2065
The repeatability in the assessment of hyperemic myocardium native T1 using a MRI-compatible ergometer pedal exerciser.1Radiology, Medical Imaging,West China School of Medicine, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China, 2Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington, WA, United States
Synopsis
10 healthy volunteers underwent rest and stress Free-breathing myocardial native T1 mapping CMR scanning twice in a 3.0T MR scanner in midventricular short-axis position using a custom-made MRI-compatible ergometer pedal exerciser. It was demonstrated that T1 reactivity (ΔT1 values) had a moderate reliability and an excellent repeatability. The assessment of native myocardial T1 value using the pedal exerciser CMR stress/rest T1 mapping holds promise for myocardium ischemia detection without injecting gadolinium contrast agents and pharmacologic agents, also shows an excellent repeatability to demonstrates for the first time that normal myocardium has distinctive ranges of T1 reactivity to exercise stress.
INTRODUCTION:
Myocardial T1 is highly sensitive to changes in myocardial water content, including myocardial blood volume. The changes of myocardial native T1 during adenosine stress may be a more comprehensive biomarker of ischemia [1]. This study assessed changes in myocardial native T1 values at rest and during exercise stress in healthy subjects using a new custom-made MRI-compatible ergometer pedal exerciser, and determined the repeatability and of myocardial T1 measurements at rest and during the exercise.METHODS:
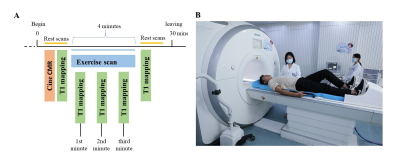
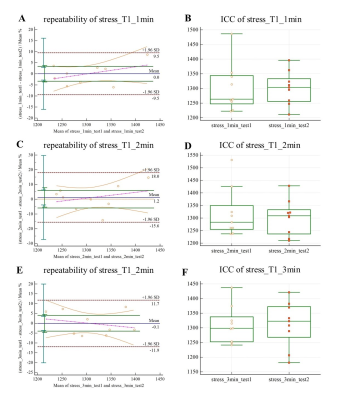
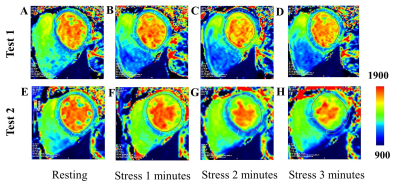
10 healthy volunteers (mean age 25.7 ± 1.8, half male and half female) underwent cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) scanning twice in a 3.0T magnetic resonance scanner (Skyra, Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics, Inc, Tarrytown, New York). Free-breathing myocardial native T1 mapping was performed by using shortened modified Look-Locker inversion recovery in the midventricular short-axis slice positions. Stress T1 maps were acquired every one minute during the exercise stress (alternately depressing pedals for 4 minutes at 60 Hz) using a customer-made MRI-compatible ergometer pedal exerciser on the MR table (Figure 1). CMR analysis was performed with CMR 42 versions 5.10.1 (Circle Cardiovascular Imaging Inc., Calgary, Alberta, Canada). Global myocardial T1 at rest and various time points during the stress were measured. Repeatability of the two tests were compared with the intra-group correlation coefficient (ICC) and coefficient of variation (CV). The consistency of the tests was analyzed by paired t test and Bland-Altman method. All statistical analyses were performed using MedCalc 19.0.7 (Ostend, Belgium). And all p values <0.05 were considered significant.RESULTS:
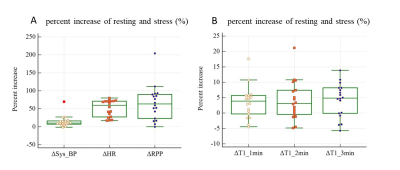
The mean exercise intensity was 2210W, with exercise duration of 4 minutes. Exercise induced a 10.3 (7.4, 16.4) % increase in systolic blood pressure, a 59.7 (27.6, 71.2) % increase in heart rate, and a 65.4 ± 48.2% increase in the rate pressure product compared with resting values (all p < 0.001). Myocardial T1 values at the 1st minute was significantly lower [3.35(95% CI, - 9.5 to 9.5)%] than those at the 2nd minute[5.99(95% CI, - 15.6 to 18)%] and third mins[4.01(95% CI, - 11.9 to 11.7)%]. It was demonstrated that T1 reactivity (ΔT1 values) had a moderate reliability (ICC=0.61) and an excellent repeatability (CV =3.4% < 5%). The stress T1 values for first, second and third mins were 1302 ± 70 ms (p=0.0063) , 1310 ± 84 ms (p=0.0188) and 1311 ± 70 ms (p=0.0032),which were significantly larger than rest T1(1260 ± 44 ms, p<0.05), and ΔT1 values were 3.4 ± 5.3% , 4.1 ± 6.4% and 4.2 ± 5.5% , p<0.05.DISCUSSION:
This pilot study demonstrates for the first time that normal myocardium has distinctive ranges of T1 reactivity to exercise stress using an MRI-compatible ergometer pedal exerciser. Our study shows a similar T1 reactivity as that using adenosine [1], indicating exercise cardiac T1 mapping could be another alternative to detect myocardial ischemia in patients who are contraindicated to pharmacologic stress.CONCLUSION:
An excellent repeatability was shown in the assessment of native myocardial T1 value using a custom-made MRI-compatible ergometer pedal exerciser CMR stress/rest T1 mapping holds promise for myocardium ischemia detection without injecting gadolinium contrast agents and pharmacologic agents.Acknowledgements
Jie Zheng,Fabao Gao and I conducted the conception and design of the study, acquisitionand interpretation of data, drafting the article, final approval of the versionto be completed. This research was support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(8193000682).References
1. Liu A, Wijesurendra RS, Francis JM, et al. Adenosine Stress and Rest T1 Mapping Can Differentiate Between Ischemic, Infarcted, Remote, and Normal Myocardium Without the Need for Gadolinium Contrast Agents. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016;9(1):27–36.
Figures