2509
Visualization of pancreas and reproducibility of metrics with diffusion kurtosis imaging in rats at 11.7T MRI1Radiology, Xinhua Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China, 2Institute of Science and Technology for Brain-Inspired Intelligence, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
This study aimed to visualize the pancreas of rats with uncontrast MRI and validate the contour of pancreas by infusing gadolinium solution into the biliopancreatic duct for post-mortem imaging at 11.7 T MRI. Also, the reproducibility of metrics with diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) were evaluated in the pancreas of rats. We found that MRI at 11.7T could facilitate preclinical experiments in rodent pancreas and DKI appeared to be a useful noninvasive imaging tool to research pancreatic diseases with satisfactory reproducibility.
Introduction
To visualize the pancreas with uncontrast MRI and evaluate the reproducibility of metrics with diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) in the pancreas of rats.Methods
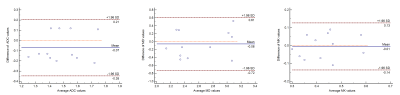
This preliminary study was performed and approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of our institution. 12 male adult Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats with body weight 300-400g were used for visualization of the pancreas at 11.7T MR without contrast. Following DKI by six b-values (0, 400, 800, 1100, 1400, and 1700 s/mm2), gadolinium solution was infused into the biliopancreatic duct for post-mortem imaging acquisition in order to validate the location and boundary of the pancreas. Then, ADC, mean corrected diffusion coefficient (MD) and mean kurtosis (MK) were quantitatively measured by two readers independently. Interobserver and short-term scan-rescan reproducibility were assessed by intra-class the correlation coefficient (ICC), coefficient of variation (CV) and Bland-Altman limits of agreements (BA-LA). (Figure1)Results
The pancreas was visible and distinguishable from surrounding tissue in uncontrast MRI (Figure 2). And in the meanwhile, the location and contour of the pancreas was validated in post-mortem imaging (Figure 3). This study showed the pancreas was outstandingly outlined by the stomach, the duodenum, the spleen, kidneys, and caudate liver lobes, as well as the other landmarks such as the common bile duct and splenic vein. In addition, interobserver agreement of ADC, MD, and MK were 0.88 (0.57-0.96), 0.89 (0.62-0.97), 0.86 (0.52-0.96), respectively. Scan-rescan reproducibility was satisfactory for ADC, MD, and MK (ICC 0.78, 0.79, and 0.86; CV 7.13%, 8.24%, and 9.18%; BA-LA -34.82-20.65%, -72.34-60.67%, and -13.7-12.7%,respectively). (Figure 4).Conclusion
MRI at 11.7T could facilitate preclinical experiments in rodent pancreas and DKI appeared to be a useful noninvasive imaging tool to research pancreatic diseases with satisfactory reproducibility.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
No reference found.Figures
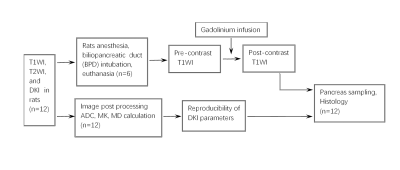
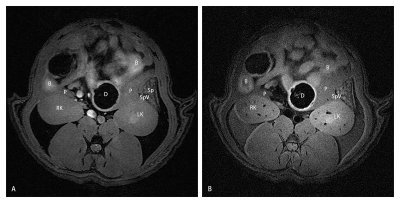
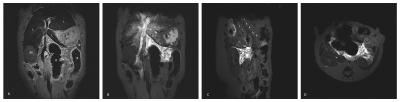
Figure 3. The T2WI coronal before (A) and T1WI coronal (B), sagittal (C), and axial (D) imaging after the gadolinium solution was infused into the biliopancreatic duct. P pancreas, RK right kidney, L liver, B bowel, Sp spleen, S stomach.