2293
Quantitative Assessment of Lung Compliance using both Hyperpolarized 129Xe MRI and Micro-CT
Hongchuang Li1, Ming Zhang1, Haidong Li1, Xiuchao Zhao1, Qiuchen Rao1, Xiaoling Liu1, Yeqing Han1, Xianping Sun1, Xinrui Wang2, Chaohui Ye1, Xin Lou2, and Xin Zhou1
1Wuhan Institute of Physics and Mathematics, National Center for Magnetic Resonance in Wuhan, Wuhan Institute of Physics and Mathematics, Innovation Academy of Precision Measurement Science and Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences-Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Wuhan, China, 2Department of Radiology, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing, P. R. China, Beijing, China
1Wuhan Institute of Physics and Mathematics, National Center for Magnetic Resonance in Wuhan, Wuhan Institute of Physics and Mathematics, Innovation Academy of Precision Measurement Science and Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences-Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Wuhan, China, 2Department of Radiology, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing, P. R. China, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Lung compliance is commonly used in clinical diagnosis of pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema, and it is generally measured using pulmonary function tests (PFTs) in clinic. In this study, the imaging methods including both hyperpolarized 129Xe MRI and micro-CT were used to quantify lung compliance in rats, and the significant correlation was found between these two imaging methods. Our study also demonstrates the feasibility of measuring lung compliance using hyperpolarized 129Xe MRI, which would contribute to fully understanding the lung function changes caused by the pulmonary diseases.
Introduction
Lung compliance is generally driven by Compliance = ∆V/∆P,where ∆P is the change of pressure of the air way and ∆V is the change of volume of the air space in the lung. Micro-CT has been reported to be used for measuring lung compliance in rats1. Hyperpolarized 129Xe MRI is a non-invasively new method used in evaluating the function and microstructure of the lung2, 3, and it can obtain the ventilation map and absolute ventilated lung volumes. In the previous study, hyperpolarized gas MRI has been used to measure the absolute ventilated lung volumes in rats, and the results agree well with those by micro-CT4, 5. However, the feasibility of hyperpolarized 129Xe MRI in measuring lung compliance and its correlations with micro-CT are still unclear. In this study, 129Xe MRI and micro-CT were used to quantify lung compliance in rats, and the correlation was also analyzed.Methods
Six Sprague Dawley rats were imaged using hyperpolarized 129Xe MRI and micro-CT scan in sequence. Before the imaging experiments, the rats were anesthetized with pentobarbital sodium solution (1%) and endotracheal intubated using a 14-gauge tube catheter. Then, they were quickly transferred to a home-built MRI‐compatible ventilator and ventilated with a mixture of 96.6% O2 and 3.5% isoflurane for the hyperpolarized 129Xe MRI. After that,the rats were transferred to another home-built micro-CT compatible ventilator for micro-CT scanning. All the MR images were acquired using a 2D Flash sequence on a 7 T animal MRI scanner (Bruker Bio Spec 70/20 USR) and a home-built double-tuned birdcage RF coil was used. The corresponding imaging parameters were as follows: field of view = 5×5 cm; matrix size = 64×64; TR/TE =160.7/2.2 ms; number of slices = 24. The MRI images were acquired during the breath-hold, and repeated 10 times for the breath-hold pressure in the air-space ranged from 0 to 15 cm H2O by setting the inspiration time of 100, 150, 200, 250, 300, 350, 400, 450, 500 and 550 ms, respectively. Micro-CT (Bruker Skyscan1176) images were also acquired using similar ventilation strategy, and four different pressures ranged from 0 to 15 cm H2O were used.Results
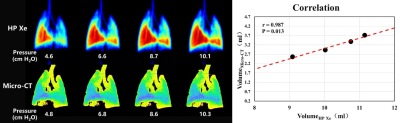
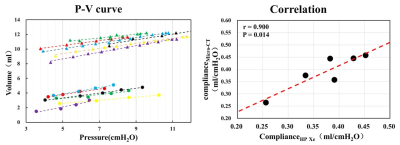
Figure 1 showed the measured lung volume using 129Xe MRI and micro-CT, and the volumes measured by hyperpolarized 129Xe are obviously greater than those measured by micro-CT for all of the six rats with the same pressure. However, the P-V curve shows consistent trend and the measured lung compliance correlated well using both methods, as shown in the figure 2.Discussion and Conclusion
Lung compliance was measured using hyperpolarized 129Xe MRI and micro-CT in rats and good correlation was found between the two imaging modalities. The difference of measured ventilation volume using 129Xe MRI and micro-CT was mostly because the different spatial resolution of the images and the different segment technique were used. In this study, the feasibility of hyperpolarized 129Xe MRI in measuring lung compliance was demonstrated, and the measured lung compliance correlated well with that measured using micro-CT. Our results indicate hyperpolarized 129Xe MRI has the potential in evaluating the lung compliance and may be helpful in diagnosing lung diseases that related to changing lung compliance.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFA0704000), National Natural Science Foundation of China (81625011, 91859206, 21921004, 81601491), Key Research Program of Frontier Sciences, CAS (QYZDY-SSW-SLH018) and Hubei Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (2017CFA013, 2018ACA143).References
- Ford NL, McCaig L, Jeklin A, Lewis JF, Veldhuizen RA, Holdsworth DW, Drangova M. A respiratory-gated micro-CT comparison of respiratory patterns in free-breathing and mechanically ventilated rats. Physiol Rep. 2017;5(2).
- Li H, Zhang Z, Zhao X, Han Y, Sun X, Ye C, Zhou X. Quantitative evaluation of pulmonary gas- exchange function using hyperpolarized (129) Xe CEST MRS and MRI. NMR Biomed. 2018;31(9):e3961.
- Li H, Zhang Z, Zhao X, Sun X, Ye C, Zhou X. Quantitative evaluation of radiation-induced lung injury with hyperpolarized xenon magnetic resonance. Magn Reson Med. 2016;76(2):408-416.
- Fox MS, Ouriadov A, Santyr GE. Comparison of hyperpolarized (3)He and (129)Xe MRI for the measurement of absolute ventilated lung volume in rats. Magn Reson Med. 2014;71(3):1130-1136.
- M Reza AS, Lam WW, Ouriadov AV, Holdsworth DW, Santyr GE, %J Nmr in Biomedicine. Comparison of hyperpolarized (3)He MRI rat lung volume measurement with micro-computed tomography. 2010;23(4):359-367.