2442
Validation of the Diagnostic Accuracy of Multi-parametric MRI with PI-RADS V2.1 for Detecting Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer1The First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, China
Synopsis
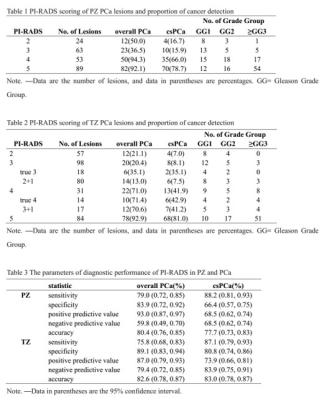
229 PZ and 270 TZ lesions were included in this study. The proportion of overall PCa and clinically important PCa detection (Gleason score≥3+4) for each PI-RADS version 2.1 category was determined. The performance of PI-RADS version 2.1 in cancer detection was evaluated. The diagnostic accuracy of the overall(82.6%) and csPCa TZ lesions(83.0%) is higher than the accuracy of PZ lesions(80.4%, 77.7%). For the csPCa diagnosis, the AUCs of PI-RADS version 2.1 in TZ(0.84) was higher than in PZ(0.77) without significance(P=0.06). Higher PI-RADS version 2.1 scores were associated with increasing likelihood of the presence of clinically important PCa (P<0.01).
purpose
To validate the diagnostic accuracy of multi-parametric MRI with Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) version 2.1 scores in clinically significant prostate cancer.Materials and Methods
499 patients underwent MRI Scan before undergoing biopsy were enrolled in this study. Prostate lesions were retrospectively categorized with the PI-RADS version 2.1 system by two readers in consensus who were blinded to histopathologic findings. The proportion of overall PCa and clinically important PCa detection (Gleason score≥3+4) for each PI-RADS version 2.1 category was determined. The performance of PI-RADS version 2.1 in cancer detection was evaluated.Results
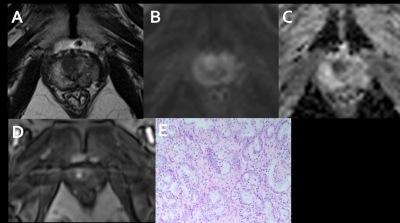
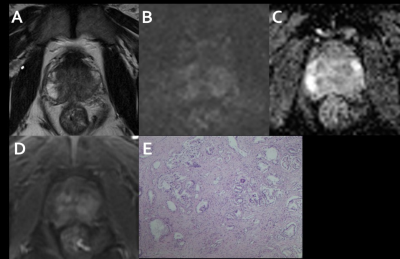
229 peripheral zone(PZ) and 270 transitional zone(TZ) lesions were included in this study. For PI-RADS category 2, 3, 4, 5 PZ and TZ lesions, the overall proportion of cancers was 50%, 36.5%, 94.3%, 92.1% vs 21.1%, 20.4%, 71.0%, 92.9%, respectively, and the proportion of clinically important cancers was 16.7%, 15.9%, 66.0%, 78.7% vs 7.0%, 8.1%, 41.9%, 81.0%, respectively. The diagnostic accuracy of the overall(82.6%) and csPCa TZ lesions(83.0%) is higher than the accuracy of PZ lesions(80.4%, 77.7%). For the csPCa diagnosis, the AUCs of PI-RADS version 2.1 in TZ(0.84) was higher than in PZ(0.77) without significance(P=0.06). Higher PI-RADS version 2.1 scores were associated with increasing likelihood of the presence of clinically important PCa (P<0.01).Conclusion
Higher PI-RADS version 2.1 scores are associated with a higher proportion of csPCa in the PZ and TZ. the diagnostic performance of PI-RADS version 2.1 in TZ is similar to that in PZ for detecting csPCa.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Clinical Research Project of Shenzhen Second Peoples' Hospital. Grant Number: 20193357008.References
1.Ahmed HU, El-Shater Bosaily A, Brown LC, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of multi-parametric MRI and TRUS biopsy in prostate cancer (PROMIS): a paired validating confirmatory study. Lancet. 2017;389(10071):815-22.
2.Choi MH, Kim CK, Lee YJ, Jung SE. Prebiopsy Biparametric MRI for Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer Detection With PI-RADS Version 2: A Multicenter Study. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2019;212(4):839-46.
3.Turkbey B, Rosenkrantz AB, Haider MA, et al. Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System Version 2.1: 2019 Update of Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System Version 2. Eur Urol. 2019;76(3):340-51.
4.Thai JN, Narayanan HA, George AK, et al. Validation of PI-RADS Version 2 in Transition Zone Lesions for the Detection of Prostate Cancer. Radiology. 2018;288(2):485-91.
Figures