accelerated cardiovascular MR imaging using many channel technology: concepts and clinical applications[J]. Eur Radiol, 2008, 18(1): 87-102.
[2] Kajita K, Goshima S, Noda Y, et al. Thin-slice Free-breathing Pseudo-golden-angle Radial Stack-of-stars with Gating and Tracking T1-weighted Acquisition: An Efficient Gadoxetic Acid-enhanced Hepatobiliary-phase Imaging Alternative for Patients with Unstable Breath Holding. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2019 Jan 10;18(1):4-11.
[3] Candès EJ, Romberg J, Tao T. Robust uncertainty principles: exact signal reconstruction from highly incomplete frequency information. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(2): 489-509.[4] Lustig Michael,Donoho David,Pauly John M,Sparse MRI: The application of compressed sensing for rapid MR imaging[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2007, 58: 1182-95.
[5] Donoho DL, Maleki A, Montanari A. Message-passing algorithms for compressed sensing[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2009, 106(45):18914-9.
Figures