2080
Identifying early stages of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rat model using 7.0 tesla cardiac magnetic resonanc1Department of Radiology, West China Hospital / West China School of Medicine, Chengdu, China
Synopsis
the aim of this study is to identify early stages of doxorubicin (DOX)-induced cardiotoxicity in rat model using 7.0 tesla cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) combining creatine kinase isoenzymes (CKMB).Comparison of Ejection fraction (EF), Global radial (GRS), circumferential (GCS) and longitudinal strain (GLS) parameters of LV and CKMB between experimental groups and controls at 4,6, 8, 10 weeks.CKMB can detect DOX-induced cardiotoxicity at the earliest time. Decreased GLS during treatment identifies impaired LV mechanic as an early marker of DOX-induced cardiotoxicity, in the absence of EF. CKMB and CMR-TT are an effective method to evaluate DOX-induced cardiotoxicity at early stage.
Objectives
the aim of this study is to identify early stages of doxorubicin (DOX)-induced cardiotoxicity in rat model using 7.0 tesla cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) combining creatine kinase isoenzymes (CKMB).Methods
34 rats included. 28 of these rats were injected DOX (2.5mg/kg) through vena caudalis weekly and were divided into four subgroup. First subgroup received DOX four weeks and underwent CMR examination after 4 weeks. The other groups received DOX six weeks and underwent CMR examination after 6, 8, 10 weeks, respectively. Two rats injected physiological saline (2.5ml/kg) also performed CMR examination at the same time of each experimental group. Thus, controls contained eight rats. All these rats were sacrificed after CMR examination and were collected venous blood to detect CKMB. Ejection fraction (EF) for LV were quantified from all CMR images. Global radial (GRS), circumferential (GCS) and longitudinal strain (GLS) parameters of LV were also obtained by CMR tissue tracking (CMR-TT). All these parameters above were compared between treatment groups and controls.Results
The earliest DOX-induced cardiotoxicity CMR parameter was GLS(-17.84±2.50 vs -21.79±5.80, P=0.007)decreasing at week 6, at this time, the other CMR parameters were unaffected. However, EF wsa declined at week 8 and week 10 (2 and 4 weeks after final DOX treatment), as well as GCS, GLS and GRS. For CKMB, it was significantly increased at week 4 (869.14±210.69u/L vs 417.50±9.20u/L, P=0.001). At this early time point, all CMR parameters were not affected. CKMB continued to rise at week 6 and week 8, however it had no significantly difference between treatment groups and controls at week 10 (376.29±65.29u/L vs 443.50±16.26u/L,P=0.210).Conclusion
CKMB, as a sensitive marker, can detect DOX-induced cardiotoxicity at the earliest time. Decreased GLS during treatment identifies impaired LV mechanic as an early marker of DOX-induced cardiotoxicity, in the absence of EF. CKMB can reverse after DOX treatment, although the impairment of LV mechanic and function still existed. CKMB and CMR-TT are an effective method to evaluate DOX-induced cardiotoxicity at early stage.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
- Young RC, Ozols RF, Myers CE. The anthracycline antineoplastic drugs. N Engl J Med. 1981;305(3):139-53.
- Bristow MR, Billingham ME, Mason JW, Daniels JR. Clinical spectrum of anthracycline antibiotic cardiotoxicity. Cancer Treat Rep. 1978;62(6):873-9.
- Cardinale D, Colombo A, Bacchiani G, Tedeschi I, Meroni CA, Veglia F, et al. Early detection of anthracycline cardiotoxicity and improvement with heart failure therapy. Circulation. 2015;131(22):1981-8.
- Lunning MA, Kutty S, Rome ET, Li L, Padiyath A, Loberiza F, et al. Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging for the assessment of the myocardium after doxorubicin-based chemotherapy. Am J Clin Oncol. 2015;38(4):377-81. 14.
- Galan-Arriola C, Lobo M, Vilchez-Tschischke JP, Lopez GJ, de Molina-Iracheta A, Perez-Martinez C, et al. Serial Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Identify Early Stages of Anthracycline-Induced Cardiotoxicity. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;73(7):779-91.
Figures
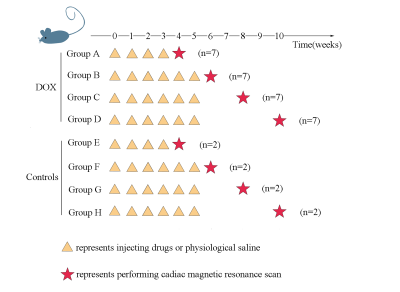
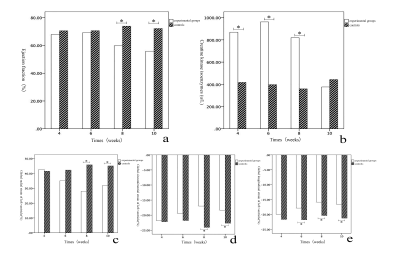
Figure 2 Cardiac magnetic resonance parameters and creatine kinase Cardiac magnetic resonance parameters and creatine kinase isoenzyme values in experimental and control rats
Comparison of left ventricular ejection fraction (a), creatine kinase isoenzyme (b), left ventricular systolic peak radial strain (c), left ventricular contraction peak circumferential strain (d) and left ventricular contraction maximum longitudinal strain (e)at the 4th, 6th, 8th, and 10th week of the experimental group and the control group. (* indicates a statistical difference between the two)