2339
Accelerating Acquisition of RESOLVE-DWI with Simultaneous Multi-slice (SMS) Technique in Diagnosing Breast Lesions1Radiology, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, HUST, Wuhan, China
Synopsis
Readout-segmented echo planar imaging (RESOLVE) has demonstrated its high diagnostic performance in breast with sharper Images, better lesion-background contrast and higher spatial resolution. However, long scan time (multi-shot strategy) may significantly decrease its clinical application due to possible motion artifacts and limitation of more complex diffusion approaches. Simultaneous multi-slice (SMS) technique allows for rapid realization of breast MR imaging, which may serve as a superior alternative for the diagnosis of breast lesions. In study , SMS was implemented into DWI to reduce the scan time by factor of 2-4, while maintaining the same anatomic coverage and basic image quality.
PURPOSE
To investigate the feasibility and effectiveness of diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) using Simultaneous Multi-slice readout-segmented echo-planar imaging (rs-EPI) to diagnose breast lesions.METHODS
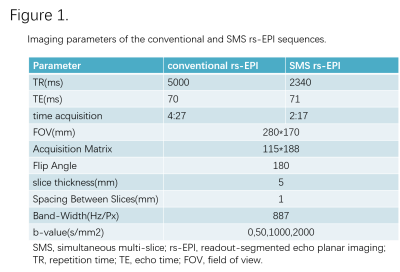
The IRB approved study was performed on a 3T scanner with a dedicated 16-channel phased-array breast coil (MAGNETOM Skyra, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany). 46 female patients (average age of 42.3 years; the range of 26-57 years) with 48 lesions (41 malignant and 7 benign) were enrolled in this study. Patients underwent bilateral breast MRI using a prototypical SMS rs-EPI sequence and a conventional rs-EPI sequence. T1-weighted MRI, T2-weighted MRI, and dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE-MRI) were also conducted as references. The details of the imaging parameters of both DWI sequences were listed in Figure 1. ADC, MK, MD values were quantitatively calculated for each lesion on both sequences. In addition, all images were qualitatively analyzed by a blinded read using a 5-point scale (1 = poor, 5 = excellent). The difference and correlation of both quantitative and qualitative parameters between conventional rs-EPI and SMS rs-EPI data were statistically analyzed.RESULTS
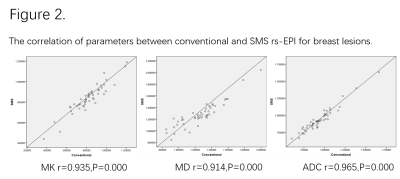
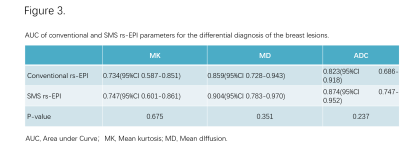
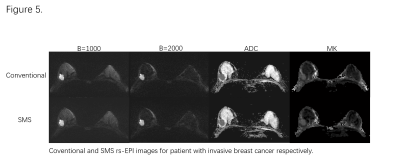
Compared to conventional rs-EPI, The acquisition time of SMS rs-EPI was markedly reduced (2:17 vs4:27 minutes). The Pearson’s correlation showed an excellent linear relationship for each parameter between SMS rs-EPI and conventional rs-EPI (r = 0.935, 0.914 and 0.965 for MK, MD, and ADC respectively; P<0.01 for all, Fig.2). Furthermore, the ROC analysis demonstrated SMS rs-EPI had better diagnostic performance than conventional rs-EPI, however, the values didn’t differ significantly (Fig.3). In blinded read, SMS rs-EPI showed comparable imaging quality with conventional rs-EPI (Fig.4&5), with moderate to good inter-rater reliability (ICC = 0.63-0.83 ).DISCUSSION
Our study showed that all the parameters derived from DKI and DWI of the two rs-EPI sequence with/without SMS have potential value in discriminating benign from malignant breast lesions. We found the lower MD, ADC and higher MK values in malignant lesions than those in benign lesions, which were consistent with the previous studies. What’s more, an excellent linear relationship for each parameter between SMS rs-EPI and conventional rs-EPI existed in our study. The results of ROC analysis suggested that SMS rs-EPI had a comparable diagnostic performance with conventional rs-EPI. These findings in our study demonstrated that quantitative analysis of SMS rs-EPI can be used in the differentiation of breast malignant and benign lesions.CONCLUSION
Compared to conventional rs-EPI technique, SMS rs-EPI can markedly reduce the acquisition time and yield similar diagnostic accuracy and comparable image quality, which may be useful to expand the scope of its clinical application in breast imaging, and increase the patient throughout.Acknowledgements
References
1. W. Bogner et al. Readout-segmented echo-planar imaging improves the diagnostic performance of diffusion-weighted MR breast examinations at 3.0T. Radiology 263 (2012) 64–76.
2. R. Frost et al. Scan time reduction for readout-segmented EPI using simultaneous multi-slice acceleration: diffusion-weighted imaging at 3 and 7 Tesla. Magn. Reson. Med.74 (2014) 136–149.
3. Nogueira L, Brandao S, Matos E, et al. Application of the diffusion kurtosis model for the study of breast lesions. Eur Radiol 2014;24:1197–1203.
4. Sun K, Chen X, Chai W, et al. Breast cancer: diffusion kurtosis MR imaging—diagnostic accuracy and correlation with clinical-pathologic factors. Radiology 2015;277:46–55.