Li Zhang1, Longchao Li1, and Min Tang1
1Department of MRI, Shaanxi Provincial People’s hospital, Xi’an, China
Synopsis
In
2019, the updated version of PI-RADS Version 2.1 was introduced. This version
did not change the entire framework, but made several modifications to address
limitations and simplify the scoring system.
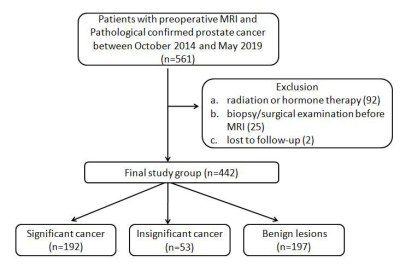
Between 442 patients, both readers had 96 discordant cases in terms of
five-point Version 2.1 scoring. Version 2.1 provides high accuracy for
detecting clinically significant PCa with category 4 as the threshold. Both
readers have good inter-reader reliability. However, agreement for TZ was lower
than for PZ lesions.
Purpose
In
2019, the updated version of PI-RADS Version 2.1 was introduced [1]. However,
as a new scoring system, the clinical utility of Version 2.1 has not been
validated. Thereby, the purpose of our study was to analyze
whether PI-RADS Version 2.1 helps improve diagnostic accuracy and reduce
inter-reader variability of prostate cancer (PCa)
at Multiparametric MRI (mpMRI).Methods
In all, 442 consecutive
patients underwent mpMRI at 3.0 T and subsequent systematic plus targeted
biopsies were included. PSA value and the score of PI-RADS Version 2.1 based
mpMRI were investigated. Two readers independently analyzed the images with
PI-RADS Version 2.1. The inter-reader agreement was calculated using kappa
statistics, and the diagnostic performance of PI-RADS Version 2.1 was analyzed
in the area under of Receiver Operating Characteristic curve (AUC-ROC),
sensitivity and specificity.Results
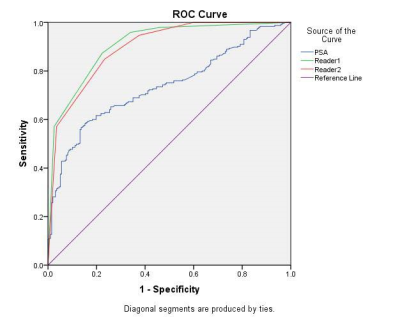
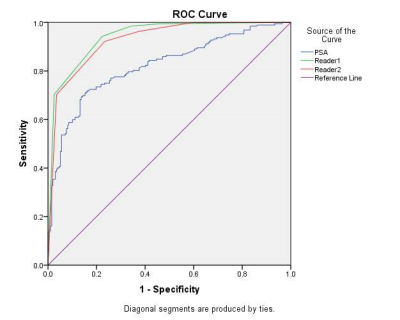
For cancer, the overall AUC
was 0.908 for reader 1 and 0.897 for reader 2, respectively. For clinically
significant PCa, the AUC was 0.942, 0.928 for reader 1 and reader 2,
respectively. With PI-RADS Version 2.1 score≥4 as a threshold, the
sensitivity and specificity were 94.3% and 77.7% for reader 1 and 92.2%and
76.6% for reader 2, respectively. ROC
analysis showed that an AUC-ROC of 0.879 and 0.877(reader 1), 0.847 and 0.865
(reader 2) for the Peripheral Zone (PZ) and the Transition zone (TZ) lesions,
respectively. The diagnostic concordance for PCa and clinically significant PCa
was good (kappa=0.732-728). Inter-reader agreement for TZ lesions (kappa=0.633)
was lower than for PZ (kappa =0.768).Discussion
The finding of our study revealed that Version 2.1
has an excellent level of inter-reader agreement (ICC 0.808(0.784-0.830).The
inter-reader agreement using kappa coefficients was also good (k =0.728) for
clinically significant PCa. Our results have shown that the new version of
PI-RADS 2.1 allowed for good diagnostic performance in predicting PCa and
clinically significant PCa. It was obvious that when we set Version 2.1
category of 4 as the best threshold, the current symptomatic method could
achieve high sensitivity and specificity for both readers. These results
support the idea that the new Version 2.1, as a more user-friendly tool, allows
for comparable or better reproducibility in analyzing PCa than with the
previous PI-RADS Version 1 or 2, or Likert scoring [2].Conclusion
It was demonstrated that
used the PI-RADS Version 2.1 helps to rule out clinically significant PCa
accurately. Version 2.1 score of 4 or greater seems to be associated with the
presence of clinically significant PCa. Both readers have good inter-reader
reliability, but the agreement for TZ lesions was lower than for PZ lesions. Prospective
studies will be necessary to validate the clinical use of Version 2.1 in the
future.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1]Turkbey
B, Rosenkrantz AB, Haider MA, et al. Prostate imaging reporting and data system
version 2.1: 2019 update of prostate imaging reporting and data system version
2. Eur Urol 2019 Mar 18https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2019.02.033.
[2]MoritzKS,
Thomas LB, René A, et al. Assessment of PI-RADS v2 for the Detection of
Prostate Cancer.Eur J Radiol 2016; 85:726-731.