2405
Multi-sequence MRI-based radiomics nomogram to predict two-year recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma after partial hepatectomy1The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Translational Medicine Team, GE Healthcare, Shanghai, China, 3GE Healthcare, Beijing, China, 4Huiying Medical Technology Inc., Beijing, China
Synopsis
In the current study, multi-sequence MRI radiomics nomogram was demonstrated to be capable to predict two-year recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma after partial hepatectomy, which will provide more prognostic information and facilitate clinical management.
Purpose
To investigate the application of multi-sequence MRI radiomics nomogram to predict two-year recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma after partial hepatectomy.Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the sixth most common cancer and ranks as the fourth cause of cancer-related death worldwide[1]. Partial hepatectomy with curative intent has been proved as one of the most important strategies for HCC patients at early-stage[2]. Nevertheless, up to 70% of HCC patients who underwent partial hepatectomy experienced a subsequent recurrence within 5 years. The time to recurrence is an independent survival factor, and patients with early recurrence (with in 2 years) tend to have lower overall survival than those with late recurrence[3, 4]. Thus, it is necessary to explore an non-invasive method of preoperative risk stratification to guide further surveillance and treatment. Radiomics is a rapidly growing field that converts medical images into high-dimensional quantitative features through different algorithms, potentially aidding in cancer detection, diagnosis, treatment response assessment, and prognosis prediction. Therefore, multi-sequence MRI radiomics nomogram was introduced in the present study to evaluate its clinical application performance in predicting two-year recurrence of HCC after partial hepatectomy.Materials and Methods
This retrospective study enrolled 105 patients who were pathologically confirmed as HCC, including 55 early recurrence HCC (within two-year recurrence) and 50 non-early recurrence HCC. All patients have underwent preoperative MR examinations, including in-phase T1WI, out-phase T1WI, T2WI, DWI and LAVA dynamic contrast enhanced MRI (arterial, venous and delayed phase). The 70% samples were randomly selected as training set and the others were testing set. On the MR images, two radiologists manually outlined the ROIs which enclosed the boundary of target lesions and extracted 1029 radiomics features, which were classified as first order statistic, shape, second-order statistics, and higher order statistics features. Then, the Spearman correlation analysis, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) algorithm, and stepwise regression method were performed to identify the most predictive radiomics features. The radiomics scores regarding combination of different MR sequences using multivariate logistic regression method for predicting early recurrence were developed, thus we obtained the optimal radiomics score. We also built clinicopathologic-radiologic nomogram and radiomics nomogram (integrating the optiminal radiomics score and clinicopathologic-radiologic independent risk factors). Diagnostic performance was evaluated by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis.Results
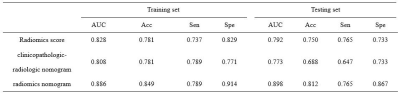
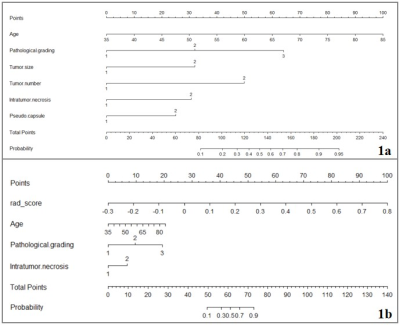
The optimal radiomics score, which selecting radiomics features from in-phase T1WI, out-phase T1WI, T2WI and enhanced MR sequences, and obtained the optimal AUC ( 0.828 in the training set, and 0.792 in the testing set). The radiomics score using the follow formula: Rad_score = 0.0378-0.2340*OUT_wavelet.LHH_glcm_Correlation- 0.1147*OUT_wavelet.HLH_glcm_Correlation-0.0773*A_wavelet.HHH_glrlm_ShortRunLowGrayLevelEmphasis+0.2750*A_wavelet.LLL_glszm_LargeAreaHighGrayLevelEmphasis+0.6019*V_wavelet.LLH_firstorder_Kurtosis+0.2537*V_wavelet.HHH_firstorder_Mean. The clinicopathologic-radiologic nomogram was constructed including age, pathological grading, tumor size, tumor number, intratumor necrosis and pseudo-capsule (Fig. 1a). The radiomics nomogram was built by incorporating the radiomics score into clinicopathologic-radiologic characters (age, pathological grading and intratumor necrosis) (Fig. 1b). The diagnostic performance of the optimal radiomics score, clinicopathologic-radiologic nomogram and radiomics nomogram were shown in Table 1. In the testing set, the AUC of the radiomics score was 0.792, an accuracy of 0.750, a sensitivity of 0.765 and a specificity of 0.733. The AUC of the clinicopathologic-radiologic nomogram was 0.773, an accuracy of 0.688, a sensitivity of 0.647 and a specificity of 0.733. The AUC of the radiomics nomogram was 0.898, an accuracy of 0.812, a sensitivity of 0.765 and a specificity of 0.867.Discussion
The multi-sequence MRI radiomics based strategy has shown great potential in predicting early recurrence of HCC, and radiomics nomogram incorporating the radiomics score and clinicopathologic-radiologic characters, seems more useful for accurate prediction of early recurrence. Discriminative features in the optimal radiomics score are composed of specific categories: two histogram-based features (kurtosis and mean), two GLCM-based features (2 of correlation), one GLRLM-based feature (ShortRunLowGrayLevelEmphasis), and one GLSZM-based feature (LargeAreaHighGrayLevelEmphasis). In the present study, the optimal radiomics score demonstrated satisfactory discriminative power both in the training and validation cohorts (AUC = 0.828 and 0.792, respectively). Meanwhile, the radiomics nomogram demonstrated promising results (AUC 0.898, sensitivity 0.765 and specificity 0.867 in the testing set), which be comparative to the results studied by Zhang (AUC 0.841, sensitivity 0.913 and specificity 0.750 in the testing set)[5].Conclusion
Multi-sequence MRI-based radiomics nomogram demonstrated good discriminative ability in predicting two-year recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma after partial hepatectomy, which will provide more prognostic information and facilitate clinical management.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Villanueva A . Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2019; 380: 1450–62.
[2] Forner A, Reig M, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2018; 391: 1301–14.
[3] Feng J, Chen J, Zhu R, et al. Prediction of early recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma within the Milan criteria after radical resection. Oncotarget. 2017; 8(38): 63299–3310.
[4] Cheng Z, Yang P, Qu S, et al. Risk factors and management for early and late intrahepatic recurrence of solitary hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection.HPB (Oxford). 2015; 17(5): 422-7.
[5] Zhang Z, Jiang H, Chen J, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma: radiomics nomogram on gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR imaging for early postoperative recurrence prediction. Cancer Imaging. 2019; 19(1): 22.