2377
A meta-analysis comparing the diagnostic performance of abbreviated MRI (ABB-MRI) and a full diagnostic protocol (FDP-MRI) in breast cancer1Department of Radiology, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, United Kingdom, 2Department of Psychiatry, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, United Kingdom, 3National Institute of Health Research, Cambridge Clinical Trials Unit, Cambridge, United Kingdom, 4University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, United Kingdom
Synopsis
The diagnostic performance of abbreviated MRI (ABB-MRI) and full diagnostic protocol MRI (FDP-MRI) in the detection and diagnosis of breast cancer was compared using meta-analysis. 13 eligible studies were included (5 screening studies and 8 enriched cohort studies) and pooled estimates of sensitivity, specificity and area under the curve were calculated for ABB-MRI and FDP-MRI for both types of study. The diagnostic performances of ABB-MRI and FDP-MRI were comparable.
Introduction
Mammography is the most commonly used screening modality in breast cancer, however it has a limited sensitivity in dense breasts1. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has a high sensitivity and specificity in the detection of breast cancer and is also increasingly used for problem solving for patients with suspicious findings on mammography or ultrasound. However, the widespread use of MRI is limited due to its high cost and long examination time. Abbreviated MRI (ABB-MRI) protocols have been proposed that reduce the examination and interpretation time. These often consist of only one pre-contrast sequence, one post-contrast sequence, and their derived subtraction or maximum-intensity projection (MIP) images. This study reports a meta-analysis comparing the diagnostic performance of ABB-MRI and full diagnostic protocol MRI (FDP-MRI) in the detection and diagnosis of breast cancer in screening and in enriched cohorts.Methods
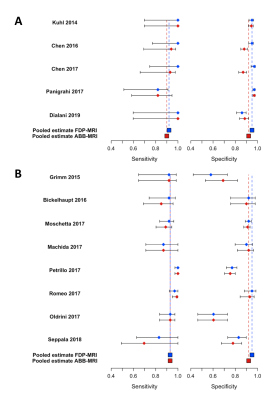
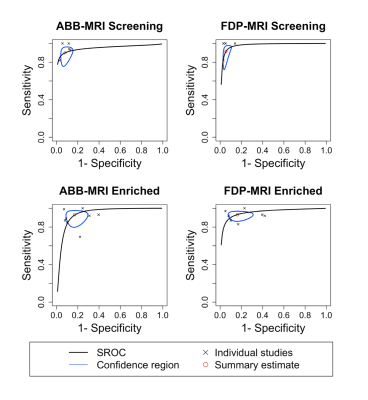
This study was reported according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines2. Databases were searched up to July 2019 for studies in English comparing the diagnostic performance of ABB-MRI and FDP-MRI in the breast. Studies were reviewed according to eligibility and exclusion criteria and split into two subgroups (studies using a screening population and studies using enriched cohorts of screening patients as well as known cancers) to avoid bias. Heterogeneity between studies was assessed using Cochran’s Q-test and Higgins’ I2 test3,4. Forest plots were constructed to compare the sensitivities and specificities of ABB-MRI and FDP-MRI for studies in each subgroup. Pooled summary estimates for sensitivity, specificity and area under the curve (AUC) were obtained for each subgroup of studies using a bivariate model5 and summary operating characteristics (sROC) curves were constructed. Additionally, the sensitivities and specificities of ABB-MRI and FDP-MRI for each study were compared using a paired t-test, with a p-value < 0.05 indicating a statistically significant result. Analysis was carried out in R (version 3.1.3., https://www.r-project.org/) using the mada package (version 0.5.8., https://CRAN.Rproject.org/package=mada).Results
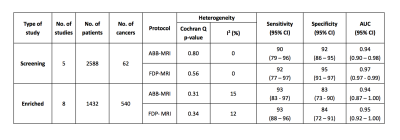
Results of pooled analysis are given in Table 1. Heterogeneity between studies was not statistically significant for screening or enriched studies, however the low number of screening studies resulted in an undefined I2 value. The pooled sensitivity/specificity/AUC for screening studies was 0.90/0.92/0.94 for ABB-MRI and 0.92/0.95/0.97 for FDP-MRI. The pooled sensitivity/specificity/AUC for enriched cohort studies was 0.93/0.83/0.94 for ABB-MRI and 0.93/0.84/0.95 for FDP-MRI. Forest plots are presented in Figure 1. sROC curves are presented in Figure 2. The sensitivities and specificities were not statistically significantly different for ABB-MRI and FDP-MRI in screening studies (p = 0.18 and 0.27) or enriched cohort studies (p = 0.18 and p = 0.93).Discussion
This is the first study to systematically compare the diagnostic performances of ABB-MRI and FDP-MRI through a meta-analysis. The pooled sensitivities, specificities and AUCs of ABB-MRI were comparable to FDP-MRI. The diagnostic performance of ABB-MRI was higher for enriched cohorts than for screening cohorts. For patients that require adjunct MRI imaging due to a suspicious mammogram or ultrasound examination, an abbreviated protocol can provide equivalent diagnostic accuracy. However, the number of eligible studies included in the meta-analysis was low.Conclusion
ABB-MRI and FDP-MRI achieve comparable diagnostic accuracy in screening studies and an equivalent diagnostic accuracy in enriched cohorts, though the number of studies to date is limited.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Wanders, J. O. P. et al. Volumetric breast density affects performance of digital screening mammography. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 162, 95–103 (2016).
2. Moher, D. et al. PRISMA 2009 Checklist. PLoS Med 6, (2009).
3. COCHRAN, W. G. THE COMPARISON OF PERCENTAGES IN MATCHED SAMPLES. Biometrika 37, 256–266 (1950).
4. Higgins, J. P. T., Thompson, S. G., Deeks, J. J. & Altman, D. G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327, 557–60 (2003).
5. Reitsma, J. B. et al. Bivariate analysis of sensitivity and specificity produces informative summary measures in diagnostic reviews. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 58, 982–990 (2005).
Figures