2424
Clinical value of accelerated three-dimensional T2-weighted turbo spin-echo imaging with compressed SENSE in prostate MRI
Tustomu Tamada1, Yu Ueda2, Kosuke Ito3, Takeshi Fukunaga1, Ayumu Kido1, Tomohiro Mochizuki4, and Akira Yamamoto1
1Radiology, Kawasaki Medical School, Kurashiki City, Japan, 2Philips Japan, Minato-ku, Japan, 3Kawasaki Medical School, Kurashiki City, Japan, 4Philips Japan, Osaka, Japan
1Radiology, Kawasaki Medical School, Kurashiki City, Japan, 2Philips Japan, Minato-ku, Japan, 3Kawasaki Medical School, Kurashiki City, Japan, 4Philips Japan, Osaka, Japan
Synopsis
T2WI is a key component of mpMRI in prostate. 2D T2WI obtained in multi plane is recommend in PI-RADS v2, resulting in prolonged examination time. The usefulness of 3D-VRFA-TSE, which has a potential to reduce scan time by multiplanar postprocessing reconstruction of images into any desired plane, has been reported. As an further effective way to accelerate scan time is provided by C-SENSE, which uses undersampling of the k-space, we compared 3D-VRFA-TSE with 3D-VRFA-TSE with C-SENSE. C-SENSE enables a reduction in acquisition time of 40% in 3D-VRFA-TSE, maintaining image quality and lesion conspicuity except for clarity of prostatic capsule.
Body of the abstract
INTRODUCTION: T2-weighted imaging (T2WI) which is used for anatomical evaluation of prostate is key components of prostate multiparametric MRI (mpMRI) in patients with prostate cancer (PC) that contributes to tumor detection as well as assessment of extracapsular extension (ECE).1,2 The T2WI acquisition in mpMRI is commonly performed with T2-weighted two-dimensional turbo spin-echo (2D-TSE) repeated in multiple planes1. The 2D TSE sequence are adversely affected by relatively thick slices and as voxels are not isotropic, several acquisitions are necessary to enable displaying the prostate in multiple planes. Therefore comparatively long examination times that are prone to motion artifacts have to be scheduled. Thus, using a three-dimensional (3D) TSE sequence would be a possible method to reduce total imaging time because it can serve as source data for multiplanar postprocessing reconstruction of images into any desired plane.3 A recent study with comparison between 2D-TSE and 3D-TSE has been demonstrated that 3D-TSE with tissue-specific variable refocusing flip angle (TS-VRFA, Philips Medical Systems, Best, The Netherlands) could potentially replace multiplane 2D-TSE for prostate cancer diagnosis while maintaining good image quality.3 Furthermore, compressed SENSE (C-SENSE) which is a combination of the parallel imaging technique SENSE (sensitivity encoding) together with compressed sensing allow for a reduction of the amount of acquired k-space data therefore enabling speeding up of MRI acquisitions.4 Thus, the aim of this study was to compare the image quality and PC detection ability between 3D-TSE with TS-VRFA (3D-VRFA-TSE) and 3D-VRFA-TSE with C-SENSE at 3-T system.METHODS: A total of 21 patients with elevated PSA levels (mean age, 71 years) underwent mpMRI including DWI on a 3-T with a 32-channel phased-array coil (Ingenia Elition 3.0T; Philips Medical Systems). Axial 3D-VRFA-TSE and 3D-VRFA-TSE with C-SENSE was acquired with the imaging parameters described in Figure 1. In qualitative visual assessment, contrast of transitional zone (TZ) and peripheral zone (PZ) (CTP, 1=none, 2= slightly high, 3= moderately high, 4=very high), clarity of prostatic capsule (CAP, 1=poor, 2= fair, 3=good, 4=excellent), blurring and motion artifacts (BMA, 1=strong, 2= moderate, 3=weak, 4=none), overall image quality (OIQ, 1=poor, 2= fair, 3=good, 4=excellent), and contrast of tumor and normal tissue (CTN, 1=poor, 2= fair, 3=good, 4=excellent) were assessed, and in quantitative analysis, signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) (SNR= mean signal intensity (SI) in normal prostate / standard deviation (SD) of SI in internal obturator muscle), and tumor-to-normal tissue ratio (TNR) (TNR=mean SI in tumor / mean SI in normal prostate) were measured. CTP, CAP, BMA, OIQ, CTN, SNR, and TNR were compared between 3D-VRFA-TSE and 3D-VRFA-TSE with C-SENSE. The Friedman and Wilcoxon signed rank tests were used for statistical analysis.
RESULTS: Acquisition time was 5 min 48 s in 3D-VRFA-TSE and 3 min 30 s in 3D-VRFA-TSE with C-SENSE. Of the 21 patients, 14 were diagnosed with PC and 7 with benign conditions. The PC was in the PZ in 57% (8 of 14) and in the transition zone (TZ) in 43% (6 of 14). There was no significant difference in CTP, BMA, OIQ, CTN, SNR, and TNR between 3D-VRFA-TSE and 3D-VRFA-TSE with C-SENSE (2.81 ± 0.96 vs. 2.90 ± 0.92, P = 0.16, 3.76 ± 0.43 vs. 3.81 ± 0.39, P=0.56, 3.24 ± 0.68 vs. 3.14 ± 0.56, P = 0.41, 2.21 ± 0.94 vs. 2.14 ± 0.83, P = 0.56, 18.1 ± 6.96 vs. 17.2 ± 6.81, P = 0.19,and 0.38 ± 0.29 vs. 0.38 ± 0.25, P = 0.93), whereas CAP in 3D-VRFA-TSE was significantly higher than that of 3D-VRFA-TSE with C-SENSE (3.38 ± 0.79 vs. 3.10 ± 0.68, P = 0.01) (Fig. 2, 3).
DISCUSSION: There was no significant difference in SNR, TNR, and image quality except for CAP between 3D-VRFA-TSE and 3D-VRFA-TSE with C-SENSE. These results suggest that qualitative and quantitative assessment of 3D-VRFA-TSE with C-SENSE are almost the same as that of 3D-VRFA-TSE while reducing 40% in acquisition time and keeping isotropic acquisition. CAP in 3D-VRFA-TSE with C-SENSE was significantly lower than that of 3D-VRFA-TSE. It is assumed that the decrease of clarity in prostatic capsule is due to blurring caused by denoising in C-SENSE. Therefore, further optimization of C-SENSE factor and denoising level in 3D-VRFA-TSE with C-SENSE will be needed to accurately assess ECE in PC.
CONCLUSION: Our study showed that C-SENSE can provide a reduction in acquisition time of 40% when applied to 3D-VRFA-TSE MRI of the prostate and demonstrated that there was no difference in the image quality and lesion conspicuity except for clarity of prostatic capsule. Further clinical investigation and optimization of imaging parameters is needed to assess if 3D-VRFA-TSE with C-SENSE can consistently provide diagnostic performance comparable to 3D-VRFA-TSE.
Acknowledgements
NoneReferences
- Weinreb JC, Barentsz JO, Choyke PL, et al. PI-RADS Prostate Imaging - Reporting and Data System: 2015, Version 2. Eur Urol. 2016;70(5):e136.
- Gupta RT, Spilseth B, Patel N, et al. Multiparametric prostate MRI: focus on T2-weighted imaging and role in staging of prostate cancer. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2016;41(5):831-843.
- Tanaka U, Ueno Y, Morinaga Y, et al. Value of three-dimensional T2-weighted turbo spin-echo imaging with tissue-specific variable refocusing flip angle for 3-T magnetic resonance imaging of prostate cancer: comparison with conventional two- and three-dimensional T2-weighted turbo spin-echo imaging. Jpn J Radiol. 2017;35(12):707-717.
- Sartoretti T, Sartoretti E, Wyss M, et al. Compressed SENSE accelerated 3D T1w black blood turbo spin echo versus 2D T1w turbo spin echo sequence in pituitary magnetic resonance imaging. Eur J Radiol. 2019 Nov;120:108667. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2019.108667. Epub 2019 Sep 14.
Figures
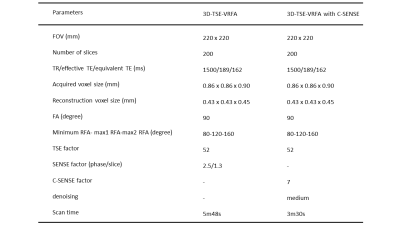
Figure 1. Details of the imaging parameters
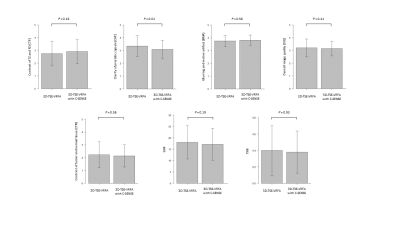
Figure 2. Comparison of qualitative visual assessment and quantitative
analysis between 3D-VRFA-TSE and 3D-VRFA-TSE with C-SENSE
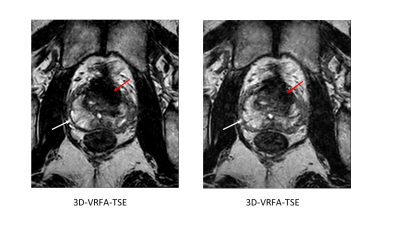
Clarity of prostatic capsule in
3D-VRFA-TSE was higher than that of 3D-VRFA-TSE with C-SENSE (white
arrow).
But, contrast of TZ and PZ and contrast of tumor and normal
tissue were comparable between both sequences
(red arrow).