2471
Motion-resistant XD-GRASP for free-breathing liver MRI: qualitative comparison with standard breath-hold hepatobiliary phase imaging1Medical Physics, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, United States, 2Radiology, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, United States, 3GE Healthcare, Waukesha, WI, United States, 4Biomedical Engineering and Imaging Institute and Department of Radiology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, United States
Synopsis
Breath-hold post contrast T1-weighted liver MRI is limited by the patient’s ability to cooperate with breathing instructions. Free-breathing radial imaging and compressed sensing-based motion-resolved image reconstruction (XD-GRASP) has been specifically developed to resolve motion artifacts over standard cartesian techniques. In this work, we apply XD-GRASP to enable free-breathing MRI in the hepatobiliary liver phase, a clinically relevant problem. We demonstrate that the image quality of free-breathing XD-GRASP is equal to or superior to the one using standard breath hold acquisitions.
Introduction
Contrast-enhanced MRI using a hepatobiliary specific agent (e.g., Gd-EOB-DTPA) is essential for the assessment of a variety of liver pathologies1. Post-contrast hepatobiliary phase images are currently obtained on the GE platform using a Cartesian T1-weighted fat-saturated Liver Advanced Volumetric Assessment (LAVA) sequence, which is routinely acquired during a breath hold. Image quality can often be degraded by respiratory motion as patients may be unable to cooperate with or to complete breath-hold (BH) instructions2. The XD-GRASP technique, with a combination of radial acquisition and motion-resolved compressed sensing reconstruction, has been proposed to resolve motion artifacts over standard Cartesian techniques3. We have recently demonstrated that the quality of XD-GRASP reconstructions on delayed-phase post-contrast (Gadobutrol) images were equivalent to, and in some cases superior to conventional delayed phase Breath-held Cartesian LAVA (BH-LAVA) acquisitions4. In this study, we aim to compare the image quality of XD-GRASP imaging at the hepatobiliary phase against those acquired with the conventional BH-LAVA.Methods
Patient selection: This is a HIPAA-compliant and institutional review board-approved prospective single center study. Five patients who were undergoing routine outpatient liver MRI with Gd-EOB-DTPA were recruited. Informed consent was obtained from all the patients prior to the MR scans.Data Acquisition: Data sets were acquired on a 3T MRI scanner (MR750w, GE Healthcare, Waukesha, WI) after contrast injection during the hepatobiliary phase. BH-LAVA was performed during a breath-hold of 20 seconds with a voxel size of 1.25x1.25x3mm3. Free-breathing golden angle radial data was acquired with a similar voxel size of 1.25x1.25x3mm3. 600 spokes were acquired in each patient and the scan time was 60 seconds.
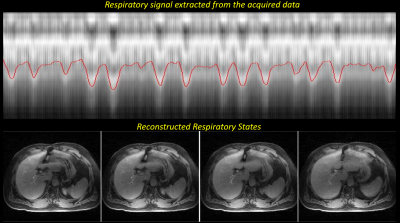
Image reconstruction: BH-LAVA data were reconstructed online on the scanner. Free-breathing radial data were reconstruction using the XD-GRASP algorithm3, where a respiratory signal was extracted directly from the data and used to sort the acquired data into 4 undersampled respiratory states. Temporal multi-coil compressed sensing reconstruction was then performed on the sorted 4-D data (3-D image + respiratory dimension).
Image comparison and assessment: Non labelled, reconstructed images were assessed by two abdominal radiologists blinded to acquisition schemes with 10 and 1 years’ experience respectively. Assessment included numerical visual scoring of the overall image quality, liver edge sharpness, bile duct sharpness and motion artifact from 1 (non-diagnostic) to 5 (excellent). If lesions were present further scoring of lesion conspicuity and lesion edge sharpness were recorded.
Results
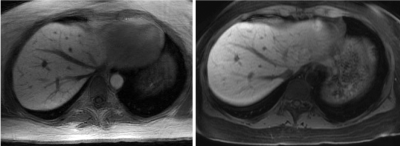
In 4 out of 5 patients, both radiologists graded XD-GRASP overall image quality, liver edge sharpness, bile duct edge sharpness and motion artifact as good or excellent. In the same 4 cases, XD-GRASP was graded equal to or superior to the standard BH-LAVA images. Liver lesions were present in 4 cases; in all these cases lesion conspicuity and lesion edge conspicuity were graded as good or excellent and in 3 of the 4 cases this was equal to or superior to the BH-LAVA images. In one case, XD-GRASP was graded by both radiologists equal to the BH-LAVA images for motion artifact, however it was graded inferior in the categories of overall image quality, liver edge sharpness and bile duct sharpness. In the same case, one reader also scored XD-GRASP inferior to BH-LAVA in lesion conspicuity and lesion edge sharpness.Discussion
We have demonstrated in a small cohort of outpatients the feasibility of high quality free-breathing hepatobiliary phase imaging using XD-GRASP, which are in most cases equal to or superior to standard BH-LAVA acquisitions. These results are promising and future studies will focus to validation in a larger prospective cohort.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Lee NK, Kim S, Lee JW, Lee SH, et al. Biliary MR Imaging with Gd-EOB-DTPA and its clinical applications. Radiographics 2009; 29:1707–1724
2. Korin HW, Ehman RL, Riederer SJ, Felmlee JP, Grimm RC. Respiratory kinematics of the upper abdominal organs: a quantitative study. Magn Reson Med. 1992;23(1):172-8
3. Feng L, Axel L, Chandarana H, Block KT, Sodickson DK, Otazo R. XD-GRASP: Golden-angle radial MRI with reconstruction of extra motion-state dimensions using compressed sensing. Magn Reson Med. 2016;75(2):775-88
4. Harrington K, Feng L, Chowdhury A, Wang K, Cashen T, Ersoz A, Fung M, Bayram E, Do K, Otazo R. Comparison of free-breathing motion-resolved radial imaging with standard breath-hold imaging on liver MRI: a feasibility study. ISMRM 2019, p. 4473
Figures