2185
Subclinical Myocardial deformation assessment in early stage hypertension patients by Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Feature Tracking1Department of Radiology, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan,Hubei province, China, 2Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan,Hubei province, China
Synopsis
Preclinical left ventricular myocardial deformation involvement in the hypertension(HTN) patients could be detected by cardiovascular magnetic resonance feature tracking (CMR-FT). Impaired GRS,GCS,GLS and relevant diastolic longitudinal strain parameters might be associated with alterlation of left ventricular myocardial microstructure and the subtle decrease of diastolic function in the early asymptomatic HTN subjects.CMR-FT derived strain analysis has great potential to predict LVEF change and guide an appropriate treatment.
Purpose
The aim of this study was to evaluate the subclinical myocardial deformation of left ventricle in hypertension(HTN) patients by cardiovascular magnetic resonance feature tracking (CMR-FT).Materials and Methods
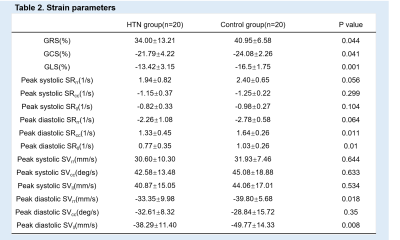
From January 2018 to October 2019,20 HTN patients (45.75± 16.51 years, 60% male) with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and 20 age- and gender- matched healthy controls (46.36± 16.19 years, 60% male) were consecutively enrolled and underwent 3.0T CMR examination. HTN group was at an early stage without left ventricular hypertrophy(LVH) and other severe cardiovascular disease. LV function variables and LV myocardial strain indices were measured using commercial software cvi42 (Circle Cardiovascular Imaging Inc, Calgary, Canada). Pearson’s correlation coefficient was used for correlation analysis for linear associations. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was used to determine the diagnostic ability of strain indices.Results
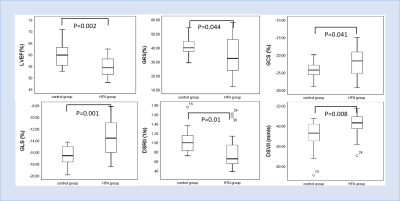
LVEF was statistically lower in HTN group (54.80±3.96%) than control group (59.76±5.26%,p=0.002). LV end systolic volume (LVESV) and LV mass (LVM) were higher in HTN group (53.47±18.05ml, 70.52±30.69g ) than control group (42.07±8.89ml,51.11±14.50g; p=0.017,p=0.016,respectively). LV global radial strain(GRS), global circumferential strain (GCS) and global longitudinal strain(GLS) were statistically impaired in HTN group (34.00±13.21%,-21.79±4.22%,-13.42±3.15%) compared with control group (40.95±6.58%,-24.08±2.26%,-16.5±1.75%; p=0.044,p=0.041,p=0.001,respectively). There were no significant difference in peak systolic strain rates and velocity. However, peak diastolic longitudinal rate (SRll) and peak diastolic longitudinal velocity(SVll) were reduced in HTN group (0.77±0.35s-1, -38.29±11.40mm.s-1) compared with control group(1.03±0.26s-1,-49.77±14.33mm.s-1; p=0.01,p=0.008, respectively). LVEF showed negatively correlation with GLS (r=-0.595,p=0.006). In addition, GLS showed the best performance to discriminate HTN patients (AUC =0.776, 95%CI, [0.630~0.922], cut-off value=-14.72%) with 60% sensitivity and 80% specificity.Conclusion
GLS was significantly lower and had better diagnostic performance than LVEF. Impaired diastolic longitudinal strain rate and velocity might relate to preclinical diastolic dysfunction.CMR-FT derived strain parameters can detect subtle alterations of left ventricular myocardial deformation in HTN patients before decreased LVEF and presence of LVH, which could be served as an early indicator to evaluate and predict subclinical myocardial involvement in HTN patients.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1.Andre F,Steen H,Buss SJ,et al.Age- and gender-related normal left ventricular deformation assessed by cardiovascular magnetic resonance feature tracking.J Cardiovasc Magn Reson.2015;17:25.
2.Pedrizzetti G,Claus P, Kilner PJ, Nagel E. Principles of cardiovascular magnetic resonance feature tracking and echocardiographic speckle tracking for informed clinical use.J Cardiovasc Magn Reson.2016;18:51.
3.Díez J,González A, Querejeta R,et al.Mechanisms of disease: pathologic structural remodeling is more than adaptive hypertrophy in hypertensive heart disease.Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med.2005;2:209–16. 4.Williams B,Mancia G,Spiering W,et al.2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension.Eur Heart J.2018;39:3021–104.
5.Taylor RJ,Moody WE,Umar F,et al.Myocardial strain measurement with featuretracking cardiovascular magnetic resonance: normal values.Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging.2015;16(8):871–81.
6.Onishi T,Saha SK,Delgado-Montero A,et al.Global longitudinal strain and global circumferential strain by speckletracking echocardiography and feature-tracking cardiac magnetic resonance imaging: comparison with left ventricular ejection fraction.J Am Soc Echocardiogr.2015;28(5):587–96.
7.Saito M,Khan F,Stoklosa T,et al.Prognostic implications of LV strain risk score in asymptomatic patients with hypertensive heart disease.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging.2016;9: 911–21.
8.MacIver DH ,Adeniran I,Zhang H.Left ventricular ejection fraction is determined by both global myocardial strain and wall thickness.IJC Hear Vasc.2015;7:113–8.
9.Mizuguchi Y,Oishi Y,Oki T,et al.Concentric left ventricular hypertrophy brings deterioration of systolic longitudinal, circumferential, and radial myocardial deformation in hypertensive patients with preserved left ventricular pump function.J Cardiol.2010;55:23–33.
Figures
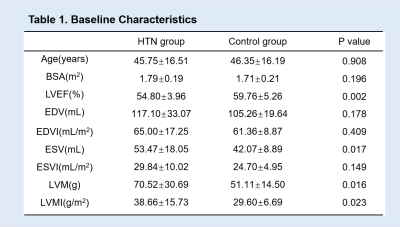
Continuous variables are presented
as mean±SD. BSA,body
surface area; LVEF,left ventricular ejection fraction; EDV,end
diastolic volume; EDVI,end diastolic volume index; ESV,end
systolic volume; ESV,end systolic volume index; LVM,left left
ventricular mass; LVM,left left ventricular mass index.
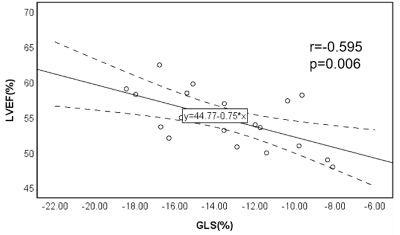
The relationship between GLS and LVEF
The best-fit linear regression line and correlation coefficientr were shown. Pearson’s correlation shows a linear negative association between GLS and LVEF(r=-0.595,p=0.006).
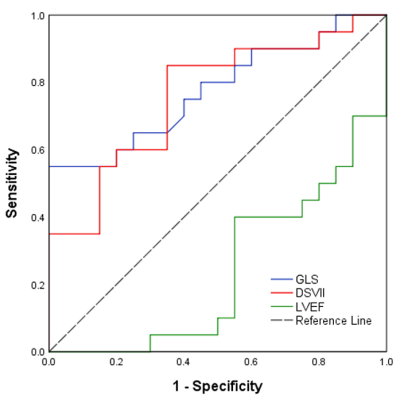
Receiver operating characteristic curves of GLS,DSVII and LVEF in discrimination HTD group from healthy group. DSVII,peak diastolic longitudinal strain velocity.