2441
Age-Related and Zonal Anatomical Microstructure Features of Normal Prostatic Tissues: A Preliminary Study with VERDICT MRI1The First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, China
Synopsis
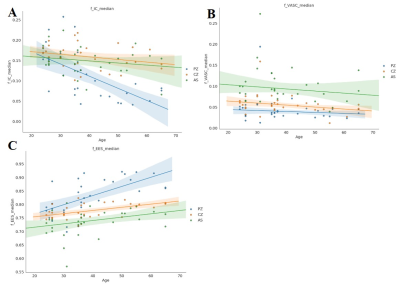
31 male volunteers were examined with VERDICT MRI of the prostate. The derived VERDICT parameters (the fIC, fEES and fVASC) were analyzed with a histogram based on the whole prostate volume and the PZ, CG and AS ROIs. There were statistical differences between histogram parameters and regions of the prostate. Among different anatomical zones, for PZ, Age has a negative correlation with fIC, and positive correlation with fEES. According to CG, there was also positive correlation between age and fEES.
purpose
The aim of this study was to identify differences in the histological features of the prostate by age- and region-related changes in normal prostatic tissues by using VERDICT MRI.Materials and Methods
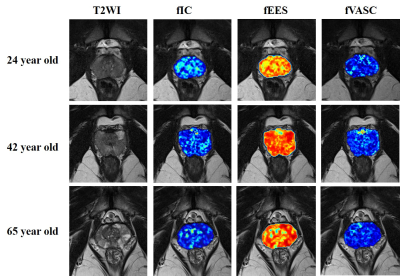
In total, 31 male volunteers were included in the study. The derived VERDICT parameters (the fIC, fEES and vascular fraction fVASC) were analyzed with a histogram. Based on the whole prostate volume and the PZ, CG and AS ROIs, histogram parameters (i.e., the median, mean, skewness and entropy) were computed. Two-way ANOVA and Pearson correlation coefficients were performedResults
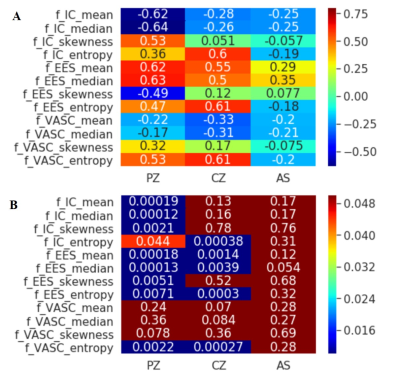
There were significant differences between the histogram parameters and regions of the prostate (P < 0.05). In the PZ, there was a correlation between age and the mean, median, skewness and entropy of the fIC (r = -0.62 and r= -0.64, r = 0.53 and r= 0.36, respectively, all P < 0.05). Age was significant correlated with the statistics of the fEES (r = 0.62, r= 0.63, r= 0.47 and r = -0.49, respectively, all P < 0.001). In the CG, age was found to have a significant positive correlation with the entropy of the fIC (r = 0.60, P < 0.001). There was a significant positive correlation between age and the mean, median and entropy of the fEES (r = 0.55, r= 0.50 and r= 0.61, respectively, all P < 0.001). Similar to the PZ (r = 0.53, P < 0.001), age also showed a significant positive correlation with the entropy of the fVASC (r = 0.61, P < 0.001), but no correlation with other parameters of the fVASC.Conclusion
VERDICT MRI successfully reveals microstructural changes across anatomical zones and age groups in normal prostate glands. Such information might be helpful for better evaluating prostatic diseases, including benign prostatic hyperplasia or prostatic cancer in the further.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Clinical Research Project of Shenzhen Second Peoples' Hospital. Grant Number: 20193357008.References
1.Panagiotaki E, Walker-Samuel S, Siow B, et al. Noninvasive quantification of solid tumor microstructure using VERDICT MRI. Cancer Res. 2014;74(7):1902-12.
2.Panagiotaki E, Chan RW, Dikaios N, et al. Microstructural characterization of normal and malignant human prostate tissue with vascular, extracellular, and restricted diffusion for cytometry in tumours magnetic resonance imaging. Invest Radiol. 2015;50(4):218-27.
3.Johnston EW, Bonet-Carne E, Ferizi U, et al. VERDICT MRI for Prostate Cancer: Intracellular Volume Fraction versus Apparent Diffusion Coefficient. Radiology. 2019;291(2):391-7.
4.Xia SJ, Xu XX, Teng JB, Xu CX, Tang XD. Characteristic pattern of human prostatic growth with age. Asian J Androl. 2002;4(4):269-71.
Figures