2410
R2* yield by IDEAL IQ MRI in Evaluating the Expression Status of Glypican-3 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma1Henan provincial people's hospital& Zhengzhou University People’s Hospital, Zhengzhou, China, 2Henan provincial people's hospital, Zhengzhou, China, 3GE Healthcare, MR Research, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Accurate diagnosis and evaluation of HCC is important for improving the efficiency of HCC treatment and patient prognosis. Glypican-3 (GPC3) has been considered as a promising diagnostic and prognostic biomarker and a target for immune-therapeutic in HCC. Our study aimed to investigate the utility of IDEAL IQ MRI to prospectively evaluate the expression status of GPC3. Our results showed that the intratumoral R2* value was significantly higher in the positive-GPC3 HCC patients than in the negative-GPC3 HCC patients (P=0.003). The IDEAL IQ MRI may have potential for non-invasively predict GPC3 expression status.
Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common primary liver cancer, ranked fourth of causing cancer-related death around the world. Accurate diagnosis and evaluation of HCC is important for guiding clinical treatment plan and predicting prognosis before surgery. Recently, Glypican-3 (GPC3) has been considered as a promising diagnostic and prognostic biomarker and an immune-therapeutic target for HCCs. Although the GPC3 expression status can be obtained from the liver biopsy before surgery, the biopsy is invasive which can cause hemorrhage and exist sample differences which may lead to unreliable results. Therefore, non-invasively evaluation of GPC3 expression status before surgery is essential for guiding the appropriate therapy for HCCs. Iterative Decomposition of water and fat with Echo Asymmetry and Least squares estimation (IDEAL-IQ) employs an iterative least-squares decomposition algorithm to simultaneous solve for a R2* map, a fat fraction map and a water fraction map to relax iron, fat, water, respectively. The purpose of this study was to prospectively evaluate the value of R2* yield by IDEAL IQ in predicting the GPC3 expression status in HCC.Methods
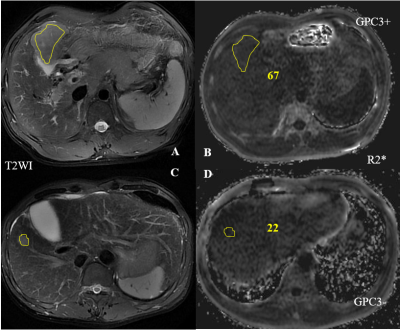
This retrospective study was approved by the local ethics committee. 27 patients with HCC were included in this study. All patients were performed the MRI examination including IDEAL IQ and T2WI on a 3.0 T MR unit (GE Discovery 750, GE Healthcare) before surgery. The patients were categorized into two groups according to the positive or negative of GPC3 expression status on immunochemical staining after surgery. Region of interest (ROI) was handed drawn on the T2WI image, including almost entire tumor and avoiding necrotic, hemorrhage areas and vessels. Then, the ROI was copied to the IDEAL IQ images. A Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare the IDEAL IQ measurements between the positive-GPC3 and negtive-GPC3 HCC patients.Results
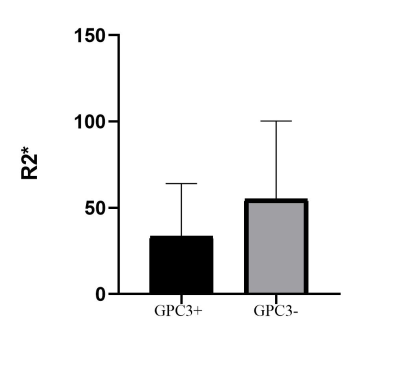
The R2* value of tumor in the positive-GPC3 HCC patients (mean ±standard deviation, 56.84 ± 46.11) is significantly higher than the negitive-GPC3 HCC patients (30.99 ± 29.48) (P = 0.003).Discussion
Our results showed that the R2* value yield by IDEAL IQ MRI was significantly higher in positive-GPC3 HCC than negative-GPC3 HCC patients. Previous studies have demonstrated that the R2* could reliably measure the iron concentration in liver diseases such as liver cirrhosis. Our results indicated that iron concentration is more abundant in the positive-GPC3 HCC than in the negative-GPC3 HCC patients. GPC3 acts as an oncofetal protein and relates to various HCC signaling pathways. Marked iron deposition has been found on the surface and in the cytoplasm of tumor cells, consistent with GPC3 expressed on the surface and in the cytoplasm. Moreover, GPC3 plays a significant role in HCC angiogenesis, which is prone to microhemorrhage that may contribute to the increased R2* value in positive-GPC3 HCC. Thus, R2* yield by IDEAL IQ may differentiate the positive-GPC3 HCC from negative-GPC3 HCC patients.Conclusion
R2* yield by IDEAL IQ may preoperatively predict the expression status of GPC3 in HCC,which may be a useful tool for guiding the treatment plan and improving the prognosis of HCC.Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFE0103600), National Natural Science Foundation of China (81720108021, 81601466), and Zhongyuan Thousand Talents Plan Project-- Basic Research Leader Talent (ZYQR201810117).References
1. Villanueva A: Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N Engl J Med 2019, 380(15):1450-1462.
2. Zhou F, Shang W, Yu X, Tian J: Glypican-3: A promising biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis and treatment. Medicinal Research Reviews 2018, 38(2):741-767.
3. Tseng HH, Chang JG, Hwang YH, Yeh KT, Chen YL,
Yu HS: Expression of hepcidin and other
iron-regulatory genes in human hepatocellular carcinoma and its clinical
implications. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol
2009, 135(10):1413-1420.
Figures